Home Care Tips for Managing Deep Vein Thrombosis Effectively
Learn effective home methods to manage Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT), including lifestyle changes, dietary tips, and precautions. Early intervention can reduce risks of serious complications such as pulmonary embolism. Always consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plans.

Home Care Tips for Managing Deep Vein Thrombosis Effectively
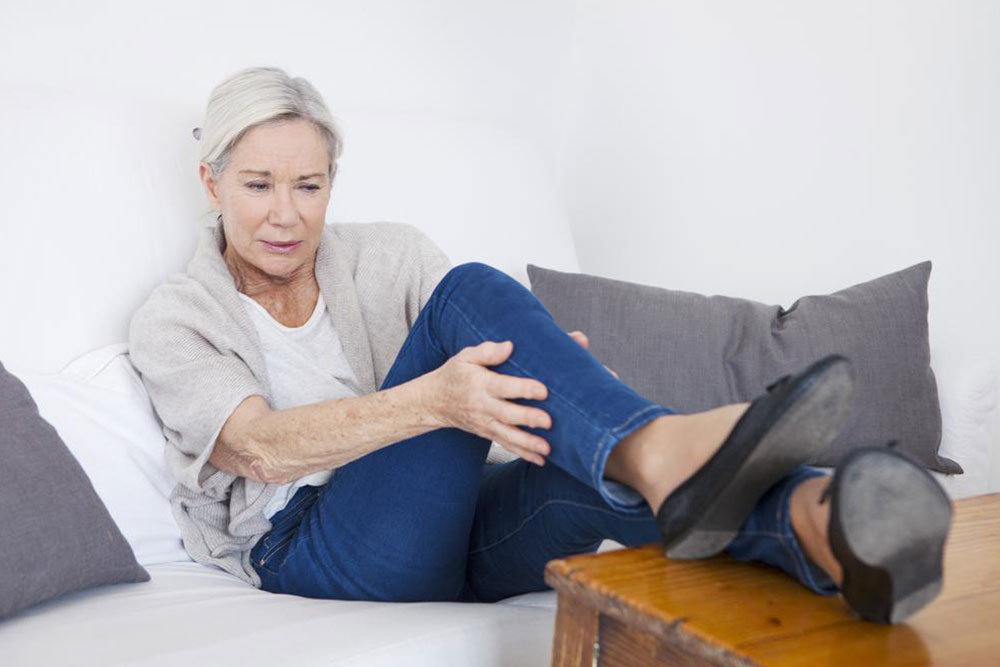
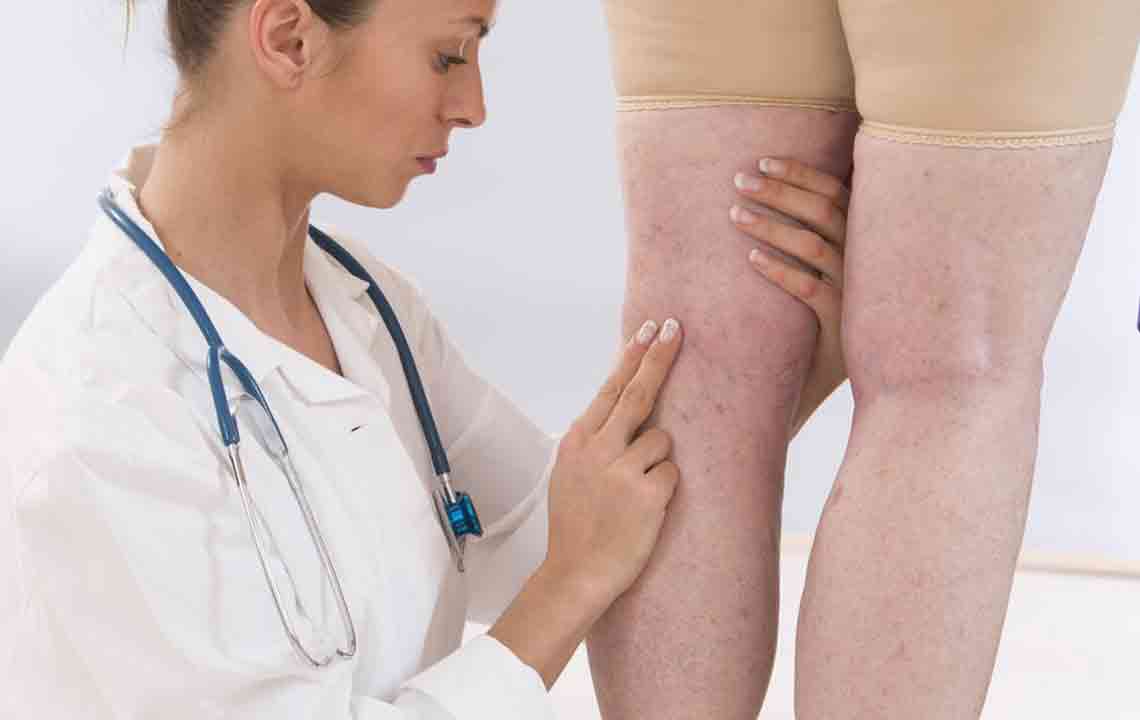
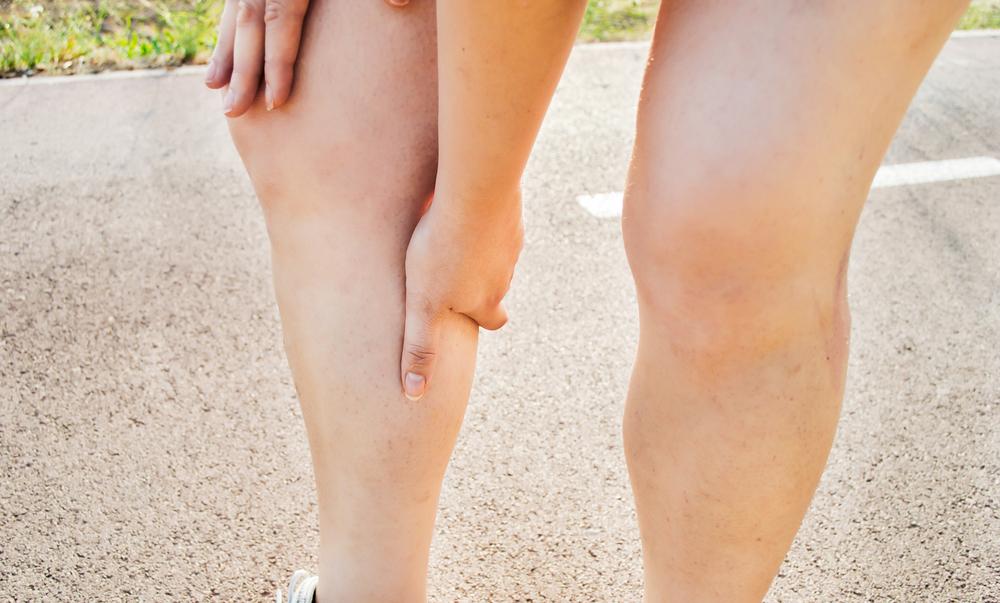
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot develops in deep veins, predominantly in the legs. Early detection and treatment are vital, as DVT can cause pulmonary embolism—a dangerous condition where a clot blocks lung arteries. Symptoms may include leg swelling, pain, redness, or sometimes no symptoms at all. Risk factors include prolonged inactivity, vascular injuries, certain health conditions, and hormonal therapies. Recognizing early signs and implementing lifestyle changes can help manage DVT at home successfully.
Triggers for DVT include prior clotting issues, family history, extended immobilization, vascular damage, and illnesses such as cancer or cardiovascular diseases. Pregnancy and hormone treatments raising estrogen levels also increase risks. Symptoms like leg swelling, tenderness, warmth, and skin discoloration are common. Immediate medical assessment is essential if symptoms occur, especially signs of pulmonary embolism such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or fainting. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, ultrasounds, and possibly venography.
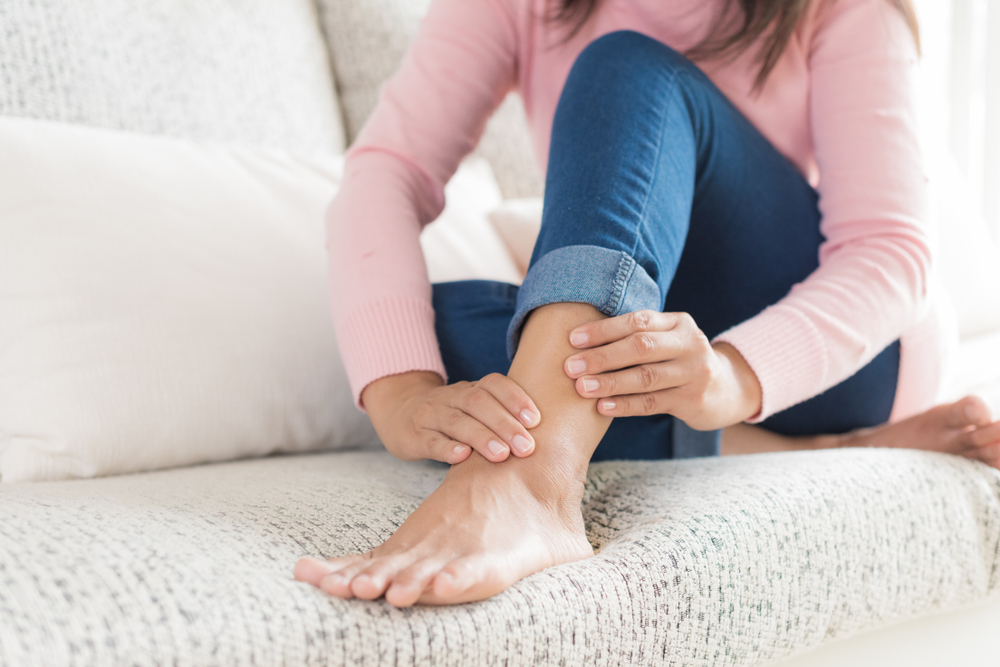
At home, elevating legs, wearing compression stockings, and gentle exercises can improve circulation. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods and herbs such as ginger, turmeric, and cayenne pepper may help naturally thin blood and enhance blood flow. Staying well-hydrated, avoiding tight clothing, and maintaining an active lifestyle are additional steps to minimize risks and support recovery. Always consult healthcare professionals before trying home remedies.
Important Reminder:
This article offers general information about DVT symptoms and home management strategies. It is not a replacement for professional medical advice. Always seek guidance from qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment.