Common Causes of Sleep Disruptions and How to Address Them
Learn about the main causes of sleep disturbances, including medical, environmental, and psychological factors. This guide highlights how health conditions, lifestyle, and environmental influences can disrupt sleep and what steps to take for better rest. Recognize symptoms and understand when to seek professional help to improve your sleep quality effectively.

Common Causes of Sleep Disruptions and How to Address Them
Health-Related Factors: Certain illnesses and medications can interfere with sleep patterns.
Kidney Disorders: Damage or fatigue can cause electrolyte imbalances and toxin retention, leading to insomnia or leg discomfort.
Thyroid Problems: Overactive thyroid function overstimulates the nervous system, resulting in night sweats and sleep challenges.
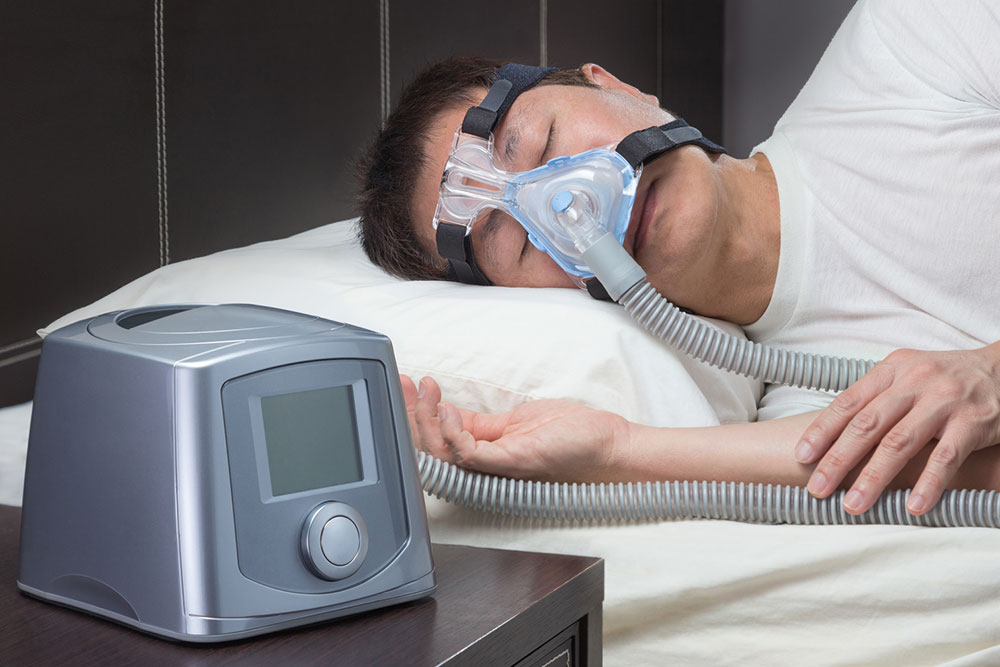
Respiratory Conditions: Asthma or bronchitis can cause breathing difficulties and coughing that interfere with rest. Medications may also have stimulating effects.
Physical Disruptors: These often relate to secondary effects of health issues.
Digestive Problems: Heartburn, ulcers, or stomach infections can disturb sleep.
Diabetes: Elevated sugar levels can cause night sweating and frequent urination, breaking sleep patterns.
Cardiac Diseases: Heart issues affecting circulation may result in breathing problems and poor sleep quality.
Joint Discomfort: Arthritic conditions and treatments can make lying down and falling asleep difficult.
Fibromyalgia: Alters sleep phases by generating abnormal deep sleep linked to slower brain activity during relaxation.
Mental Health Conditions: Anxiety, depression, and related disorders can cause trouble falling asleep or frequent awakenings due to tension or fears. Severe anxiety may lead to panic attacks and phobias, further disturbing sleep. Bipolar disorder and schizophrenia also influence sleep patterns.
Nervous System Disorders: Conditions like dementia, epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, or strokes involve nervous system dysfunctions that can cause insomnia.
Environmental Influences: Poor diet, caffeine, alcohol, genetics, shift work, and aging can disrupt circadian rhythms, affecting sleep-wake cycles.
Note: The information here is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment options. Use this information responsibly and seek advice when necessary.