Comprehensive Overview of Fibromyalgia: Signs, Causes, and Diagnosis
This article provides a detailed overview of fibromyalgia, covering its symptoms, causes, diagnostic criteria, and management strategies. Understanding this complex condition helps in early detection and effective symptom control, improving quality of life for affected individuals.

Comprehensive Overview of Fibromyalgia: Signs, Causes, and Diagnosis
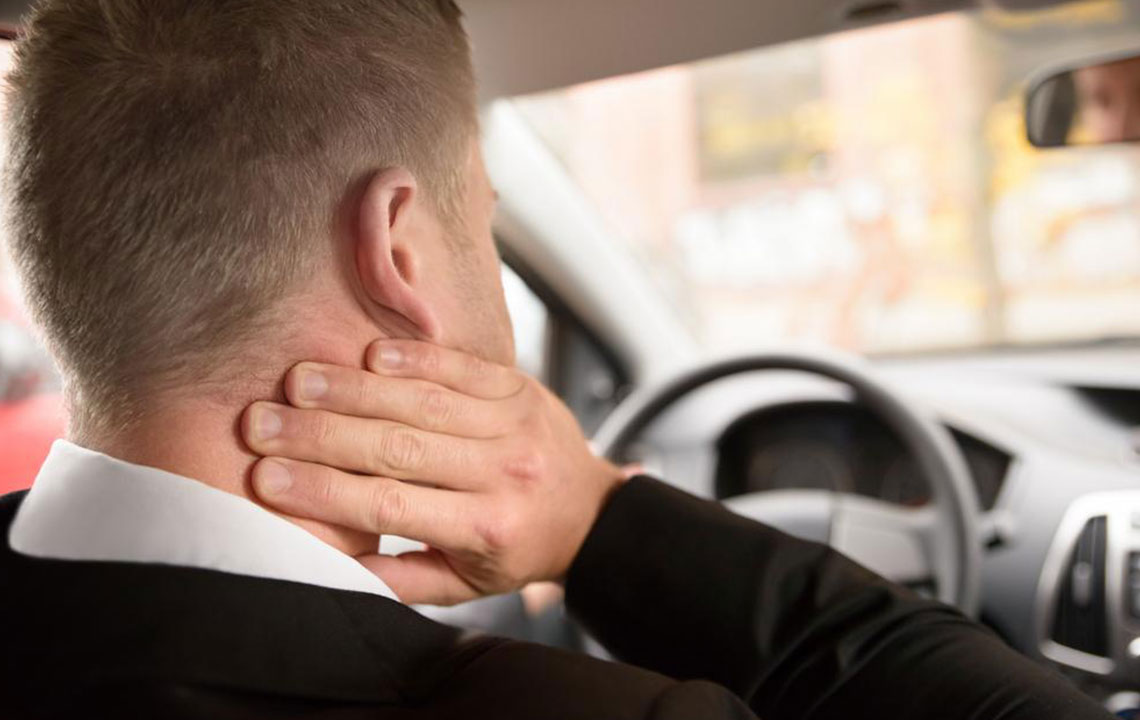
Fibromyalgia is a complex neurological disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, often accompanied by sleep issues, exhaustion, and mental fog. The condition arises from abnormal processing of pain signals in the brain. Its onset may follow trauma, infections, or psychological stress, gradually developing without a clear cause. Women are diagnosed more frequently than men.
Many individuals with fibromyalgia also suffer from anxiety or depression. While the precise cause remains unknown, factors such as genetics, infections, and stress may contribute. Diagnosis involves identifying 18 tender points and symptoms lasting over three months, with no other explanation. Blood tests can support diagnosis, but there’s no definitive test. Treatment focuses on symptom relief via medications, physical activity, and stress management.
Important considerations include symptom duration, current treatments, and ruling out other conditions. Pain distribution is assessed through mapping, and ongoing fatigue or unrefreshing sleep should be reported. Typical signs include widespread pain, fatigue, cognitive issues, headaches, digestive problems, numbness, dizziness, and mood shifts. Nerve hypersensitivity may heighten pain perception, affecting daily life and mental health. Although a cure is unavailable, therapy and lifestyle modifications can improve quality of life. Early detection promotes better management.
Disclaimer: This article offers general informational content based on current research. It does not replace professional medical advice. Consult healthcare providers for personal health concerns.