Effective Methods for Identifying and Preventing Scabies Outbreaks
Learn effective methods to identify, treat, and prevent the spread of scabies. This article provides practical tips on medical treatments, hygiene practices, and environmental cleaning to manage and stop outbreaks effectively.

Strategies to Detect and Avoid Scabies Skin Rash
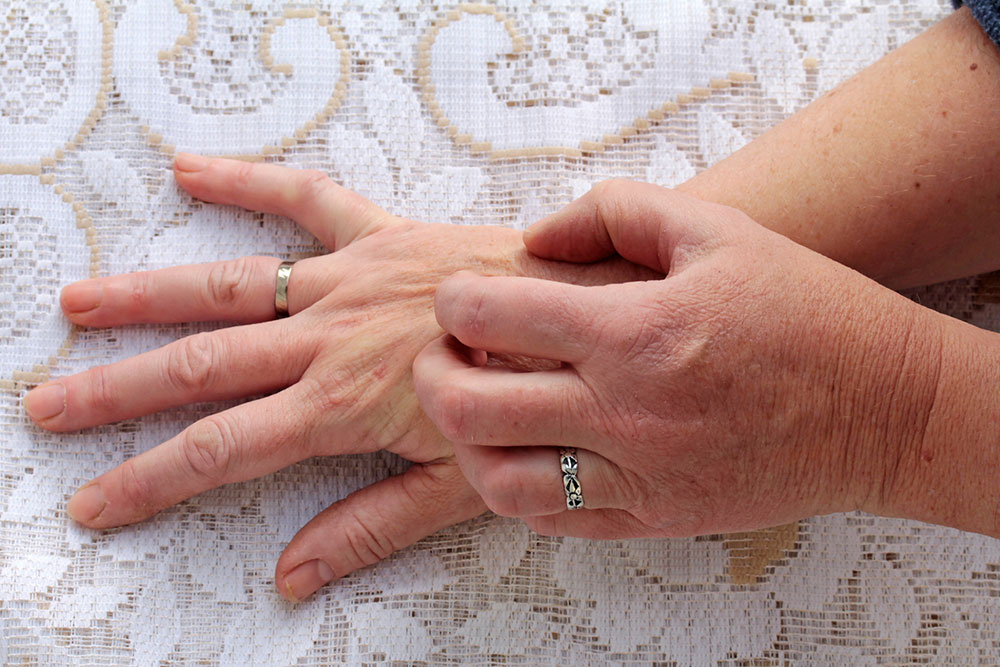
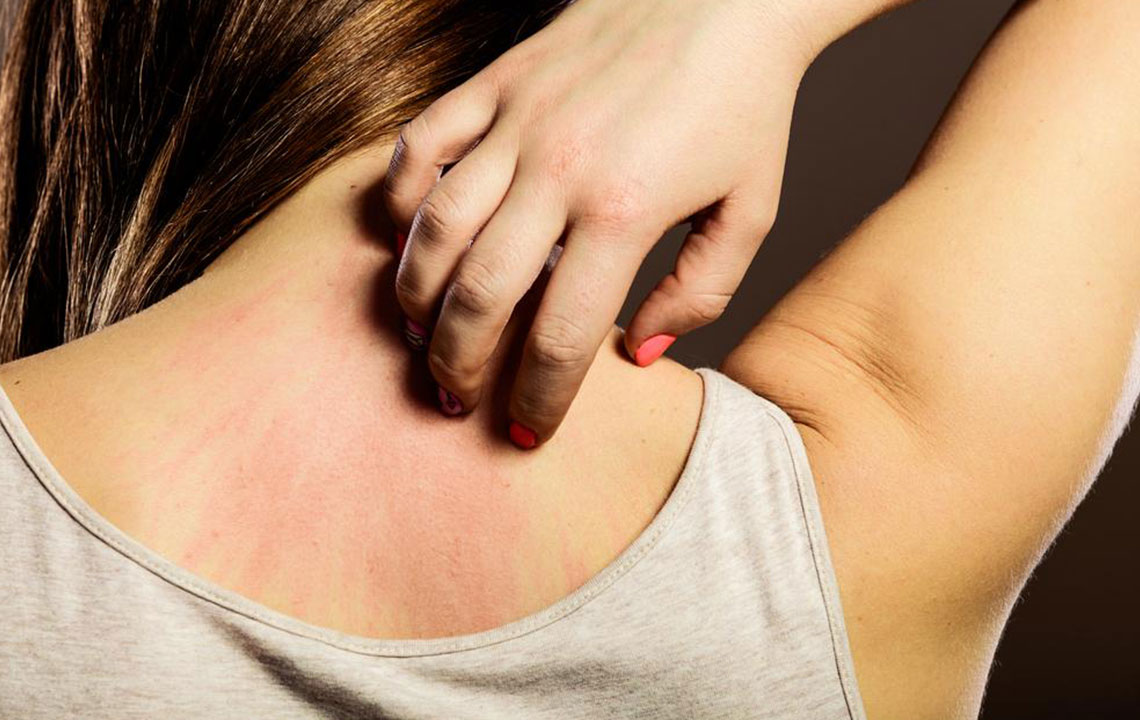
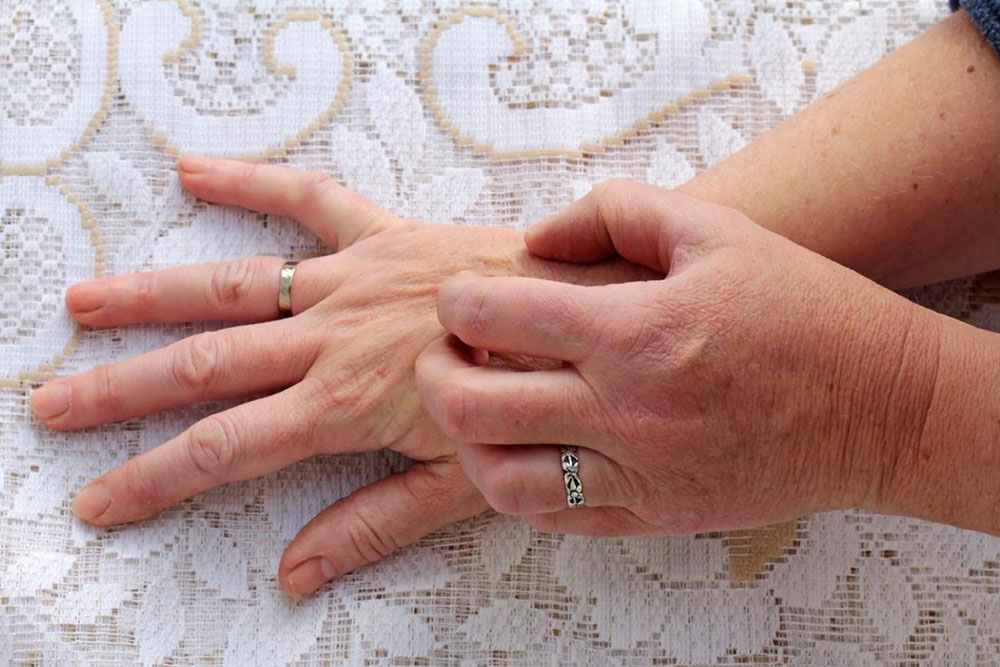
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by mites, characterized by small, itchy red bumps and blisters. These signs can be mistaken for allergies or bacterial infections, complicating diagnosis. Common symptoms include intense nighttime itching, red and flaky patches, gray skin lines, and widespread rashes. Accurate diagnosis requires medical evaluation—over-the-counter treatments are ineffective. Following prescribed therapies and preventive strategies is vital to limit spread and support recovery.
Consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options such as medicated ointments that target mites, typically applied overnight from the neck down.
Specialized creams effectively eradicate mites, reduce itching, and contain infections. Avoid skin contact with infected individuals and do not share personal items like clothing, bedding, or towels used by someone with scabies.
Washing clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water (minimum 50°C) is essential to kill mites. Dry items thoroughly on high heat for at least 10 minutes. Cleaning your environment—vacuuming and disinfecting—prevents re-infestation and maintains a mite-free space.