Comprehensive Guide to Influenza B and Its Health Risks
This article provides essential information about Influenza B, highlighting its symptoms, potential complications, prevention methods, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and vaccination to reduce health risks associated with the virus.

Comprehensive Guide to Influenza B and Its Health Risks
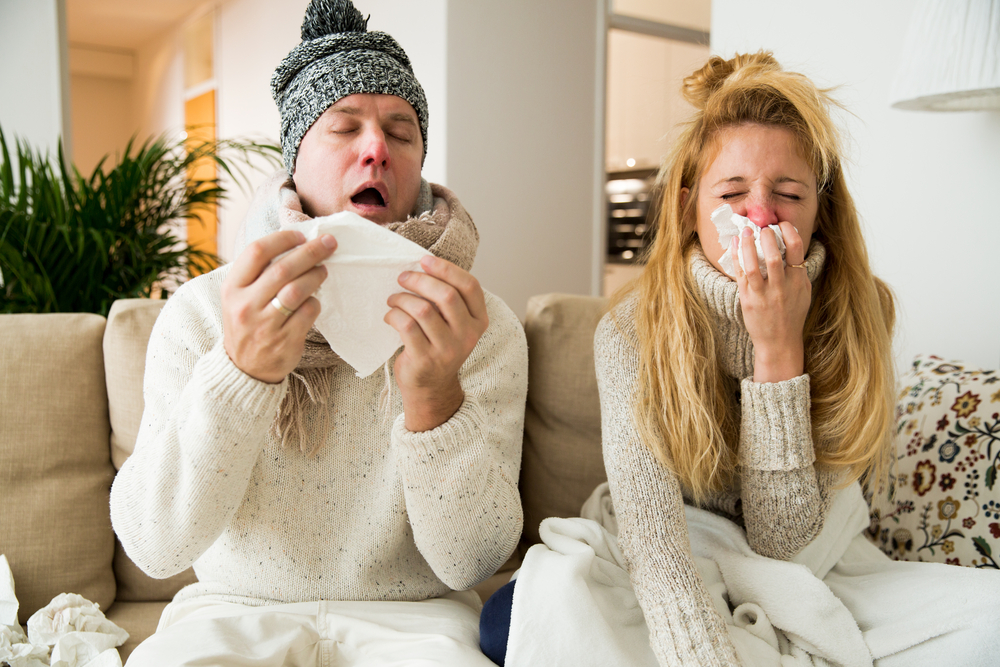
Influenza, or the flu, is a highly contagious respiratory infection caused by different flu viruses, mainly types A, B, and C. While type A is linked to large outbreaks and zoonotic transmission, type B exclusively affects humans and spreads domestically. Despite common beliefs that type B is less severe, it can cause serious illness comparable to type A.
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to avoid complications. Symptoms include high fever, sore throat, cough, chills, fatigue, muscle pain, and nasal congestion. Rapid action can prevent more serious health issues.
Respiratory signs like congestion, sore throat, and cough may worsen, especially in individuals with conditions like asthma. If untreated, influenza can lead to complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, organ failure, sepsis, and myocarditis. Children may display symptoms like nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, and diarrhea, which can be mistaken for stomach illnesses.
Preventative steps include antiviral drugs and pain remedies prescribed by healthcare professionals. Rest, hydration, and early medical consultation are vital, especially for children. Annual flu vaccination remains the best method to lower infection risk.