How Hepatitis C Affects Your Health and Body Functions
This article explains how hepatitis C affects the body, focusing on liver damage, digestive issues, neurological effects, and circulation problems. Understanding these impacts is vital for managing and treating the disease effectively, emphasizing the importance of awareness and early intervention.

How Hepatitis C Affects Your Health and Body Functions
Hepatitis C (hep C) is an infection caused by a virus that damages the liver, leading to inflammation and possible long-term harm. Transmission happens mainly through contact with infected blood, such as sharing needles or unclean tattoo equipment. Reviewing a detailed hep C overview helps understand its progression and impact.
Effects of Hepatitis C on the Body
Sometimes, individuals carry the virus without symptoms yet still face health issues.
The main effects include:
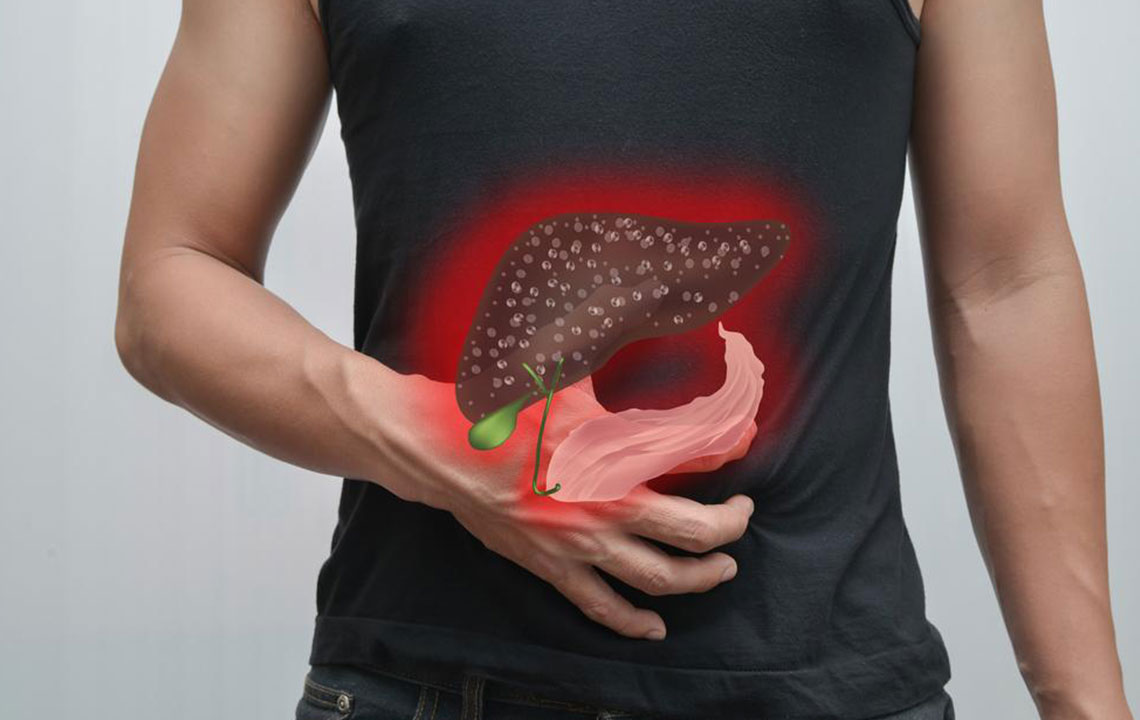
The virus primarily attacks the liver, causing inflammation that hampers its vital functions. Severe cases may cause extensive liver damage, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
A healthy liver produces bile essential for digesting fats. Hepatitis C impairs bile production, leading to digestion issues and overall digestive health decline.
If liver function declines, toxin buildup can affect the brain, resulting in memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and confusion.
Blood flow may become disrupted, raising pressure in the portal vein, risking variceal bleeding and circulatory problems.
The infection can also contribute to skin, hair, and nail conditions.
Learning about these effects through a hep C guide can assist in effective management and treatment of the disease.