Strategies to Effectively Control Gout Pain
Learn effective strategies to manage gout pain with a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Recognize early signs, improve diet, and adopt habits that reduce uric acid levels to prevent future flare-ups and maintain joint health.
Strategies to Effectively Control Gout Pain
Experiencing gout discomfort can be extremely painful and disruptive. The sudden onset of intense joint pain often hampers daily routines and comfort. As gout becomes more common, finding swift and effective relief methods is essential. Recognizing the underlying causes of gout and its impact on health is key to managing it properly.
What Is Gout?
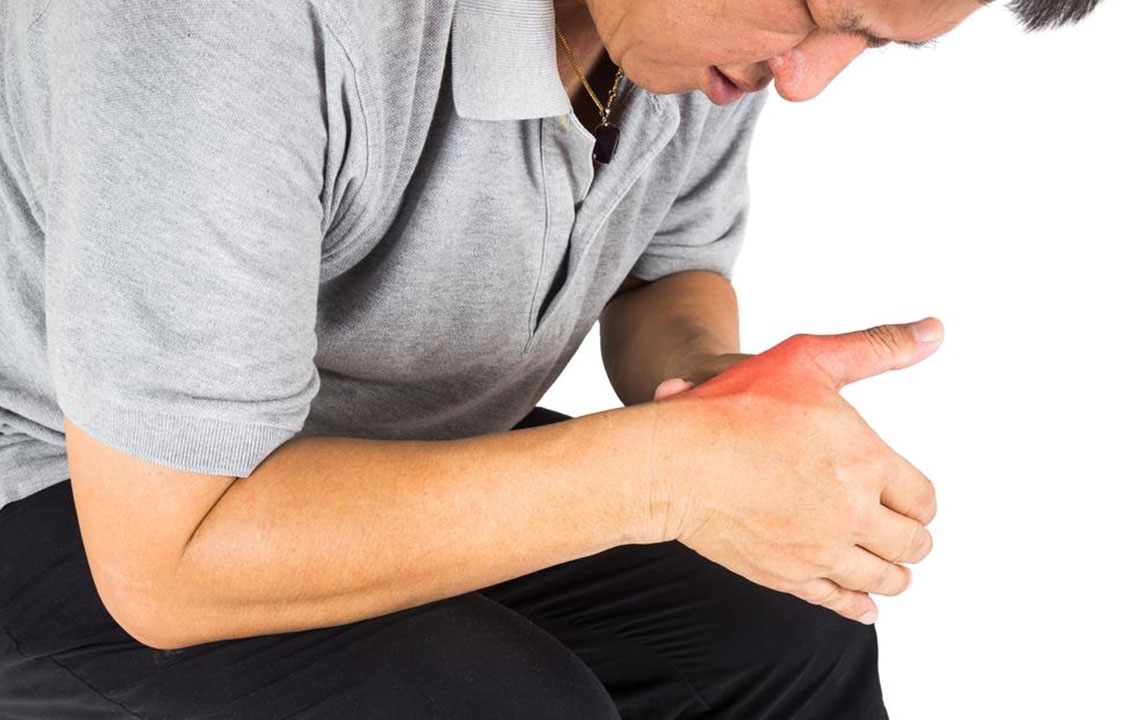
Gout is a type of arthritis driven by elevated uric acid levels in the bloodstream. Contributing factors include genetics, stress, alcohol consumption, and dietary choices. Excess uric acid forms sharp crystals within joints, causing rapid, severe pain, swelling, redness, and tenderness. Prompt pain management is necessary to protect joints and restore movement.
Gout attacks often occur unexpectedly and may be preceded by early warning signs like burning sensations or tingling in the affected joints. Many sufferers experience intense pain awakening them at night, making early detection crucial. Spotting these cues enables timely treatment and can prevent severe flare-ups.
Effective gout management combines immediate treatment with lifestyle changes. Using medication along with dietary and activity adjustments provides the best outcomes for reducing symptoms and avoiding future episodes.
Medications for Fast Gout Relief
Physicians often recommend NSAIDs for quick relief during flare-ups. Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation rapidly. To prevent recurrences, medications such as Allopurinol, Febuxostat, or Probenecid are used to decrease uric acid levels. Long-term adherence to these prescriptions can lower attack frequency and severity.
Lifestyle Changes for Long-Term Control
Maintaining a balanced diet, staying active routinely, and managing weight are vital for ongoing gout control. Consuming more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and plant proteins helps reduce uric acid. Avoid excessive red meat, sugary drinks, and alcohol. Keeping a healthy weight can decrease uric acid and lower the risk of associated cardiovascular concerns.
During a flare-up, immediate actions include taking anti-inflammatory medications, elevating the affected joint, increasing water intake, and minimizing stress. These steps ease pain and help prevent further attacks until medical treatment takes effect.