Comprehensive Overview of Gum Infections: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
This article explores gum disease, highlighting symptoms, causes, and treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, proper oral hygiene, and professional care to prevent disease progression and maintain oral health. Suitable for those seeking comprehensive dental guidance on managing periodontal conditions effectively.
Comprehensive Overview of Gum Infections: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Strategies
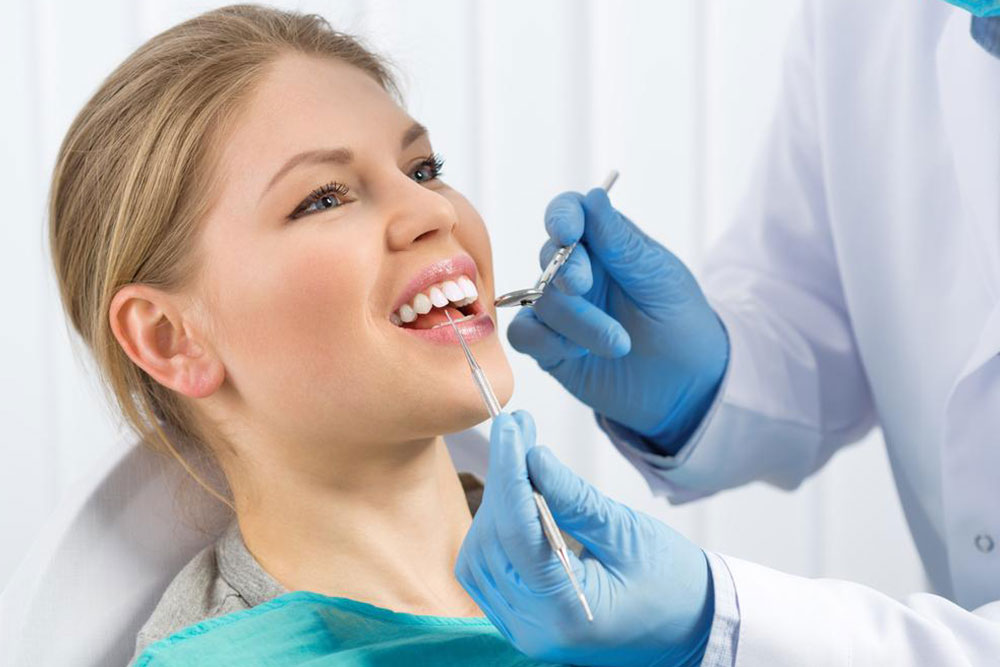
The oral cavity is highly exposed, making it susceptible to infections and various periodontal issues. Gum infections, such as gingivitis and advanced periodontitis, affect many individuals. Detecting key symptoms and understanding root causes are vital for timely care. These issues often arise from inadequate oral hygiene, hormonal shifts during pregnancy or menopause, and habits like smoking. Signs include bleeding gums, foul breath, and plaque buildup. Visiting a dentist for proper diagnosis, combined with dental treatments or surgical options, can slow or stop disease progression and restore oral health.
• Causes: Poor oral hygiene practices, such as inconsistent brushing and flossing, lead to bacterial buildup and plaque formation. Hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause can heighten risk. Additional factors include systemic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, acid reflux, as well as lifestyle choices such as smoking and drinking alcohol excessively.
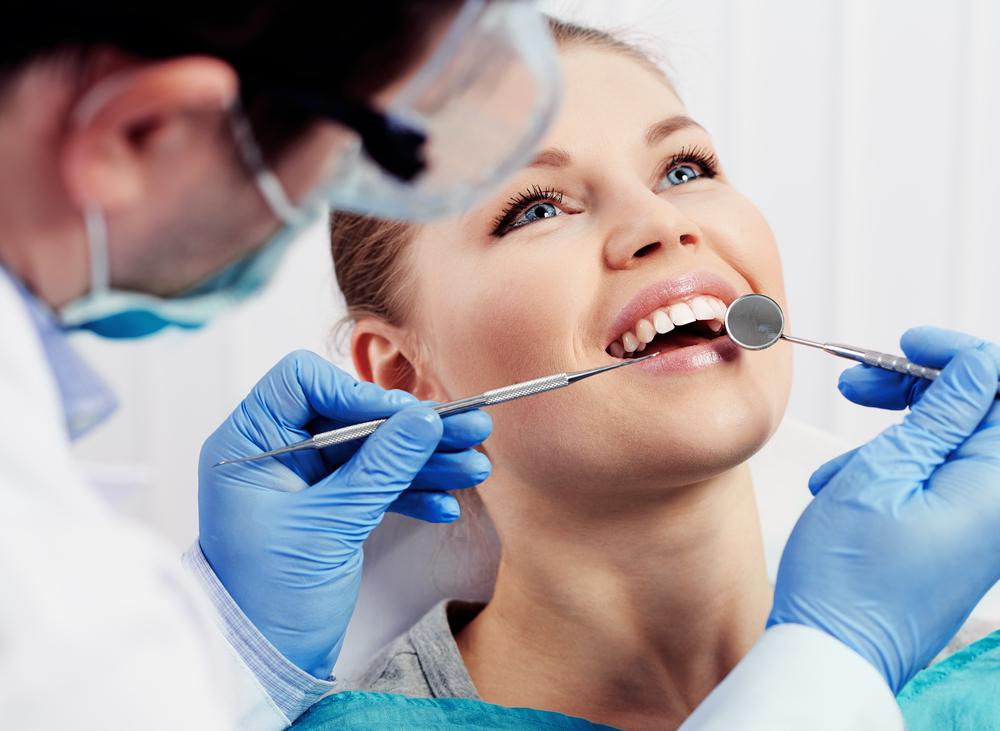
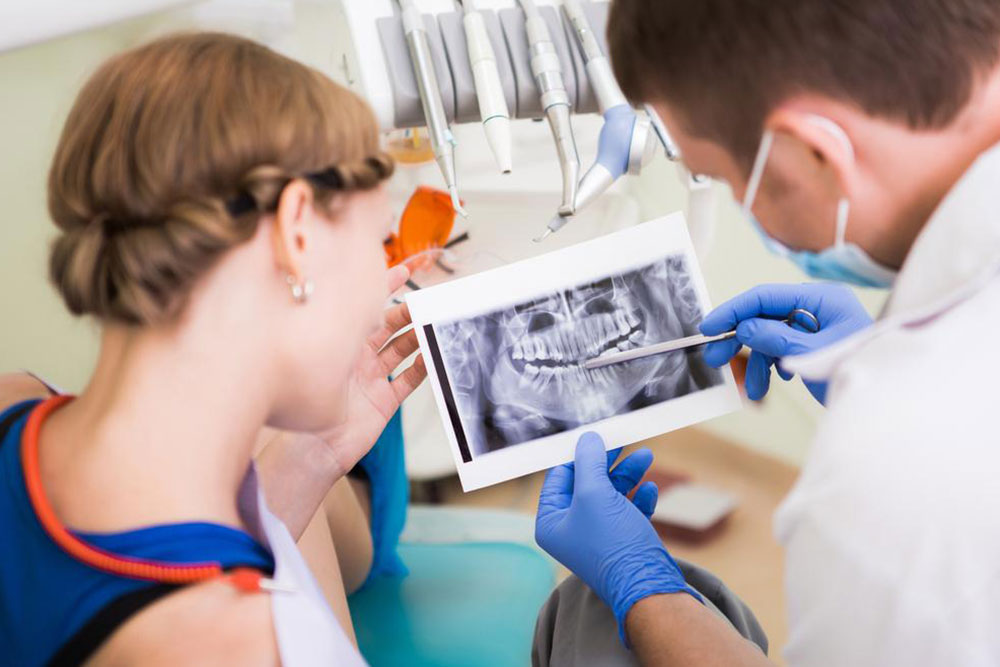
• Signs and Symptoms: Noticeable symptoms include inflamed, bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and plaque accumulation. More severe signs may be loose teeth and compromised immune response. Differentiating between mild gum inflammation (gingivitis) and serious tissue damage (periodontitis) is essential. Dental exams and X-rays aid in diagnosis and tailored treatment plans.
Treatment Methods: Dentists usually start with professional cleaning and recommend improved oral care routines. For advanced cases, treatments may involve medication or surgical procedures to remove infected tissue and reinforce gum tissue. Early management prevents further damage and promotes oral health recovery.