Effective Management Strategies for Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
This article discusses modern strategies for managing cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, highlighting surgical options, radiation therapy, cryotherapy, and lymph node dissection. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and tailored treatment approaches, including Mohs surgery for complex cases. The content aims to guide patients and healthcare professionals in choosing the most effective management methods for various tumor stages, ensuring optimal outcomes and quality of life.
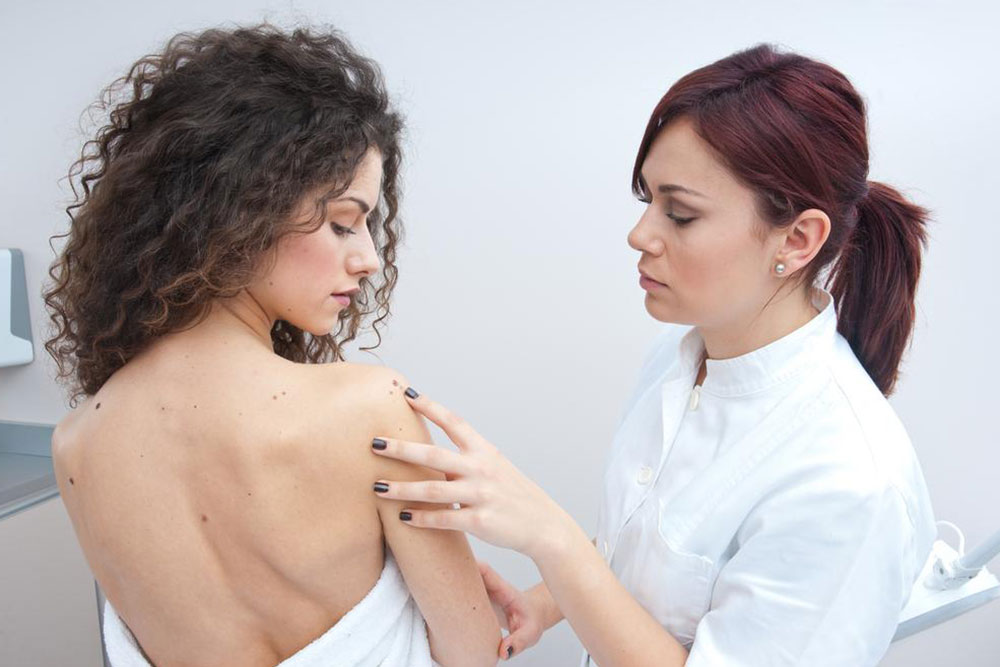
Diagnosing squamous cell carcinoma early can significantly improve treatment prospects. Small lesions are commonly managed through targeted removal or destruction methods, often leading to successful cures. However, larger tumors tend to grow quickly and have increased recurrence risks. In some cases, the cancer can spread to lymph nodes or distant sites. Recommended treatments include surgical removal, radiation therapy, cryotherapy, and lymph node dissection, depending on tumor size and location. Mohs surgery is highly effective, especially for larger or recurrent cases, while radiation is preferred for inoperable tumors. Always seek specialist advice for optimal management.
Surgical Removal
Various techniques are used based on tumor size and site, including excision and Mohs surgery, the latter offering high cure rates for complex cases.
Excision involves removing the tumor with healthy skin margins. For small tumors under 1 cm, curettage with electrodesiccation may be sufficient but less effective for larger lesions. Mohs surgery is preferred for extensive, recurrent, or delicate areas, providing precise removal and excellent outcomes. Radiation therapy serves as an alternative for larger or inoperable tumors, especially near critical structures like the eyes or nose. Cryotherapy is suitable for early-stage or patients unfit for surgery, but not for large or invasive tumors. In advanced cases, lymph node removal and postoperative radiation help prevent recurrence and manage metastasis.
Note: Our website offers extensive medical information for educational purposes. For diagnosis and personalized treatment, consult healthcare providers. We do not guarantee the accuracy of all data and recommend seeking professional advice for medical decisions.