Effective Tips for Managing Eczema in Children and Adults
Discover effective strategies to control eczema symptoms in children and adults. Learn about skincare routines, trigger avoidance, and medical treatments that help manage this chronic skin condition. Proper management can alleviate discomfort, prevent skin damage, and improve quality of life.

Effective Tips for Managing Eczema in Children and Adults
Proven Methods to Control Eczema Symptoms
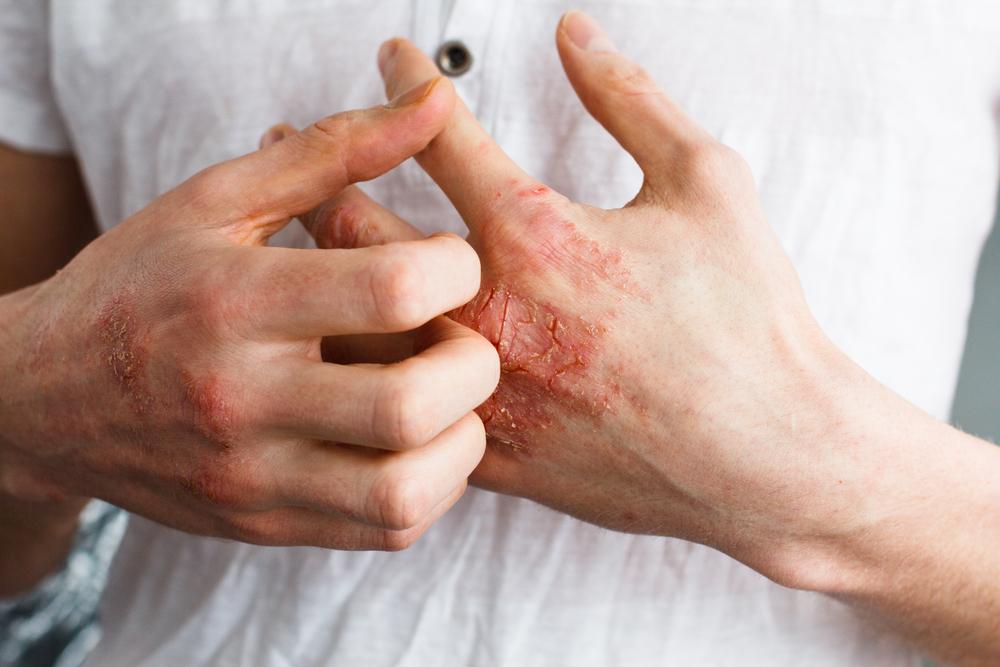
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a common skin disorder characterized by itchiness, dryness, redness, and cracked skin. While it primarily impacts young children, especially those under one year old, adults can also suffer from this persistent condition. Although chronic, many children experience improvement or resolution of symptoms as they age.
Strategies to Relieve Discomfort
There is no cure for eczema, but various treatments are effective in managing symptoms. Many young patients find their condition improves naturally with time.
Key treatments focus on symptom relief:
Applying moisturizers or emollients daily to maintain skin hydration and reduce dryness
Using topical steroids like ointments and creams to reduce redness and swelling during flare-ups
Additional options include:
Calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus or pimecrolimus for delicate skin areas
Antihistamines to alleviate severe itching
Specialized clothing or bandages that promote skin healing
Prescription medications administered by dermatology professionals
Prevent Skin Damage by Avoiding Itching
The urge to scratch worsens skin damage and raises infection risk. It can cause thickening, leathery texture, and scarring. Wearing loose, breathable fabrics and avoiding scratching—opting for gentle rubbing—can help. Keeping nails short and clean minimizes skin injuries from accidental scratching.
Identify and Eliminate Triggers
Work with your healthcare provider to pinpoint personal triggers. Common factors include irritating fabrics, excessive heat, and harsh soaps or detergents. Using soft, natural textiles like cotton, controlling room temperature, and selecting mild cleaning products can help prevent flare-ups.
Dietary Adjustments
Some foods, including eggs and dairy products, may trigger or worsen eczema. Always consult your doctor before making dietary changes, especially if food allergies are suspected. A registered dietitian can assist in creating a nutritious plan that avoids allergens but meets nutritional needs.
Effective eczema management often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including dermatologists, immunologists, or pediatricians. Breastfeeding mothers should seek medical advice before altering their diet during their child's treatment.
Importance of Moisturization
Consistent application of emollients helps retain moisture, soothe dryness, and reduce flare-ups. These products form a protective barrier, decreasing water loss and calming inflammation. Your healthcare provider can recommend suitable ointments, lotions, or creams tailored for different skin areas. Early intervention is crucial if symptoms appear.