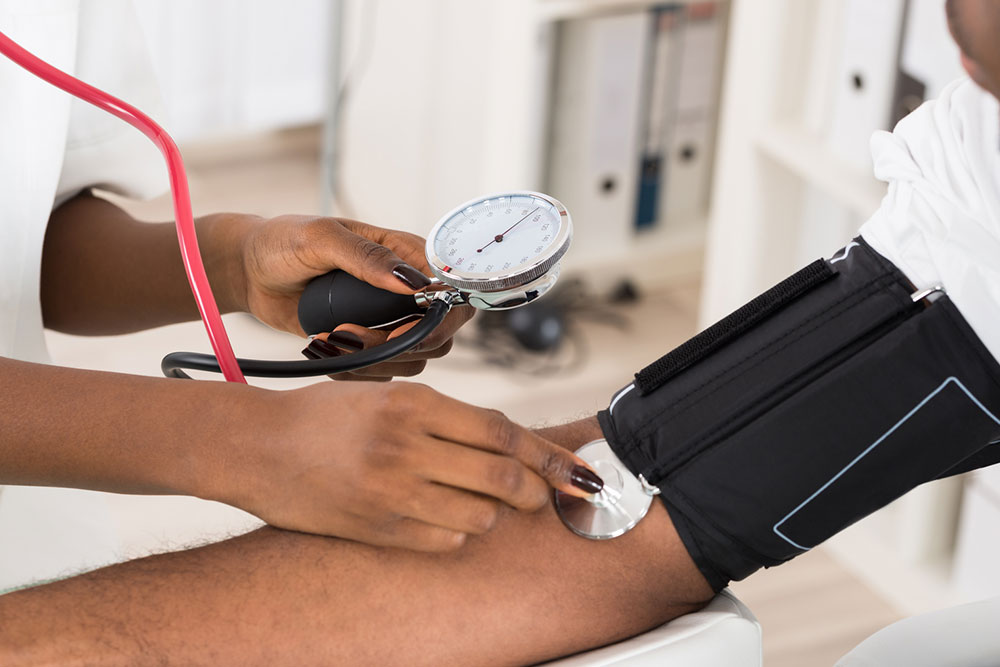
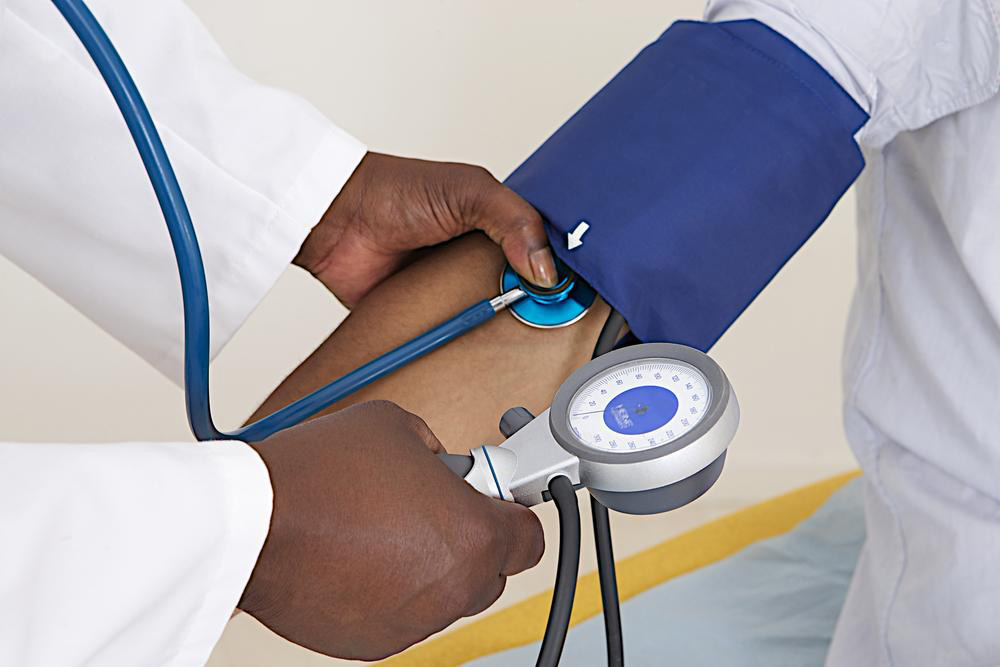
Understanding Hypertension: Causes, Risks, and Health Consequences
This article explores the causes, risks, and health impacts of hypertension. It highlights how high blood pressure can damage arteries, kidneys, and the brain, emphasizing the importance of regular monitoring. Understanding key blood pressure thresholds helps in managing and preventing severe health issues related to hypertension.
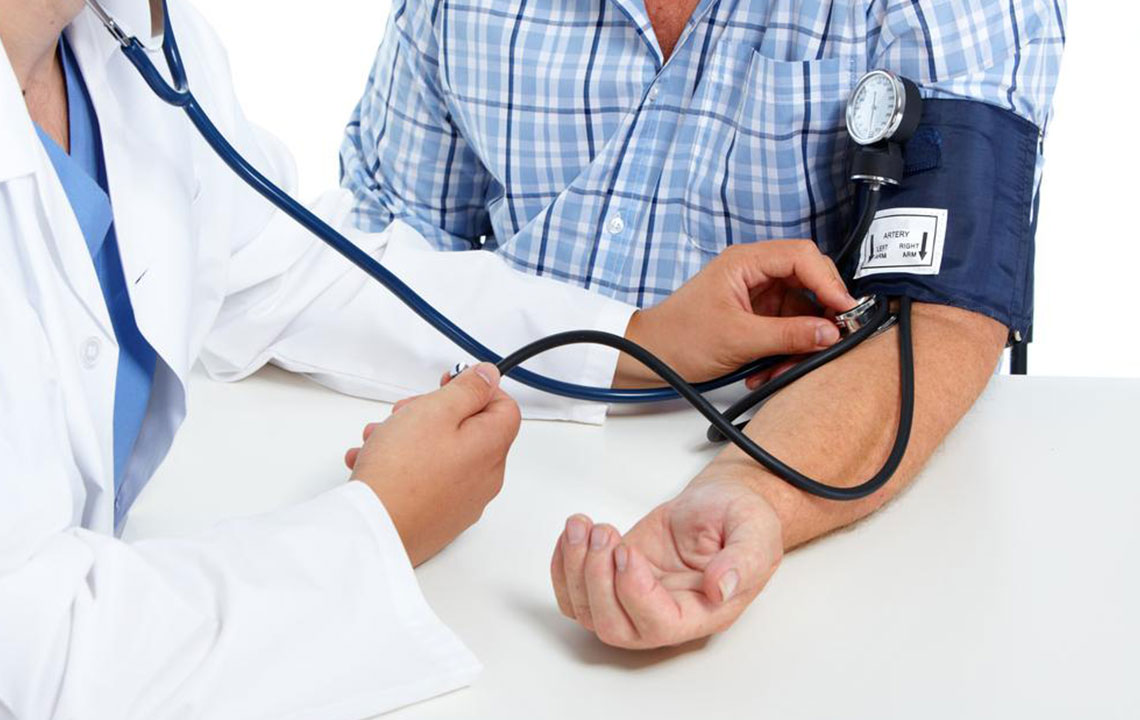
Understanding Hypertension: Causes, Risks, and Health Consequences
While the exact origins of high blood pressure are not fully understood, multiple factors can contribute to its development, including:
• Smoking and alcohol intake
• Family history of hypertension
• Excess weight or obesity
• High dietary salt consumption
• Stress and aging processes
Hypertension can lead to significant health complications:
Blood vessel damage
Elevated blood pressure hampers blood flow to limbs, leading to plaque buildup, which can cause pain, cramps, and numbness. It can also weaken arterial walls, requiring medical attention.
Kidney health issues
High blood pressure can constrict blood vessels in the kidneys, increasing the risk of renal failure.
Brain-related concerns
Uncontrolled hypertension may reduce brain blood flow or promote clot formation, raising stroke risk. Regular blood pressure checks are crucial for management.
Eye problems
Elevated blood pressure can damage eye vessels, potentially resulting in vision loss.
Keep track of your blood pressure using standard charts to understand your health status.
Here's a chart to help interpret your readings:
Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension): Systolic 50-90 / Diastolic 35-60
Normal: Systolic less than 120 / Diastolic less than 80
Pre-Hypertension: Systolic 120-139 / Diastolic 80-89
Note: Systolic measures the heart's pressure during beats, and diastolic measures when the heart relaxes. Monitoring these helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels.