Proven Methods for Treating and Preventing Urinary Tract Infections
This article reviews effective strategies for managing urinary tract infections, emphasizing early diagnosis, symptom recognition, and both medical and home treatment options. It highlights the importance of hydration, proper hygiene, and medical consultation to prevent complications and promote recovery. Suitable for individuals seeking practical advice on UTIs, the article aims to inform and support timely management of this common condition.

Proven Methods for Treating and Preventing Urinary Tract Infections
Dealing with a urinary tract infection? Stay calm—this condition is common and manageable. Many symptoms can be eased with simple home care, but professional medical advice is essential to prevent complications. Prompt consultation with a healthcare provider ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate therapy.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) results from bacterial invasion affecting organs such as the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys. Given their role in urine processing, infections here can cause significant discomfort.
Bacteria responsible mostly for UTIs include Escherichia coli (E. coli). Importantly, UTIs are non-contagious.
Common causes of UTIs
Bacteria entering during sexual activity
Using unsterilized or unhygienic bathroom facilities
Kidney stones obstructing urinary passageways
Weakened immune systems, such as in diabetics
Medical interventions like catheters or chemotherapy
Prolonged holding of urine increases infection risk.
Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, spinal injuries, or anatomical anomalies can also contribute to UTIs.
Early diagnosis is key for effective management. Women are more susceptible due to their shorter urethra and proximity to the rectum.
Symptoms to watch for
Recognizing these signs can lead to timely treatment:
Pain or burning during urination
Sudden urge to urinate (bladder spasms)
Frequent urination without relief
Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
Foul-smelling or discolored urine
Pelvic or lower abdominal discomfort
Blood or cloudiness in urine
Pain during sex
Fever, chills, fatigue
Treatment tips for UTIs
Antibiotics are commonly prescribed based on severity and patient history. Always complete the full course as directed. Alongside medication, consider these home remedies for symptom relief:
Hydration – Drink plenty of water to help flush bacteria. Caution: consult your doctor if kidney issues exist.
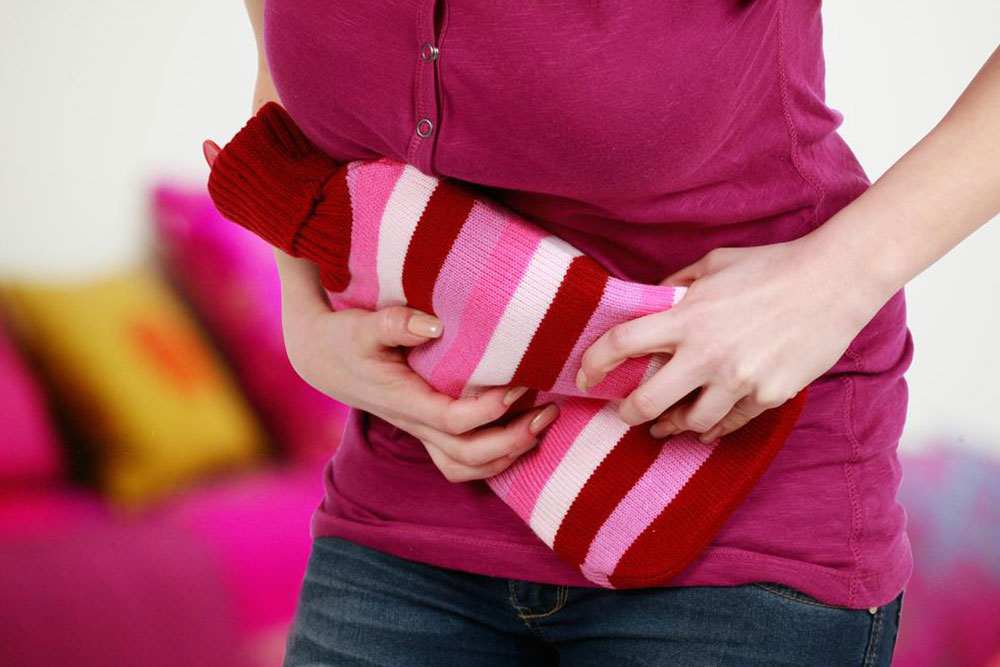
Heat application – Use a heating pad to relieve pain temporarily, avoiding direct skin contact and limiting session duration.
Diet adjustments – Avoid spicy, caffeinated, carbonated, or alcoholic foods that may worsen symptoms. Focus on nutrient-rich, high-fiber diets to aid recovery.
Urination habits – Urinate frequently to eliminate bacteria, supported by increased fluid intake.
Clothing choices – Wear loose, clean clothing to reduce moisture and bacterial growth in the genital area.
Remember, while home remedies can ease discomfort, professional medical care is essential for proper treatment. Always consider your medical history and current medications under professional guidance.