Ultimate Guide to Modern Contraceptive Methods: Pros, Cons, and Choices
This comprehensive guide explores modern contraceptive methods, highlighting their benefits, potential side effects, and choices available for effective family planning. It offers valuable insights for couples seeking to manage pregnancy timing responsibly with professional medical advice.

Ultimate Guide to Modern Contraceptive Methods: Pros, Cons, and Choices
Starting a family is a significant milestone that requires careful planning and readiness. Effective contraception plays a vital role in helping couples manage pregnancy timing. Choosing the right family planning method can be daunting, especially for young couples, but exploring available options helps identify what best suits their needs. Understanding the benefits and potential side effects of various methods ensures informed decisions for a healthy future.
Read on for an in-depth look at the advantages, disadvantages, and different family planning choices available today.
Advantages of Family Planning
Deciding how many children to have and spacing pregnancies appropriately is essential. Allowing 2-3 years between births gives mothers time to recover physically and mentally, lowering health risks. Economically, family planning enables couples to secure financial stability before expanding their family.
Possible Drawbacks
Different contraceptive methods can have side effects like fatigue, dizziness, weight fluctuations, or headaches. Rare complications such as blood clots or ectopic pregnancies may occur. It’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals to ensure safe and effective choices.
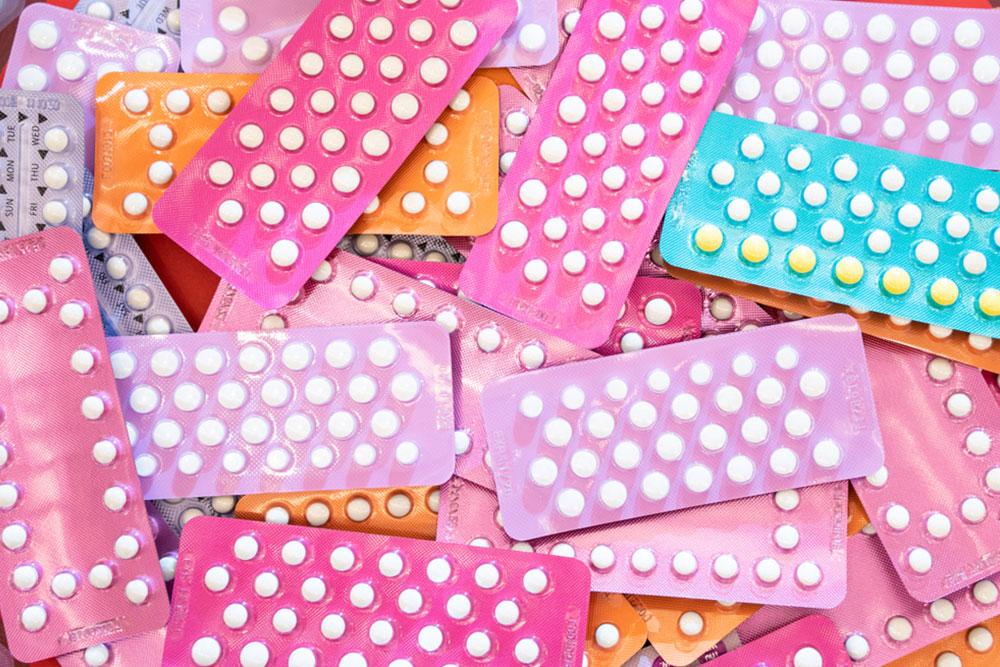
Widely Used Contraceptive Options
Barrier methods: These prevent sperm from reaching the egg by blocking pathways. Common options include condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, and spermicides. Condoms are highly effective and additionally protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Hormonal methods: Tailored for women, these use hormones like estrogen and progestin to temporarily prevent pregnancy. Examples include pills, injections, vaginal rings, and patches.
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): For long-term, reversible contraception, IUDs are inserted into the uterus. They include hormonal types lasting 3-4 years and copper ones up to 10 years, both effectively preventing fertilization.
Permanent methods: When childbearing is complete, sterilization procedures like tubal ligation and vasectomy provide permanent contraception options.
Natural family planning involves tracking menstrual cycles to avoid fertile days, but it may be less reliable than modern methods.
Note:
This overview provides general information about family planning methods. It’s essential to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice. The content does not cover all available options or specific offers; professional guidance ensures the safest choice.