Effective Strategies for Preventing and Treating Urinary Tract Infections
This article explores the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for urinary tract infections, emphasizing early detection and effective management to promote health. It highlights how simple measures and medical interventions can help recover swiftly from bladder infections.

Effective Strategies for Preventing and Treating Urinary Tract Infections
Understanding and Managing Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), commonly known as bladder infections, happen when bacteria infiltrate the bladder through the urethra. The urethra's function is to eliminate urine from the body. Bacteria attaching to the bladder lining multiply rapidly, causing infection.
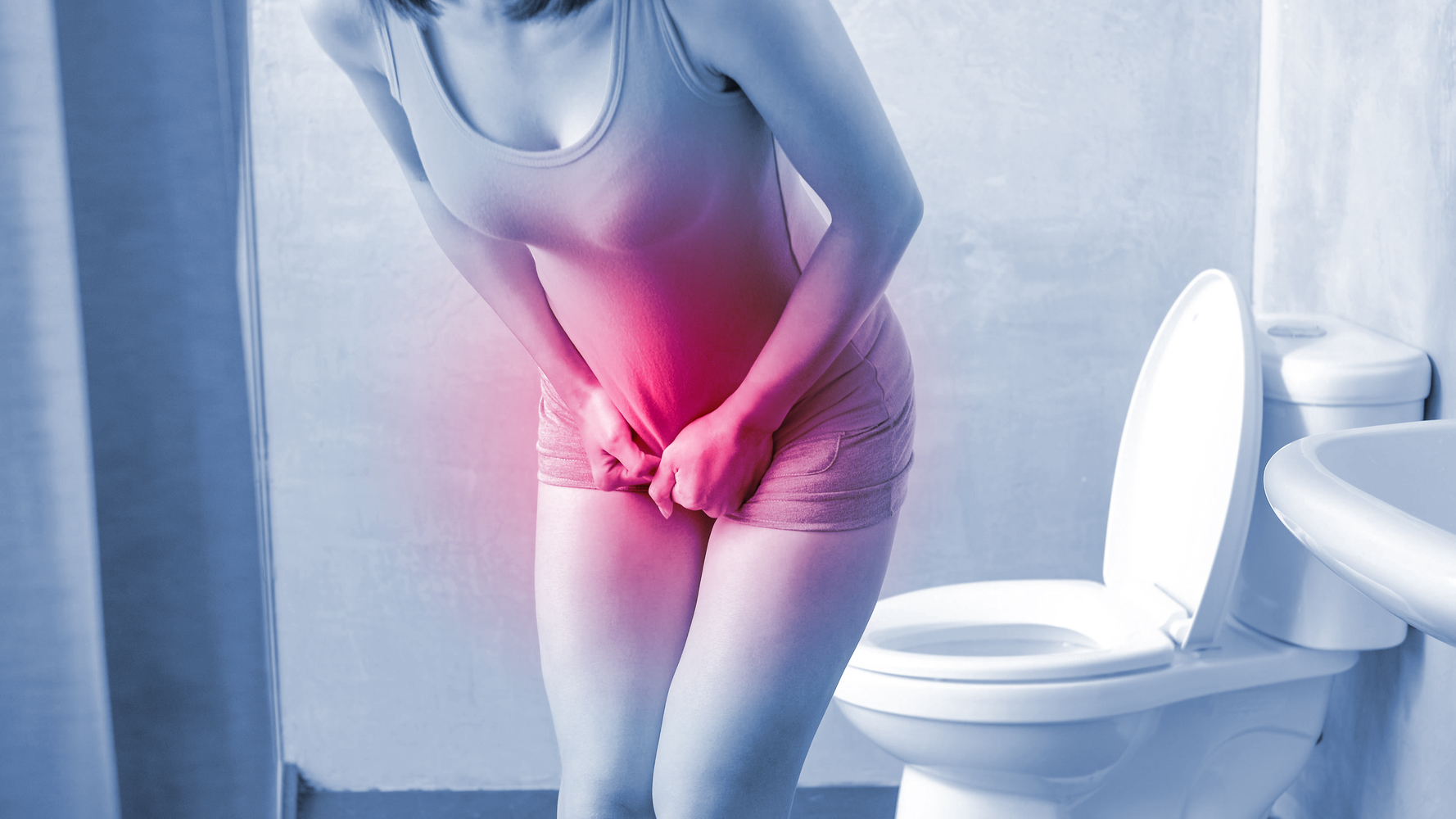
Typical symptoms include a sudden, strong urge to urinate, often with burning pain, discomfort during urination, and lower abdominal pain.
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam by a healthcare provider, along with urine analysis to detect bacteria, blood, or pus. More complicated cases, especially in children or individuals with kidney problems, may require imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT, MRI, or cystoscopy. Treatment varies based on infection severity; mild cases often improve with increased fluid intake and rest, while more persistent infections are treated with antibiotics for three to seven days. Chronic or complex infections might need longer medication courses or additional interventions like estrogen therapy for postmenopausal women or extended antibiotic use for prostate infections. Pain relief options are available to ease discomfort. Prompt diagnosis and proper treatment are vital for a full recovery.