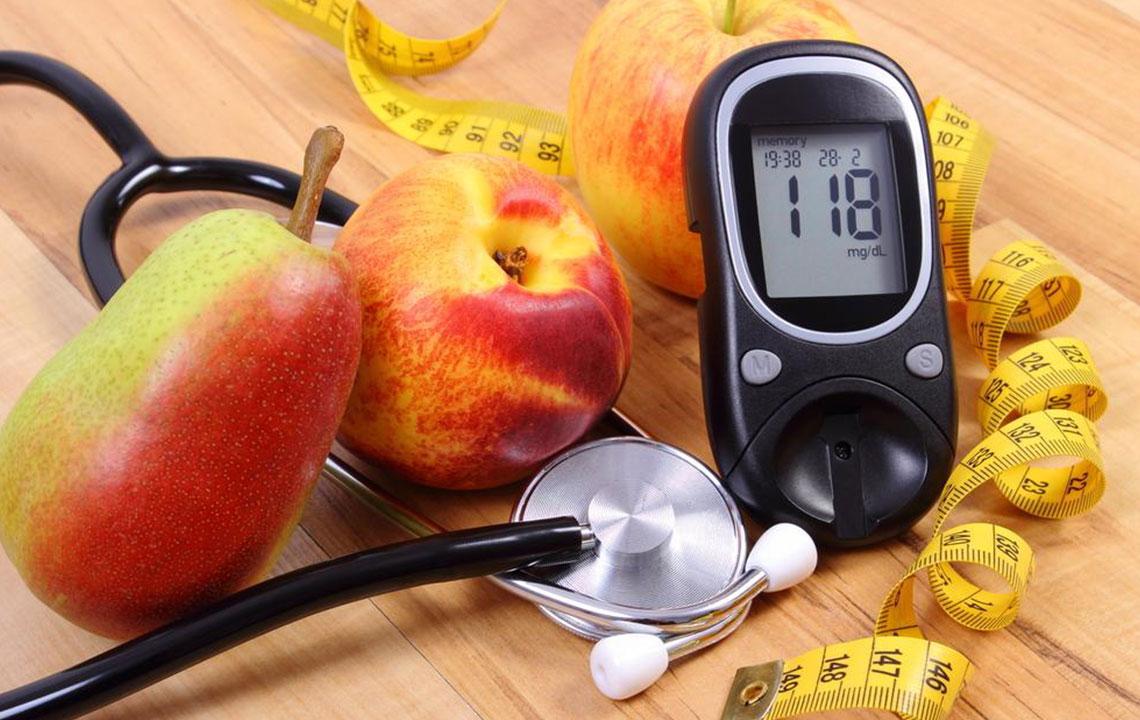
Essential Insights for Managing and Understanding Diabetes
This guide offers comprehensive insights into diabetes, highlighting symptoms, risk factors, and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions to control blood sugar levels. The article also explores various treatment options and supportive therapies, empowering individuals to better manage this chronic condition effectively.
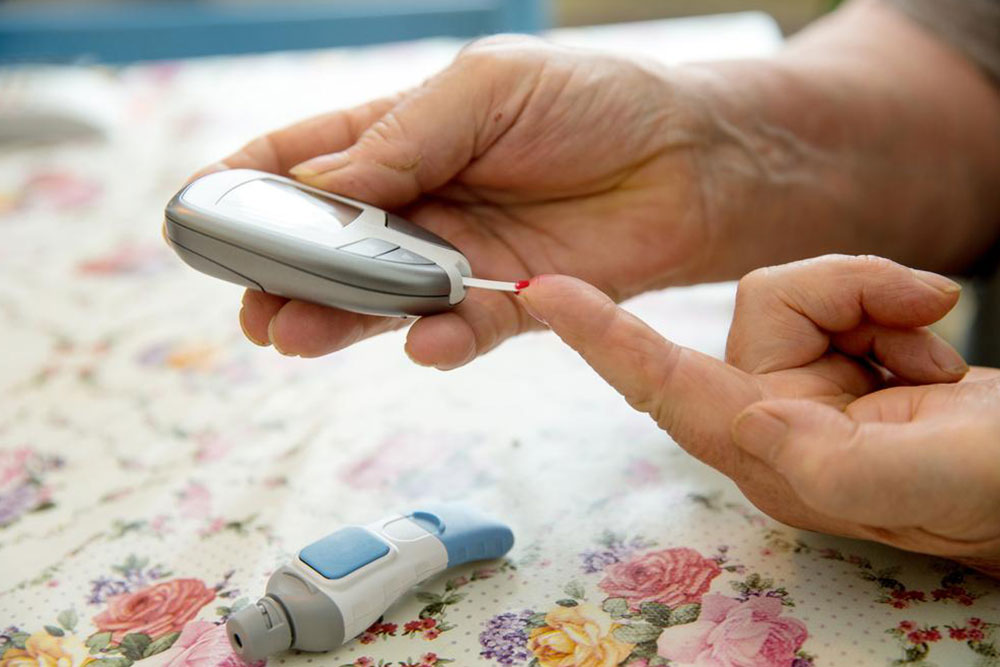
Essential Insights for Managing and Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes, or diabetes mellitus, is a chronic metabolic condition marked by high blood sugar levels. It arises when the body either produces insufficient insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. Common indicators include excessive thirst, frequent urination, and persistent hunger. As of 2013, over 382 million individuals worldwide were living with diabetes, a number that has increased significantly over recent years.
Recognizing Diabetes Symptoms
Some people may experience subtle or no symptoms initially, causing delays in diagnosis and increasing risks of complications. Typical symptoms consist of:
Frequent urination: Insufficient insulin causes the kidneys to filter more water alongside glucose, leading to increased urination.
Intense thirst: Fluid loss through urination results in dehydration, prompting a strong urge to drink.
Persistent hunger: Disrupted insulin activity affects how the body manages energy, resulting in constant hunger.
Additional signs can include unexplained weight changes, blurred vision, fatigue, and mood swings. Timely detection and proper management, including medications and lifestyle modifications, are essential.
Strategies to Manage and Control Diabetes
While there is no current cure for Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, symptoms can be effectively controlled. Lifestyle interventions, especially healthy eating and physical activity, are key. Regular exercises such as walking, swimming, or jogging help reduce blood sugar and prevent nerve damage. In cases of ongoing foot or nerve pain, medications may be prescribed, with caution for individuals with heart issues. Complementary therapies like meditation, acupuncture, and biofeedback can aid in symptom management. Always seek medical advice before starting new treatments.