Essential Guide to Blood Sugar Monitoring: Importance, Key Factors, and Control Strategies
This article offers an insightful overview of blood sugar monitoring, emphasizing its significance, key components of blood glucose charts, and strategies to maintain stable levels. Understanding these elements helps prevent complications related to diabetes and supports overall health through diet, exercise, and stress management.
Blood sugar levels indicate the amount of glucose circulating in your bloodstream at any moment. Glucose provides energy to your body’s cells and originates mainly from your diet. The body maintains tight control over blood glucose to prevent dangerous highs and lows. Unlike table sugar, blood sugar is solely composed of glucose, crucial for maintaining good health.
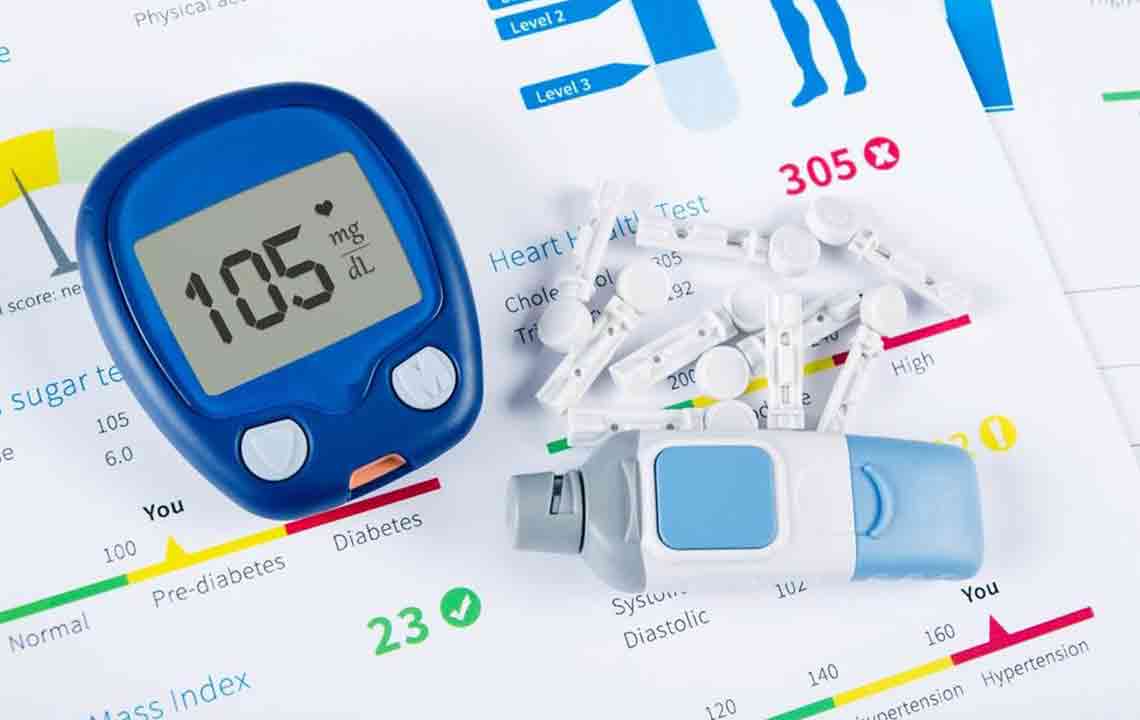
Levels of blood sugar change throughout the day. They reach their lowest early mornings, increase after meals, then stabilize. Normal fasting levels are generally below 99 mg/dL, whereas diabetics often aim for below 130 mg/dL pre-meal and under 180 mg/dL post-meal.
What Is a Blood Glucose Monitoring Chart?
Regularly tracking blood glucose helps maintain health. Diet, medication, and exercise influence these levels. A glucose chart records these readings over time, highlighting patterns necessary for effective diabetes management. Monitoring fluctuations allows for better health decisions and early detection of problems.
Stable blood sugar is vital for protecting organs like kidneys, eyes, and the heart. Frequent recording helps identify dangerous spikes or dips, reducing health risks. People with diabetes especially benefit from diligent monitoring to avoid complications and support overall wellness.
Many devices assist with blood sugar measurement, but consulting healthcare providers before using them is recommended. Key components include fasting and post-meal readings. Comparing results against normal ranges indicates whether blood sugar levels are safe. For non-diabetics, fasting below 100 mg/dL and post-meal under 140 mg/dL are ideal.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for balanced blood glucose. This involves eating a nutritious diet, getting enough sleep, engaging in regular physical activity like walking, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol. Managing stress is also important for keeping glucose levels stable and preventing metabolic issues.