Managing Overactive Bladder: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Treatment Options
This article explores the key symptoms of overactive bladder and outlines effective management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and personalized treatment options, including lifestyle changes, medications, nerve stimulation, and surgery. Recognizing signs early can greatly improve quality of life and prevent complications related to this common condition, especially among older adults.

Managing Overactive Bladder: Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Treatment Options
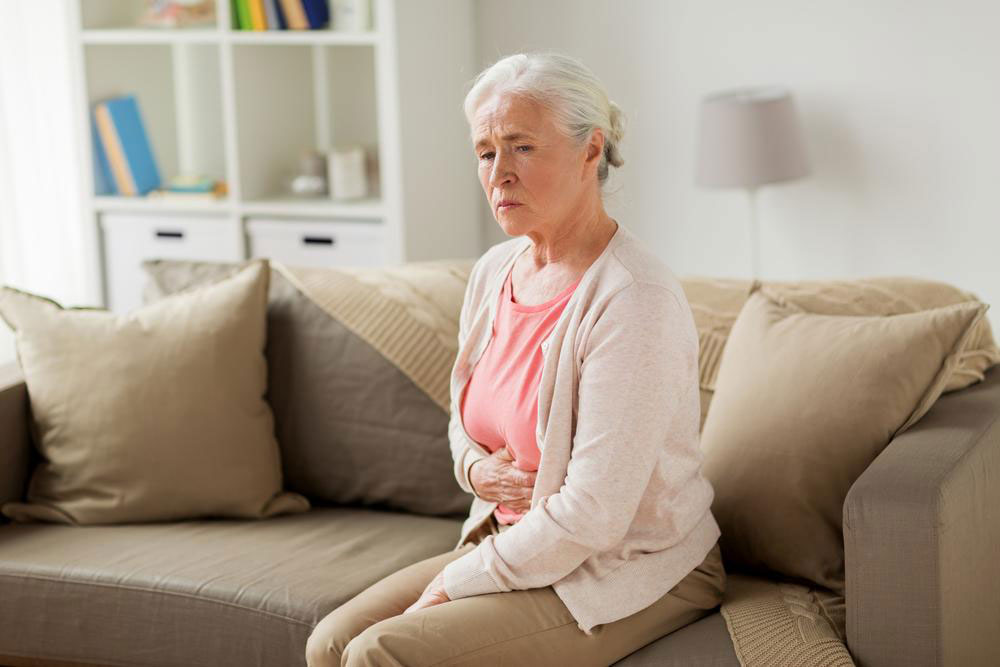
Overactive bladder (OAB) is characterized by a sudden, uncontrollable need to urinate, often accompanied by frequent trips to the restroom and occasional leakage. Especially common among older adults, untreated OAB can severely affect daily activities and mental health. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial, as timely diagnosis enables effective management. If persistent urgency or leakage occurs, consult a healthcare provider who may recommend tests like physical exams, urine analysis, and bladder function assessments.
Diagnostic procedures help determine severity by evaluating urine flow, pressure, and volume. Treatment strategies include lifestyle changes, dietary modifications, pelvic exercises, medications, nerve stimulation, and in extreme cases, surgery, based on individual needs.
Reduce caffeine and alcohol consumption to lessen bladder irritation
Perform pelvic floor exercises such as Kegels to strengthen bladder muscles
Maintain a healthy weight and avoid smoking to minimize risks
Use medications prescribed by your doctor to relax bladder muscles
Consider nerve stimulation therapies if medications are ineffective
Surgical procedures are reserved for severe, unresponsive cases
In conclusion, managing OAB involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medical treatments, and possibly surgery. Early intervention and personalized care significantly enhance quality of life for patients.