Early Signs and Factors of Hearing Loss: What You Need to Know
Learn about the key signs and risk factors of hearing loss, including age, noise exposure, genetics, medication effects, and health conditions. Early detection and treatment options like hearing aids can help maintain auditory health and improve quality of life.
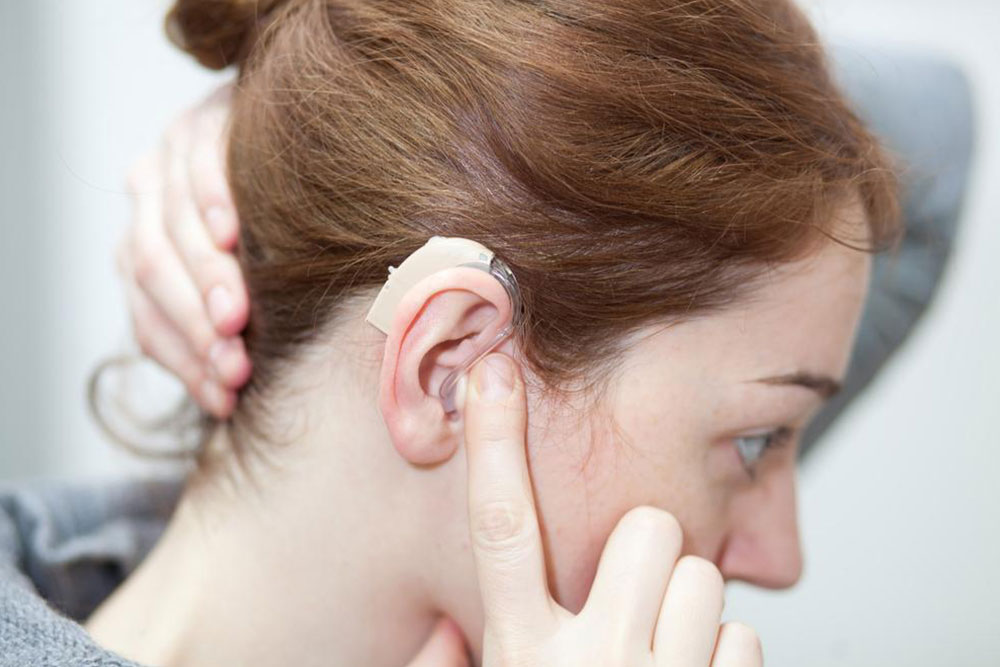
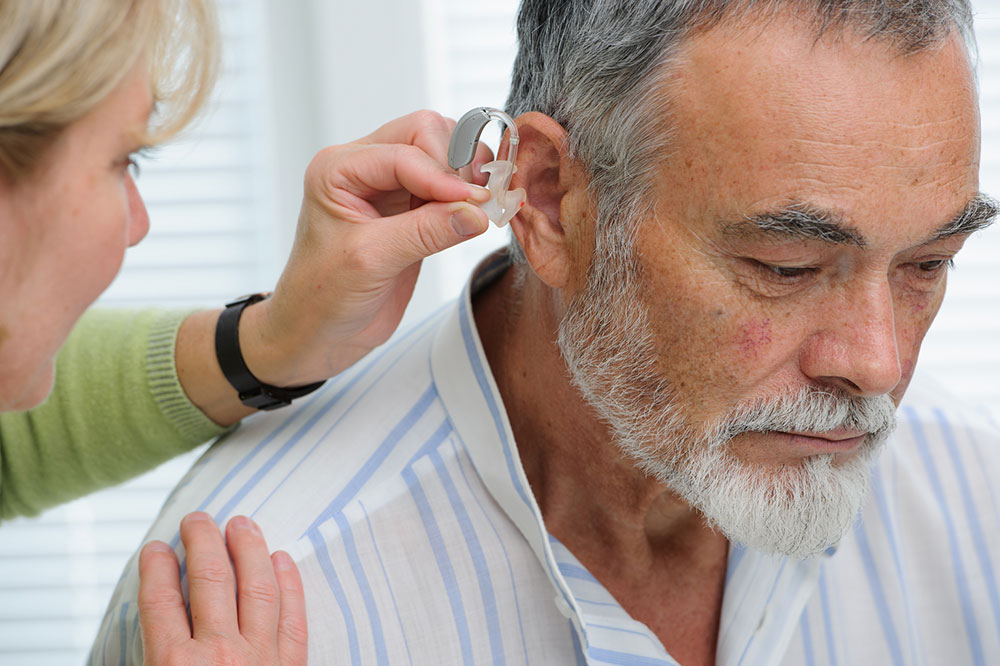
Hearing decline can occur at any age, even if your hearing appears normal from birth. Over time, you might notice difficulty understanding conversations or sounds, leading to permanent hearing loss. Fortunately, devices like hearing aids can improve sound clarity by amplifying ambient noises.
Several risk factors contribute to hearing deterioration, including:
Age: The structures within your inner ear become weaker as you grow older, raising the risk of hearing problems.
Extended noise exposure: Consistent exposure to loud sounds above 80 decibels, especially between 80-110 decibels, damages inner ear cells.
Sudden exposure to very loud sounds, such as explosions, can cause temporary or permanent hearing damage. Using ear protection in noisy settings is crucial.
Genetic factors: Hearing loss often runs in families; if relatives experience it, your risk increases.
Medication effects: Certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, high-dose painkillers, and aspirin may harm hearing or cause temporary ringing.
Health issues: Conditions like meningitis can damage the cochlea, affecting hearing ability.
Recognizing early warning signs allows for prompt diagnosis and treatment, which may involve hearing aids, surgery, or cochlear implants, especially when inner ear damage occurs.
Watch for symptoms such as muffled sounds, difficulty distinguishing speech, trouble hearing consonants, and requiring louder volumes on devices. Ignoring these signs can lead to social isolation, emotional stress, and depression. Early intervention helps preserve hearing and improve overall well-being.
Our selection of hearing solutions and medical treatments support those with hearing challenges. Timely detection is essential for effective management and improved auditory health.
Note: The information provided is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and personalized care.