Complete Guide to Skin Rashes Associated with HIV
This guide provides comprehensive information on HIV-related skin rashes, including their causes, symptoms, and complications like cellulitis and herpes. It offers practical insights for early recognition and management of skin issues associated with HIV infection, emphasizing the importance of medical evaluation and treatment. Understanding these rashes can aid in timely diagnosis and improve quality of life for affected individuals.
Complete Guide to Skin Rashes Associated with HIV
Understanding HIV-Related Skin Reactions
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) gradually weakens the immune system, raising the likelihood of cancers and serious infections. Although manageable with treatment, a cure remains elusive. This article offers vital information about skin rashes linked to HIV infection.
What Are HIV-Related Rashes?
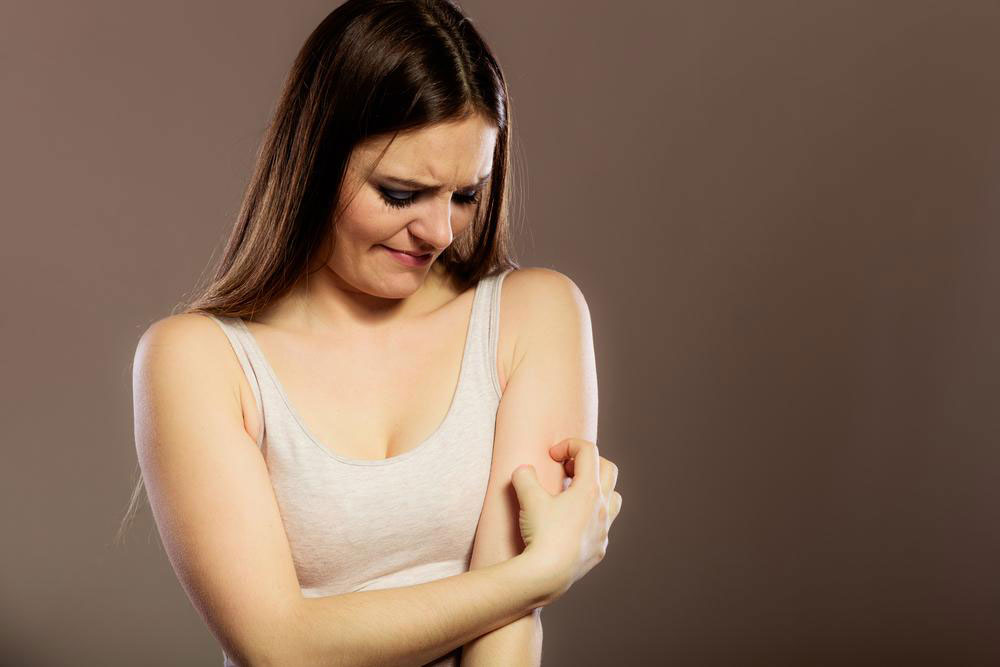
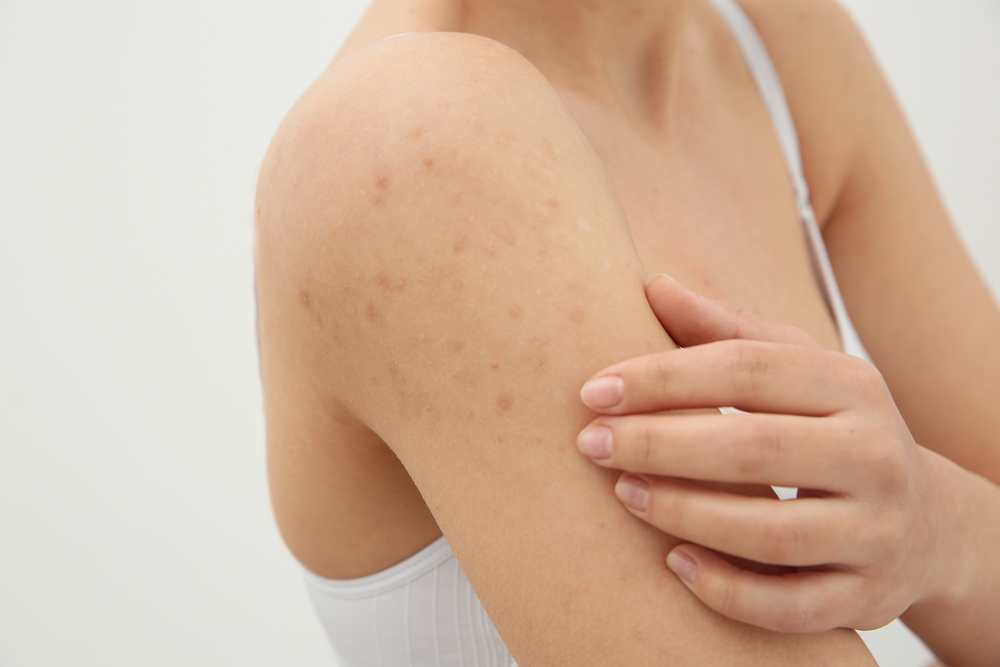
Skin lesions and rashes are some of the earliest visible signs of HIV infection.
These symptoms generally appear within two months after contracting the virus.
Common areas where HIV rashes occur include the hands, legs, face, and chest.
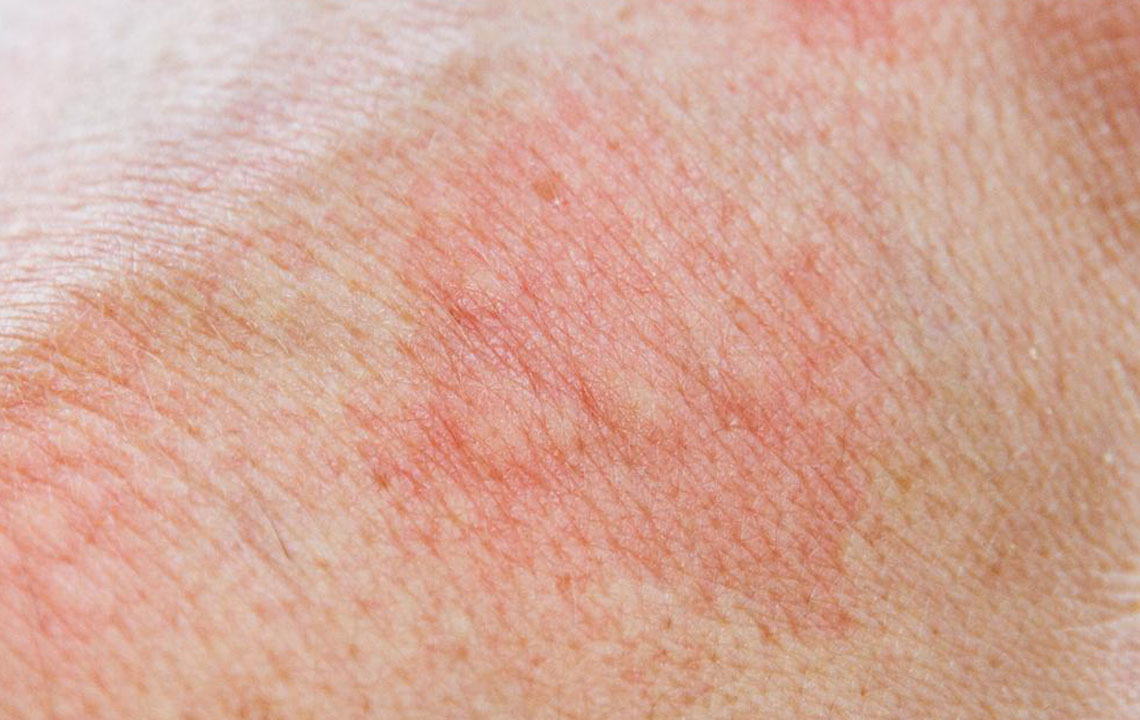
These rashes typically look like red, flat patches with small bumps. Checking images online can help identify whether a rash is related to HIV or other causes.
They often result in persistent itchiness and discomfort.
Causes Behind HIV Skin Rashes
The rashes may be caused directly by HIV or as side effects or allergic reactions to HIV medications, especially antiretrovirals.
Identifying the exact cause can sometimes be difficult in individuals with HIV.
Factors That Can Worsen Rashes
Allergic responses, other infections, or illnesses might aggravate skin rashes.
Certain drugs can exacerbate the condition.
Prolonged sun exposure can intensify rash severity.
Dietary or skincare routine changes may impact skin health.
Frequent changes in hygiene habits, exposure to extreme weather, or hot showers can worsen symptoms.
Seroconversion Skin Reaction
Within weeks of acquiring HIV, the body begins producing antibodies, often resulting in a rash called seroconversion rash.
This rash appears as flat red patches on the chest or back and usually does not itch.
Understanding Cellulitis
Cellulitis is an acute bacterial skin infection affecting the deeper layers, marked by swelling, intense pain, and fever.
It often arises from minor cuts but can develop without visible wounds.
The affected area becomes warm, red, and inflamed, with possible streaks extending from it.
Herpes Virus Skin Infections
People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV, may experience more severe herpes infections.
Herpes presents as painful blisters that may crust over, affecting areas like the mouth or genitals.
Shingles (herpes zoster) can appear on one or both sides of the body in HIV-positive individuals.
What Is Tinea (Ringworm)?
Ringworm is a common fungal infection that causes skin rashes and is easily acquired by HIV-positive individuals.