Essential Insights into MRSA: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Learn about MRSA, a resistant bacterial infection, including its causes, symptoms like boils, and effective prevention and treatment strategies. Early detection and proper hygiene are key to managing this superbug, with medical and natural remedies available to aid recovery.

Essential Insights into MRSA: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
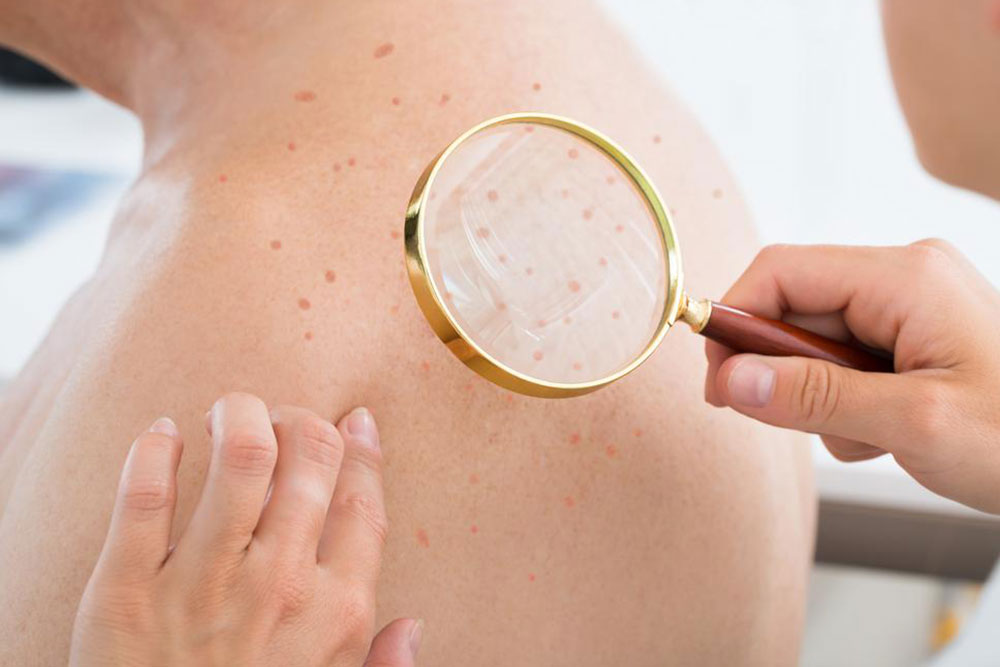
MRSA, or Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus, is a highly contagious bacteria classified as a "superbug" because of its resistance to multiple antibiotics including methicillin, amoxicillin, penicillin, and oxacillin. When it breaches the skin or enters the bloodstream, it becomes challenging to treat and often requires intravenous antibiotics. Detecting small skin abscesses early and draining them can prevent severe complications. The bacteria spread through direct skin contact and contaminated objects. Symptoms typically appear as boils or pimples that may intensify without care.
Individuals with compromised immune systems, recent cuts, surgical wounds, or chronic illnesses are more vulnerable to MRSA. The bacteria can survive on everyday surfaces and spread via touch. Elderly populations, or those with frequent antibiotic use, face higher risks. Skin irritations or rashes can provide entry points for infection. To prevent infection, practice good hygiene, clean wounds promptly, avoid sharing personal items, and stay away from contaminated environments. Vigilance and proper hygiene are critical measures to stay safe.
The bacteria responsible for MRSA is Staphylococcus, which many carry unknowingly. Minor skin injuries or weakened immunity can lead to infection. Maintaining cleanliness, avoiding sharing personal grooming tools, and steering clear of contaminated areas help reduce risk. Proper wound management and hygiene are vital for prevention.
Preventive Strategies
To lower MRSA risk, keep your surroundings clean, treat wounds immediately, and avoid contact with infected individuals or objects. Regular hand sanitization, not sharing towels, razors, or makeup, and seeking medical advice for suspicious skin infections are essential. Practicing good hygiene and cautious behaviors significantly diminish infection chances.
Medical Treatment Options
Managing MRSA requires prompt medical care. Since most standard antibiotics are ineffective, doctors often prescribe drugs like trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, or combinations with rifampin depending on the infection severity. Completing the full prescribed course and using topical treatments help eliminate the bacteria and prevent recurrence.
Natural Remedies for MRSA
Some natural therapies may support recovery. Tea tree oil, known for its antibacterial properties, can aid healing. Olive leaf extract contains oleuropein, which combats bacteria. Herbs like thyme taken orally can enhance immunity. Drinking Lapachol tea multiple times daily introduces antibacterial compounds. These remedies should complement, not replace, professional medical treatment.