Comprehensive Guide to Heartburn: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Remedies
This article offers a detailed overview of heartburn, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment methods. It emphasizes lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and medication options for relief. Suitable for those experiencing frequent discomfort or seeking to prevent episodes, the guide provides practical advice on managing and understanding this common condition effectively.

Comprehensive Guide to Heartburn: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Remedies
Learn everything about heartburn, a common discomfort often triggered by large meals or certain lifestyle choices. This article details the main causes, key symptoms, and practical solutions to ease this burning sensation.
Causes of Heartburn
Heartburn is primarily linked to acid reflux, where stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation. Factors such as alcohol, caffeine, fizzy drinks, and acidic foods can aggravate it. Smoking combined with fatty foods also increases risk.
Pregnancy raises abdominal pressure, often leading to heartburn. Other esophageal conditions may produce similar symptoms.
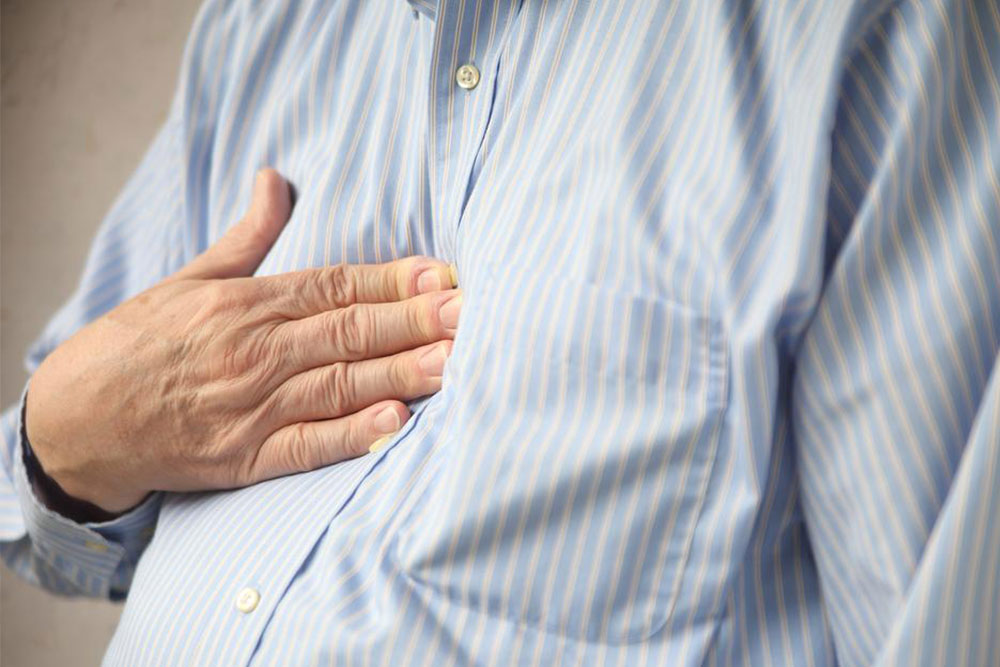
Identifying Symptoms
Heartburn typically causes a burning feeling behind the chest, especially in the lower chest area. It may feel like spasms or sharp pain, persisting from minutes to hours. Symptoms worsen after meals or when lying down.
People who are overweight are more susceptible. Additional indicators include a sour taste in the throat, coughing, hoarseness, and swallowing difficulties. Acid can also erode tooth enamel. Persistent heartburn could lead to esophageal ulcers and be mistaken for cardiac issues.
Managing Heartburn Effectively
Long-term habits
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes is essential. Eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding lying down right after eating can improve symptoms. Reducing alcohol and quitting smoking have positive health effects and lessen reflux risk.
Immediate relief methods
Over-the-counter remedies like antacids quickly neutralize stomach acid. H2 blockers decrease acid production within half an hour, while Proton-Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) take about four days for full effect. Persistent cases may require prescription medications.