Key Insights into Early-Onset Distal Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1
Discover vital information about Distal Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1, a genetic disorder affecting infants with muscle weakness and respiratory problems. Learn about causes, symptoms, and the importance of early diagnosis to manage this challenging condition effectively.

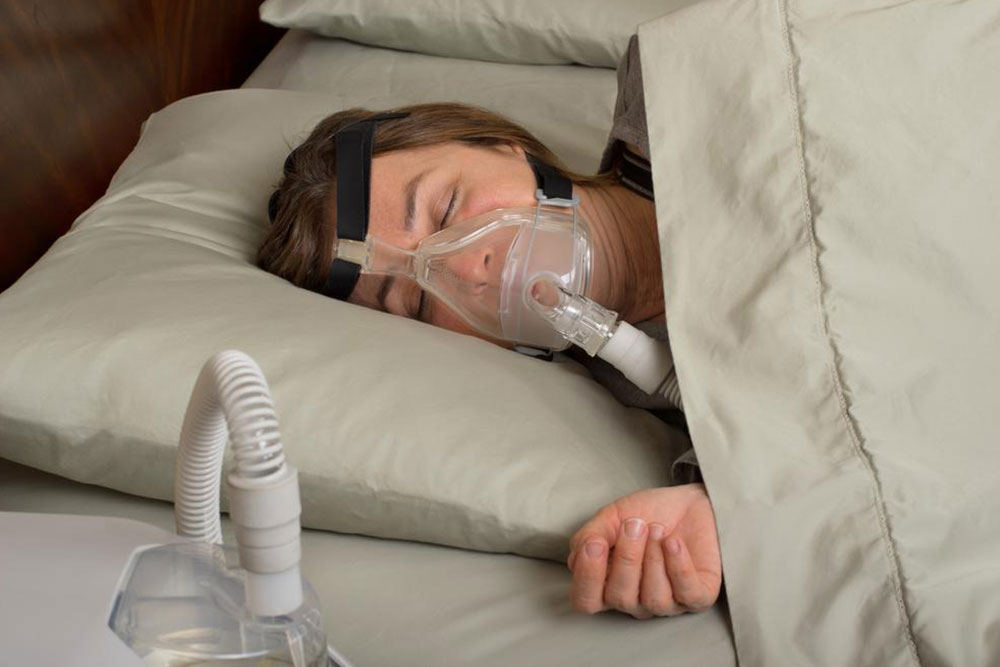
Distal Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 1 (dSMA1), also known as SMARD1, is a hereditary condition that manifests in infants and young children, leading to severe muscle weakness and breathing difficulties. Usually diagnosed within the first six months, this rare disorder presents a poor prognosis due to limited treatment options. Early detection is essential for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Understanding the disease's causes helps families and healthcare providers plan appropriate interventions and monitor potential complications.
This genetic disorder results from mutations inherited from both parents, impairing the production of a crucial muscle-supporting protein. Children with dSMA1 exhibit floppiness, delayed motor skills, swallowing problems, and respiratory challenges, though cognitive functions typically remain unaffected. Recognizing these signs early is vital for prompt support and care.
Muscle weakness leading to flaccidity
Delayed motor milestones like sitting and rolling
Feeding difficulties and poor weight gain
Breathing and swallowing issues