Debunking Myths About Diet and Arthritis: Fact vs. Fiction
This article clarifies common misconceptions about diet and arthritis, separating facts from myths. It emphasizes the safety of foods like tomatoes and citrus fruits, and dispels myths about vinegar, dairy, gelatin, and salt in footwear. The goal is to help individuals with arthritis make informed dietary choices and understand what scientific evidence supports or refutes popular beliefs, promoting healthier management of the condition.

Arthritis impacts people of all ages, including children, though it mainly affects older adults. It causes joint stiffness and muscle discomfort. Many misconceptions exist about its causes and treatment, especially regarding diet. This article aims to clarify these myths, offering accurate nutritional guidance for those with arthritis.
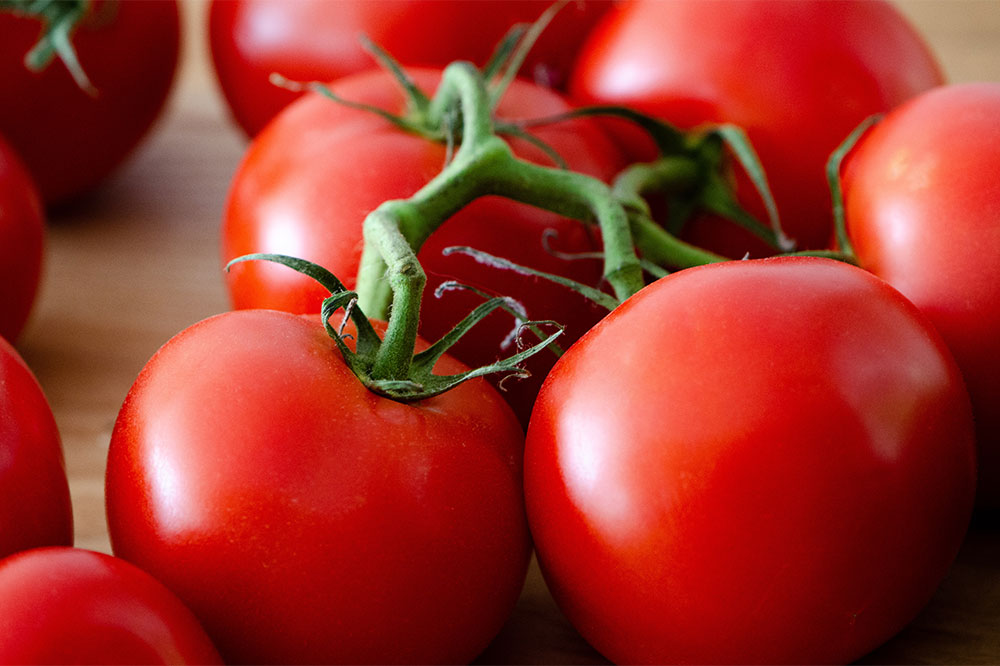
Are tomatoes harmful?
Once labeled poisonous due to solanine, tomatoes were thought to worsen arthritis. Scientific research confirms they are safe to consume. Similarly, eggplants and potatoes are also harmless.
Do citrus fruits increase inflammation?
Contrary to claims, citrus fruits are beneficial, rich in vitamin C, which supports joint health and reduces inflammation. They assist in collagen formation and cartilage protection.
Can vinegar reduce joint stiffness?
Current studies do not support vinegar as an arthritis remedy. Use in moderation, especially in salads or dips.
Is gin-soaked raisins a cure?
No, this is a myth. There is no scientific evidence that spirits or soaked raisins provide relief, and such remedies are not effective treatments.
Does dairy worsen arthritis?
Those allergic or intolerant to dairy should avoid it. For others, dairy can be part of a healthy diet and may be beneficial for joint health.
Does gelatin ease joint pain?
While collagen supports joint health, there is no conclusive proof that gelatin or collagen supplements reduce arthritis symptoms.
Does salt in shoes help?
No scientific data supports the use of salt application in footwear for joint pain relief caused by weather conditions.
Disclaimer: The information provided is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always seek advice from healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment of health conditions.