Comprehensive Guide to Managing Atopic Dermatitis
This comprehensive guide covers the essentials of atopic dermatitis, including symptoms, causes, risks, and management strategies. Ideal for those seeking reliable information on this chronic skin condition, it emphasizes the importance of medical consultation for proper care and treatment. Learn how to identify flare-ups, avoid triggers, and maintain healthy skin through effective skincare routines and medications, ensuring better quality of life for individuals affected by this common dermatological issue.
Everything You Need to Know About Atopic Dermatitis
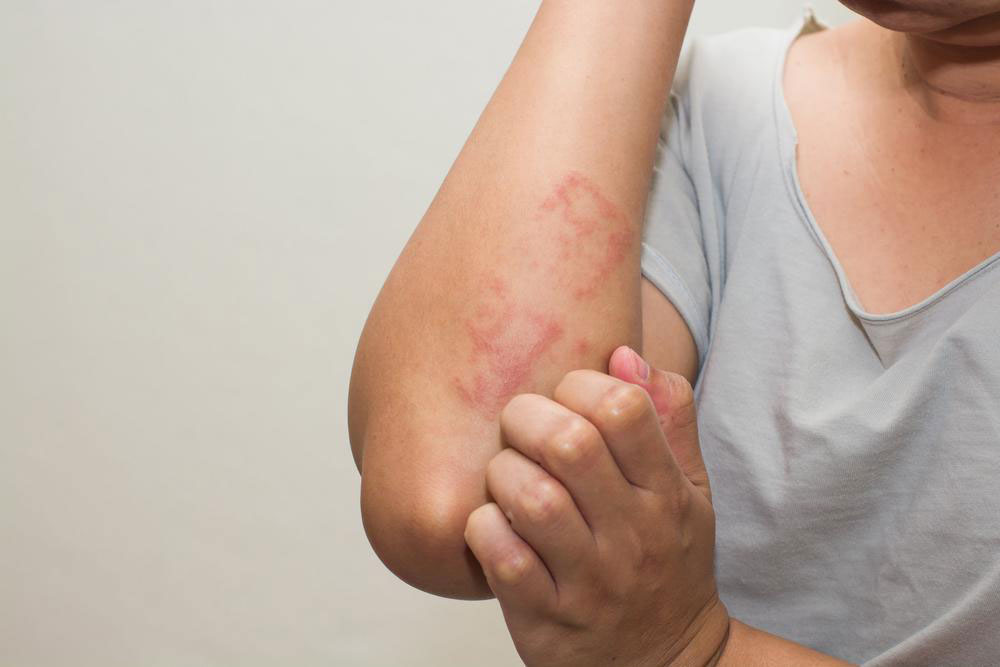
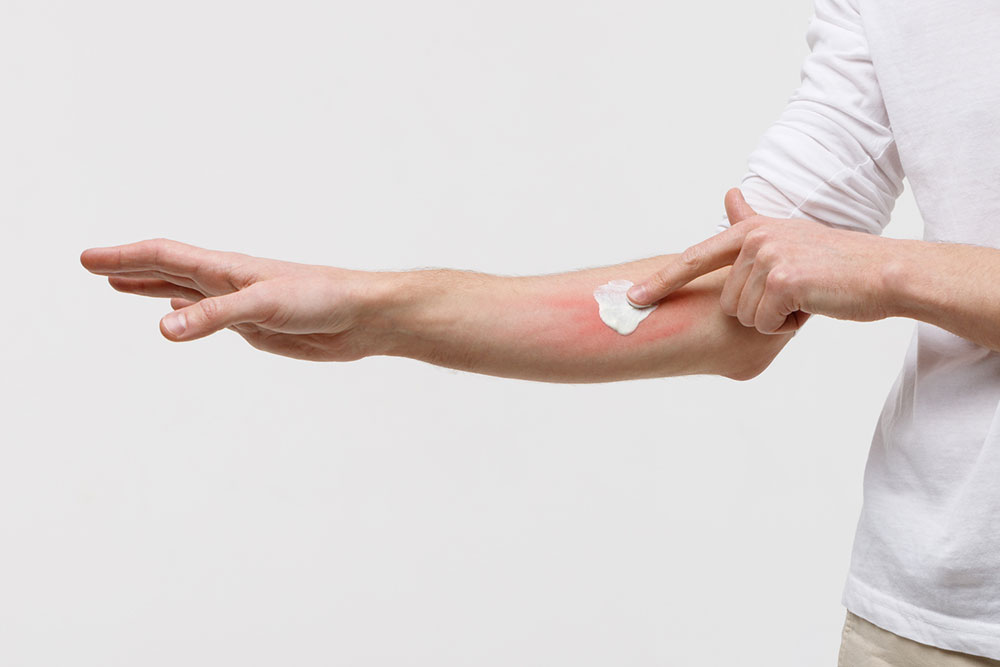
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic skin disorder marked by redness, dryness, and intense itching. Although common in children, people of all ages can be affected. The condition can remain dormant for periods and then flare unexpectedly, occasionally with asthma or fever episodes. Management includes medications for flare-ups, moisturizing routines, and avoiding irritants to soothe affected skin.
Symptoms and Causes
Chronic dry, itchy skin that worsens at night.
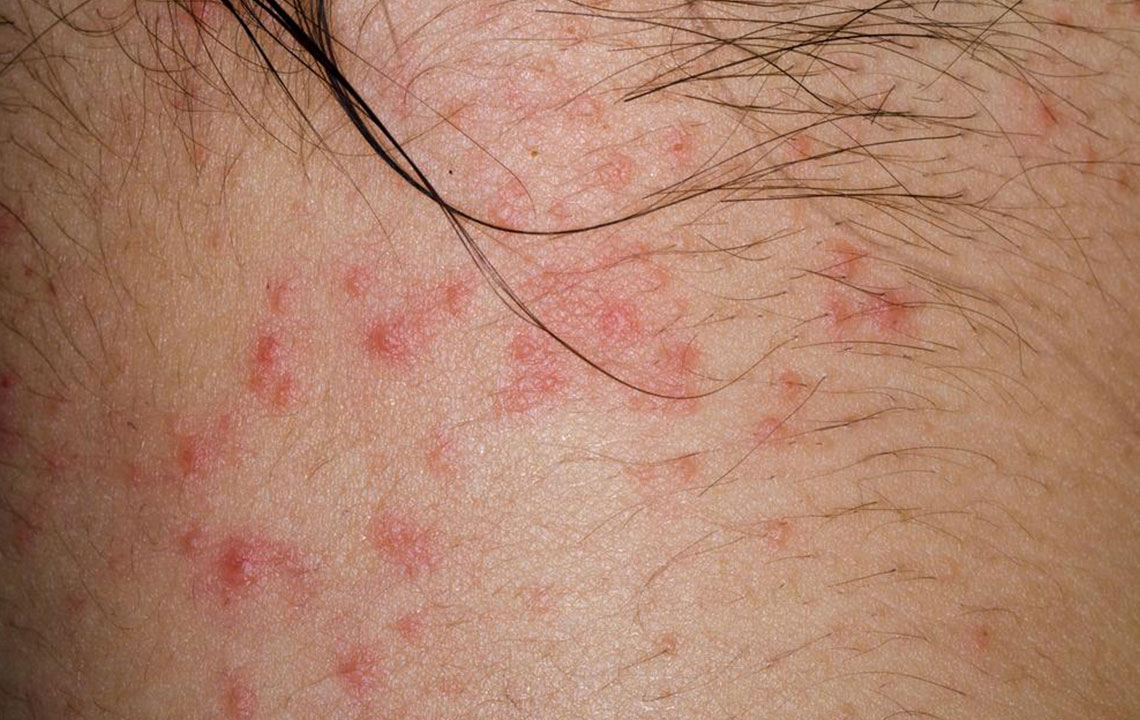
Red to brown patches on hands, feet, ankles, wrists, eyelids, neck, and chest.
In infants, patches often appear on the face and scalp.
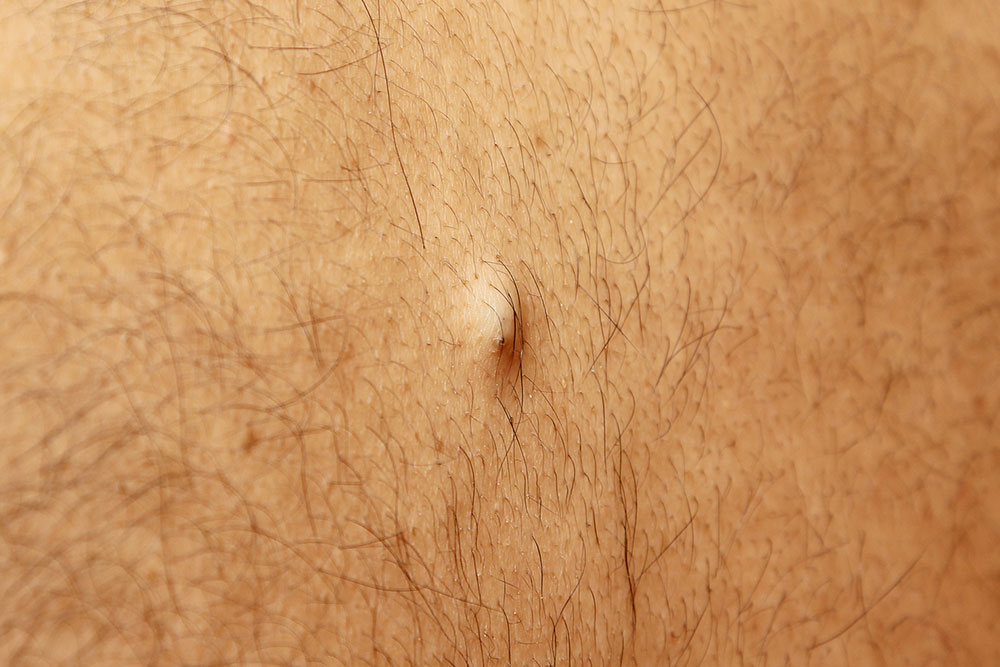
Small raised bumps may cover affected areas.
Scratching can cause swelling and heightened skin sensitivity.
While the precise cause remains uncertain, genetic factors are believed to influence the condition. It hampers the skin's ability to act as a barrier against irritants and allergens from the environment.
Risks and Complications
Linked Conditions: Many children with eczema develop asthma or hay fever; over 50% experience one of these by age 13.
Infections: Persistent scratching may lead to open sores, increasing bacterial or viral infection risk, including herpes simplex.
Although no cure exists, treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and limiting flare-ups through medications, gentle skincare, and avoiding harsh irritants.
Disclaimer:
This content is meant for educational purposes and not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment.