Effective Nutrition Strategies for Diabetes Management
Discover effective dietary strategies for managing diabetes through balanced meal planning. The article provides nutritional tips on choosing healthy carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, along with key food groups to include. Learn practical advice to control blood glucose, avoid harmful foods, and maintain a nutritious, consistent diet for better overall health and long-term wellness.

Essential Dietary Tips for People with Diabetes
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in controlling diabetes. The foods eaten influence blood sugar, cholesterol, and overall wellness. Many with diabetes struggle to find nourishing meals, often choosing processed options that worsen health. Implementing targeted dietary strategies can enhance quality of life. This article outlines key nutritional principles and meal planning tips tailored for diabetics, helping them stay energized and healthy. If you're looking for reliable methods to control blood glucose through diet, read on for expert advice.
Carbohydrates
Carb intake directly impacts blood glucose levels. Proper insulin adjustment according to carbohydrate consumption is essential. Incorporate fruits, whole grains, and vegetables, favoring options low in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats to maintain control over blood sugar.
Proteins
Proteins support overall health without causing significant blood sugar spikes. Consume protein-rich foods in moderation, watching portion sizes to prevent weight gain. Use protein shakes cautiously, especially with Type 2 diabetes, as they can accelerate insulin response and may not suit everyone.
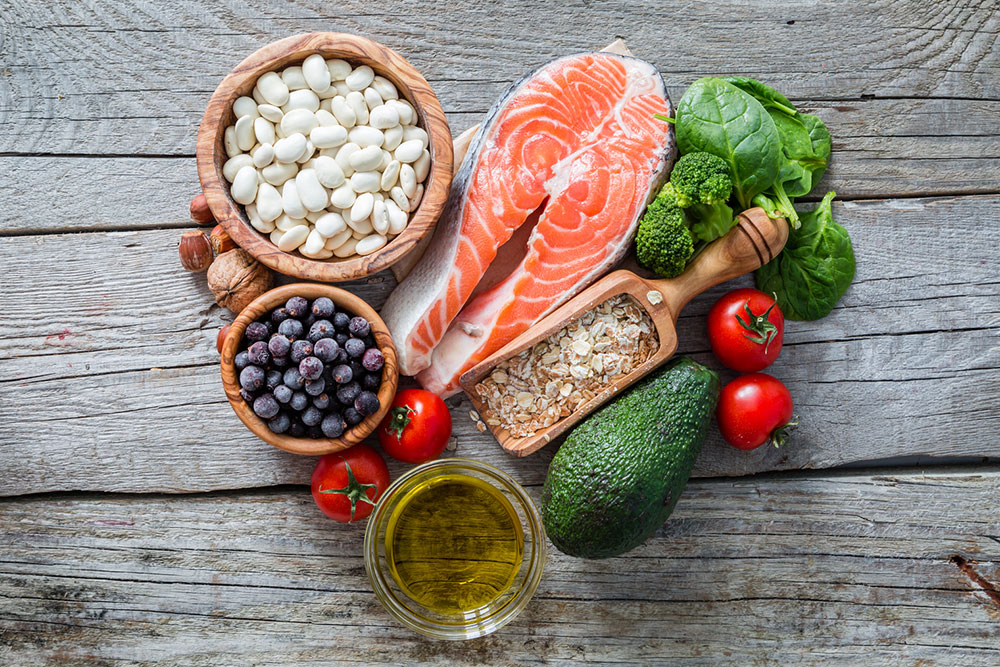
Healthy Fats
Incorporate healthy fats like omega-3-rich fish and olive oil to promote heart health and reduce inflammation, essential components of a diabetic-friendly diet.
The Five Food Groups
Diabetics can enjoy a wide variety of nutritious foods. A balanced diet includes:
Fruits
Vegetables
Meat and plant-based protein sources
Milk and dairy products
Whole grains and starchy foods
Dietary Recommendations for Diabetics
Work with healthcare providers or dietitians to develop personalized meal plans. Basic advice includes:
Eat a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods from all five groups daily
Follow consistent meal times; avoid delaying meals over six hours
Consume fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Limit added sugars; consider sugar substitutes if needed
Opt for water, unsweetened coffee, or tea over sugary drinks
Foods to Limit or Avoid
To keep blood sugar stable, reduce intake of:
Skips in meals
High-fat or greasy foods
High-salt products
Foods with added sugars
Sodas and sweet beverages
Saturated fats such as butter and certain oils
High-sugar desserts like candies and honey
Tips for a Healthy Eating Habits
Plan meals ahead for balanced nutrition and variety. Tracking meals helps with shopping and preparation. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods and maintain consistent meal timing to prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
Conclusion
Adopting a structured diabetic diet can improve glucose control and overall health. Though initial changes may feel challenging, they provide long-term health benefits. Use these guidelines to sustain vitality and avoid diabetes-related complications.