Recognizing Signs and Early Indicators of Pulmonary Embolism
This article explains the key symptoms and warning signs of pulmonary embolism, a serious condition caused by blockage in the lung arteries. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and prompt treatment to prevent life-threatening outcomes, highlighting common signs like sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing blood. Understanding these symptoms helps individuals seek immediate medical attention, particularly among at-risk groups such as those with recent surgeries or prolonged immobility.

Key Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot or other material obstructs the arteries in the lungs, leading to impaired blood flow. Typically caused by a clot traveling from deep veins elsewhere, PE can also result from air bubbles, fat from fractured bones, or amniotic fluid. This blockage can damage lung tissue or decrease oxygen levels in the blood. Symptoms often develop suddenly, necessitating prompt medical care to prevent severe outcomes.
Sudden onset of breathlessness, intensifying with activity and not alleviated by rest
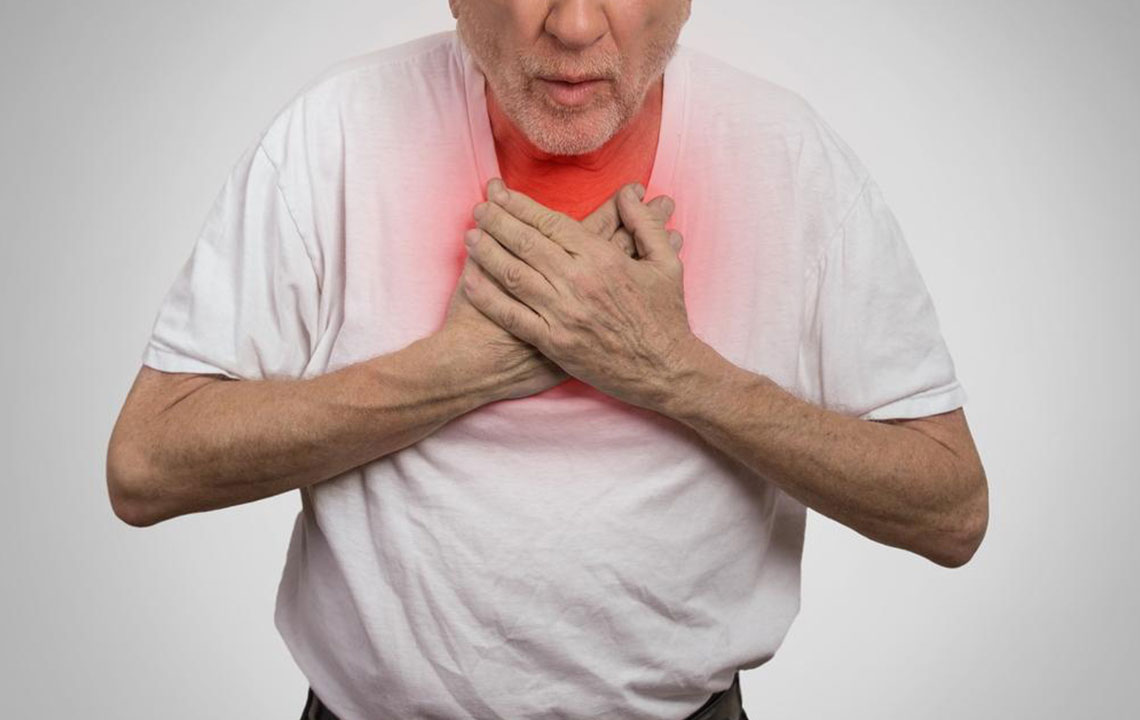
Chest discomfort similar to a heart attack, persistent despite rest
Coughing up blood or blood-streaked mucus
Swelling, warmth, or pain in the calves
Skin turning bluish (cyanosis), rapid or irregular heartbeat
Fever, excessive sweating, lightheadedness
If left untreated, PE can be fatal. Treatments aim to quickly dissolve the clot and restore normal blood flow using anticoagulants like heparin. Oral medications and newer rapid-acting drugs are also used. Risk factors include prolonged immobility, surgeries, pregnancy, obesity, and certain cancers. Recognizing early signs is vital for timely treatment and prevention of severe complications.