A Complete Overview of Scabies Skin Rash: Causes, Signs, and Remedies
This article provides a detailed overview of scabies, focusing on its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Learn how to identify the characteristic rash, understand common symptoms, and recognize the importance of early diagnosis to prevent spread and improve outcomes.
A Complete Overview of Scabies Skin Rash: Causes, Signs, and Remedies
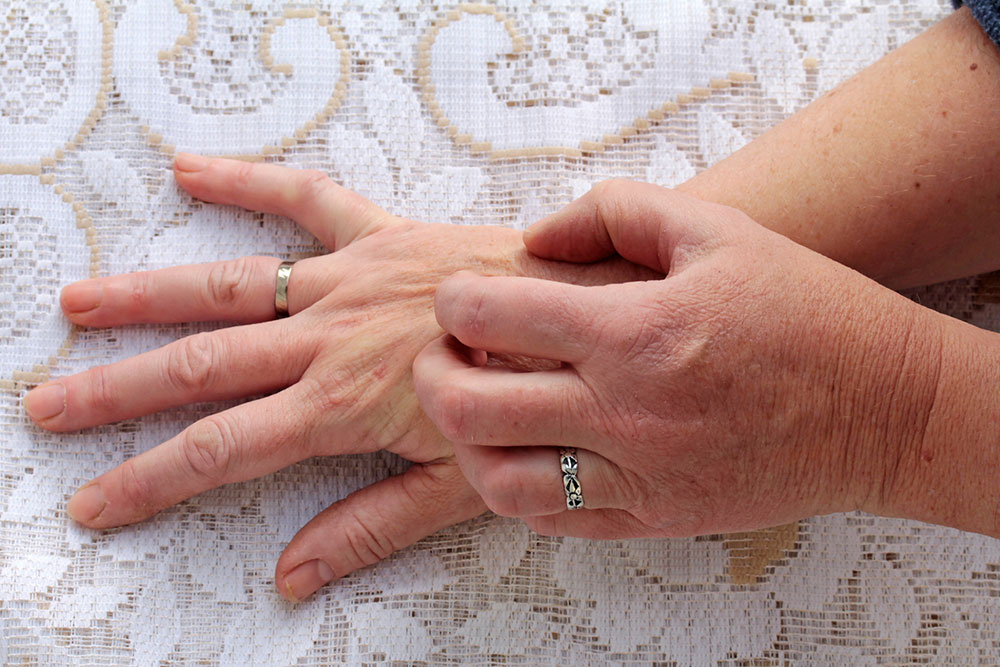
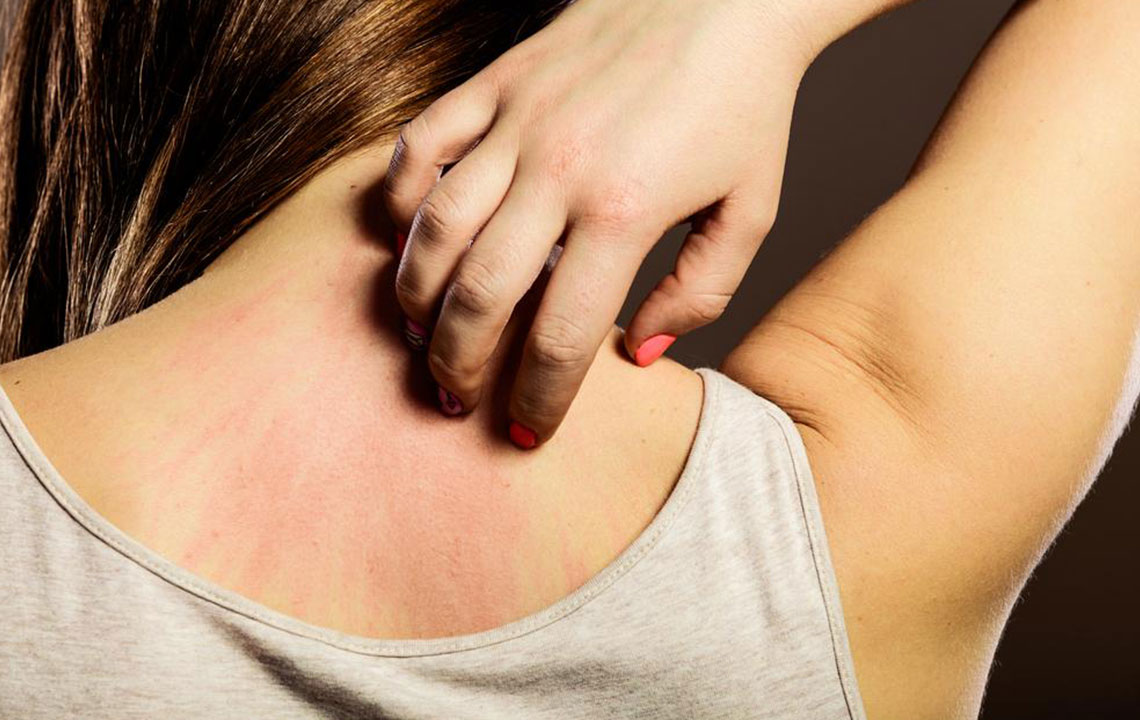
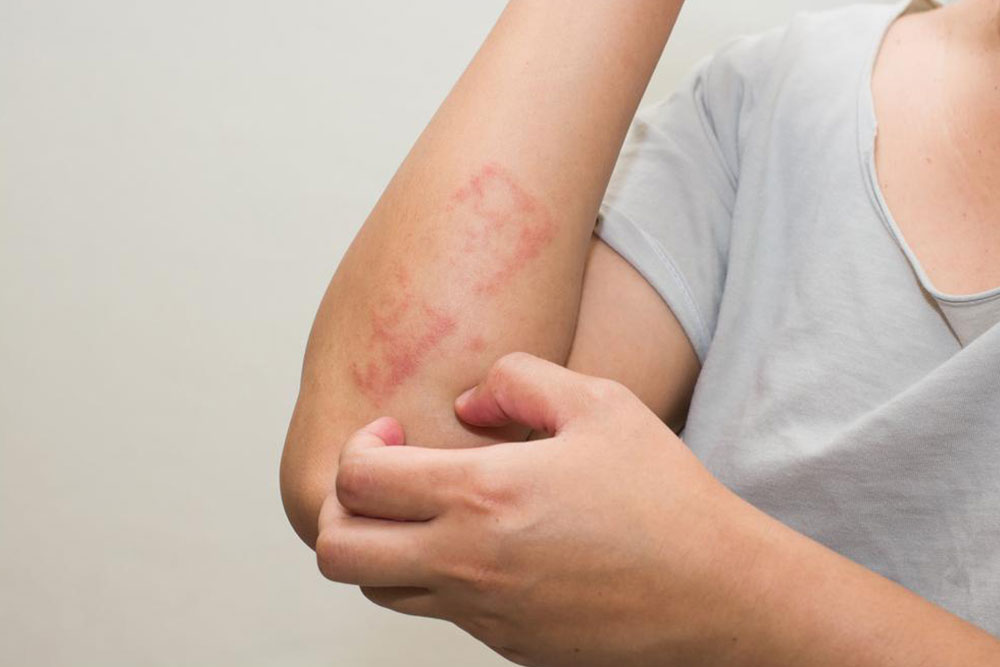
Scabies is caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabei, tiny parasites that penetrate the skin, resulting in a highly contagious and intensely itchy skin condition. The infestation leads to a rash marked by small red bumps, blisters, and observable burrows. These mites prefer warm environments above 20°C and often target areas like fingers, wrists, elbows, knees, and genital regions. Anyone, from children to adults, can contract scabies, which affects millions globally, with over 300 million cases annually.
The rash typically appears as grouped bumps, sometimes crusted with blood, and may show tunneling lines or burrows that look like thin, red, brown, or gray streaks. Healthy individuals can carry up to 15 mites but may still develop skin lesions. Common symptoms include persistent nighttime itching and scratch marks, which can mimic other skin issues.
Scabies frequently occurs in healthcare environments like hospitals and nursing homes, particularly among vulnerable groups such as the homeless. In children and infants, rashes often appear on the face, scalp, and palms; in adults, they tend to develop in concealed areas like between fingers, underarms, and genitals. Diagnosis involves recognizing burrows or small blisters along with the itch. Visual signs are often due to skin reactions around the mites’ tunnels rather than the mites themselves. Early detection is key for effective treatment and to prevent spreading.
Important:
This blog offers detailed insights into various health topics. Our articles are based on reputable sources and scientific research but are not substitutes for professional medical advice. Please consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options. The information provided may not cover all available therapies.