Signs and Remedies for Vision Blurriness: A Guide to Maintaining Eye Health
This article explores common causes of blurry vision, including eye conditions and systemic diseases. It emphasizes the importance of timely treatment and offers practical eye exercises to improve eye health. Regular eye check-ups, a balanced diet, and healthy habits are vital for maintaining clear vision. When symptoms persist, seeking professional medical advice ensures proper care. Learn effective strategies to preserve your eyesight and prevent future eye problems with this comprehensive guide to eye health.

Recognizing Causes of Vision Blurriness and Effective Eye Care Strategies
Blurry vision, where objects lack clarity and appear fuzzy, can affect near and far sight. It may stem from minor issues or serious health conditions. Identifying the underlying cause is vital for effective treatment. Common reasons include dry eyes, corneal injuries, infections, eye disorders, allergies, prolonged screen time, and systemic diseases like diabetes and hypertension. Timely intervention can protect eyesight. Additionally, practicing specific eye exercises and healthy habits can help reduce eye strain and improve visual sharpness.
Key Factors Leading to Blurred Vision:
Dry Eye Syndrome: Causes morning blur, worsened by dry environments or extended screen use without blinking. Sleeping with contact lenses may also contribute.
Corneal Injuries: Scratches or abrasions on the cornea from foreign objects, which typically heal but can sometimes require medical treatment.
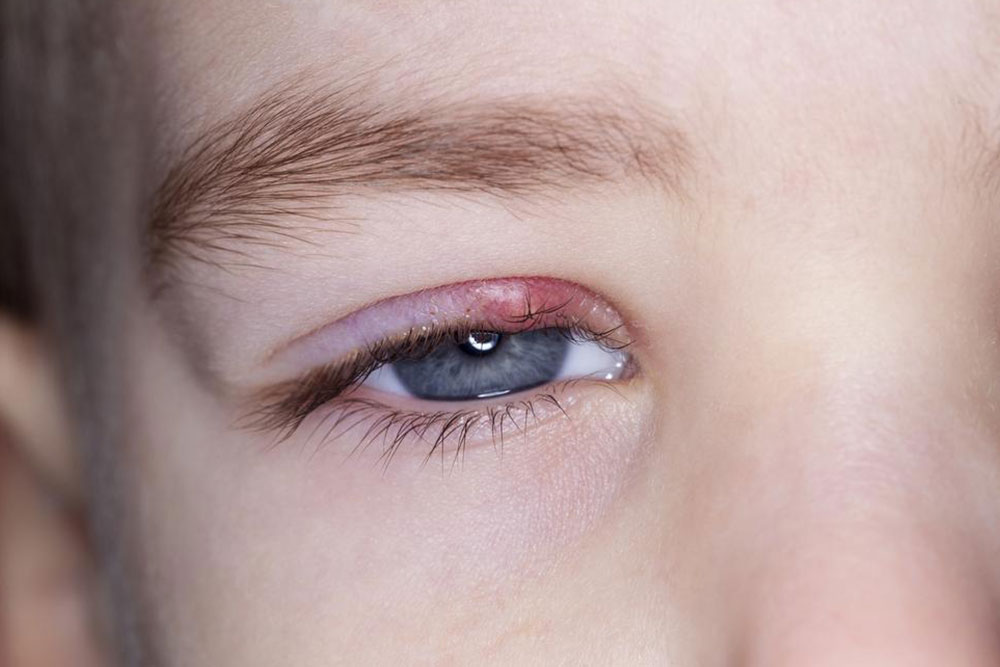
Eye Infections: Conditions such as conjunctivitis lead to irritation and temporarily blurry vision, often needing medication.
Eye Conditions: Diseases like cataracts, glaucoma, or retinal detachment can impair clarity and necessitate prompt medical attention.
Allergic Reactions: Allergies cause itchy, inflamed eyes and brief vision disturbances.
Eye Fatigue: Spending long hours in front of screens causes dryness, tiredness, and blurring, known as digital eye fatigue.
Overall Health Issues: Conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure can harm retinal vessels, leading to lasting vision problems if untreated.
Methods to Address Blurry Sight:
Corrective lenses such as glasses or contact lenses for refractive errors.
Eye drops for dryness and infections.
Surgical options like LASIK or cataract removal for severe cases.
Eye Exercises to Improve Vision:
Palming: Warm your palms by rubbing them, then gently cover closed eyes to relax eye muscles for five minutes.
Blinking Practice: Be conscious of blinking regularly during screen time to prevent dryness and maintain tear health.
Focus Switching: Alternate focus between nearby objects and distant views to enhance eye flexibility.
20-20-20 Rule: Every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds to minimize eye strain.
Maintaining regular eye exams, following a nutritious diet, and practicing eye exercises can support good vision. For persistent symptoms, consult an ophthalmologist for precise diagnosis and treatment options.