Comprehensive Guide to Fibromyalgia: Causes and Symptoms
This article explores fibromyalgia's causes, symptoms, and effective management options. It highlights common signs like widespread pain, fatigue, and sleep disturbances, along with contributing factors such as trauma and stress. Understanding these aspects aids in early diagnosis and better treatment approaches for those affected by this chronic condition.

Comprehensive Guide to Fibromyalgia: Causes and Symptoms
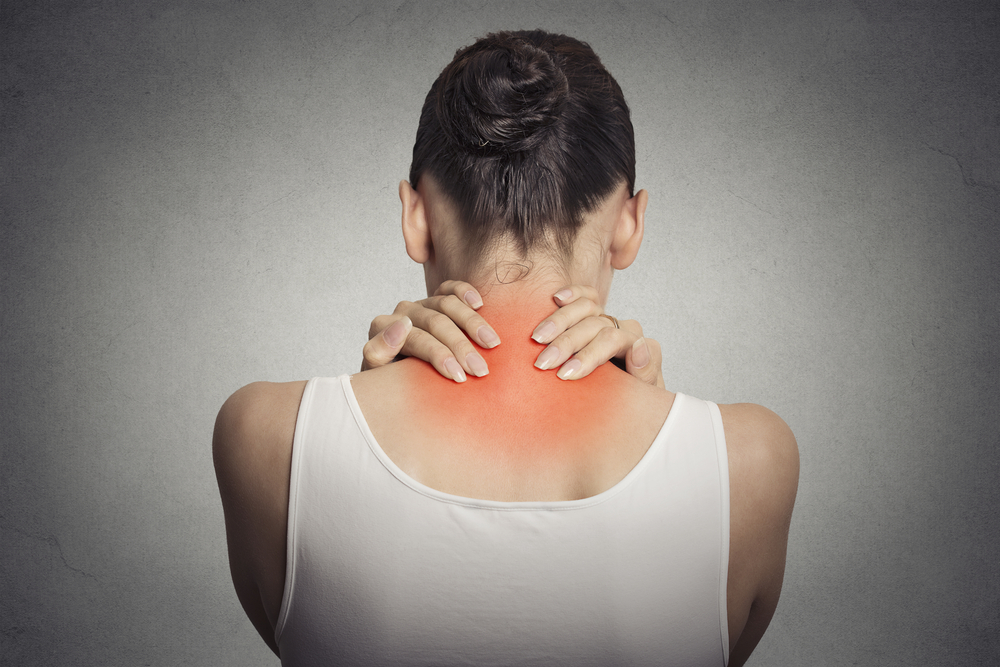
Fibromyalgia is characterized by ongoing, burning pain spread throughout the body, often accompanied by muscle spasms and exhaustion. Discomfort commonly affects areas like hips, shoulders, spine, and neck, interfering with daily routines.
Potential Causes
Factors associated with fibromyalgia include:
Trauma—physical or emotional
Arthritis-related conditions
Stress-induced disorders
Depressive states
Low physical activity levels
Key Symptoms
The pain intensity and types differ among individuals. Typical signs encompass allodynia, increased pain sensitivity, muscle and joint ache, tingling, and stomach discomfort.
Common indicators include:
Widespread pain: Persistent discomfort across various parts of the body, especially in the neck and back, with varying levels of severity.
Greater sensitivity: A heightened response to gentle touches or stimuli, causing discomfort even with light contact.
Chronic fatigue: Persistent tiredness that ranges from mild exhaustion to complete depletion.
Sleep issues: Challenges in attaining restful sleep due to ongoing pain, resulting in non-restorative sleep patterns.
Additional symptoms often include difficulties with concentration, memory lapses, mental fog—sometimes called ‘fibro-fog’—as well as gastrointestinal problems like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Depression may also occur, influenced by hormonal fluctuations and continuous discomfort, affecting overall health. Therapies such as acupuncture, physical therapy, massage, and medications like muscle relaxants can help alleviate symptoms.