Hyperkalemia Explained: Causes, Risks, and Prevention Tips
This article explores hyperkalemia, highlighting its causes, symptoms, and preventive measures. It emphasizes the importance of kidney health, medication management, and dietary habits in controlling potassium levels. Lifestyle modifications such as a balanced diet, hydration, and exercise can help prevent complications. Recognizing early symptoms and consulting healthcare providers are vital for effective management, making prevention more effective than cure.
Hyperkalemia Explained: Causes, Risks, and Prevention Tips
Balancing essential minerals is crucial for maintaining good health. Potassium, an important electrolyte, influences blood pressure regulation, heartbeat stability, and muscle coordination. Kidney problems can impair potassium elimination, leading to elevated blood levels termed hyperkalemia. Factors such as certain medications for hypertension, muscle damage from illnesses like rhabdomyolysis, high alcohol consumption, and substance abuse can raise potassium levels. Preventative steps include careful medication management, dietary adjustments, adequate hydration, and regular physical activity. Early detection of symptoms and lifestyle modifications are key to preventing serious complications associated with high potassium.
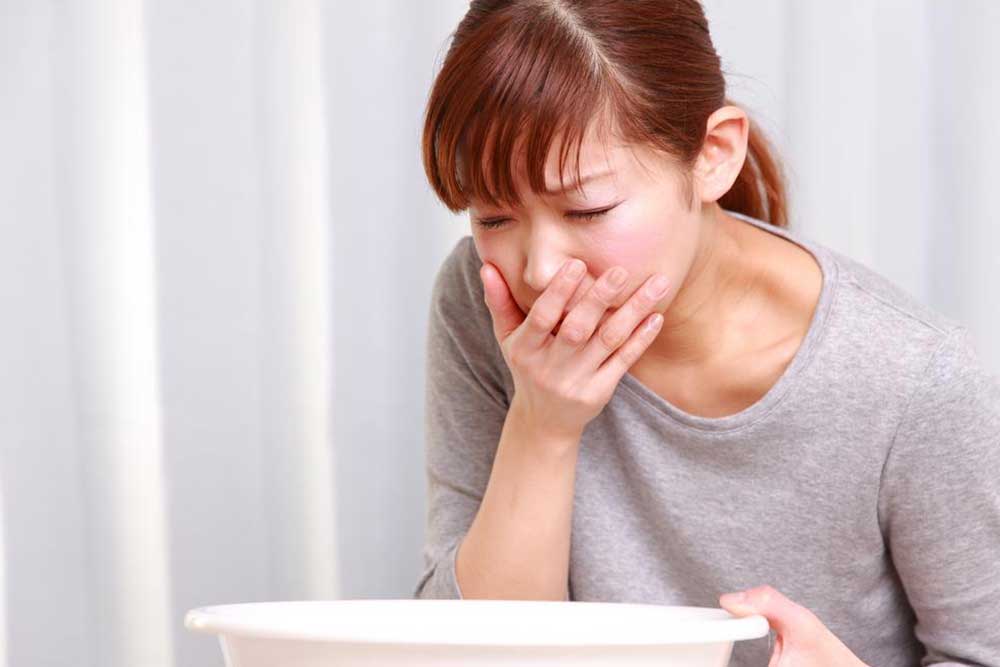
Common signs of hyperkalemia include fatigue, weakness, numbness, nausea, chest discomfort, and breathing issues. Seeking medical advice promptly is essential if symptoms are noticed. Reducing intake of potassium-rich foods like bananas, potatoes, tomatoes, nuts, and some fish can help maintain healthy levels. Incorporating healthy fats such as olive and coconut oil, choosing lean meats, drinking plenty of water, and staying active support mineral balance. Proactive lifestyle changes are more effective than treatment after symptoms appear, helping to lower risks linked to elevated potassium.