Comprehensive Guide to Hearing Impairment: Causes, Types, and Prevention Strategies
Learn about the causes, types, stages, and prevention of hearing loss. This guide highlights symptoms detection methods, risk factors, and tips for safeguarding your hearing health. Understand how to identify and manage hearing impairment effectively with expert advice.

Comprehensive Guide to Hearing Impairment: Causes, Types, and Prevention Strategies
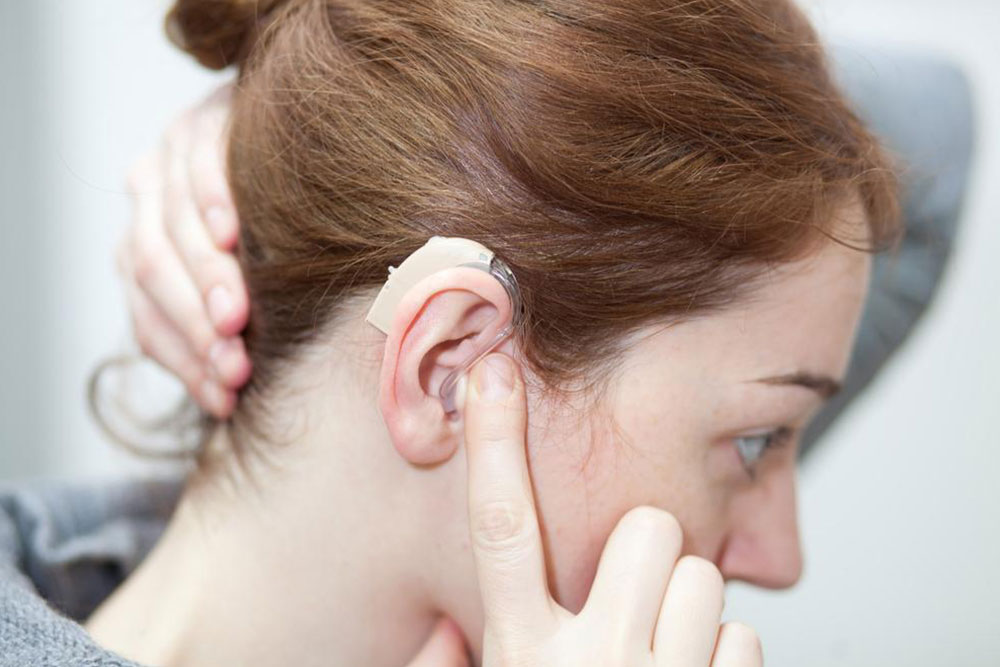
Hearing loss often develops gradually with advancing age, making it common among seniors. However, it can also result from birth defects or ear injuries at any age. Nearly 33% of Americans aged 65 to 75 experience some level of hearing difficulty. It is classified based on the part of the ear affected:
Conductive: Issues in the outer or middle ear
Sensorineural: Damage to the inner ear
Mixed: A combination of both types
This includes features of both conductive and sensorineural loss.
Stages of Hearing Loss
Mild: Detectable between 25-40 decibels, faint sounds like dripping may go unnoticed. Conversations are still manageable.
Moderate: Hearing drops to 41-55 decibels, impacting speech understanding and household sounds like phones ringing.
Severe: Hearing loss becomes significant; speech and usual sounds may be inaudible without aids. Hearing devices can help but might not fully restore hearing.
Profound: The most severe level, where sounds below 90 decibels are hardly heard, with limited aid effectiveness.
Detection Methods
Physical Evaluation: Check for earwax, infections, or swelling.
Basic Hearing Tests: Simple whisper tests to identify hearing issues.
Mobile Screening: Apps designed to evaluate moderate hearing impairment.
Audiometry: Detailed assessment using headphones to measure hearing loss extent.
Prevention Tips
Exposure to loud noises and aging are primary causes of hearing problems. Earwax buildup can cause temporary loss. While some damage is irreversible, consulting an audiologist can help minimize effects. Protect your hearing by avoiding loud environments, using ear protection, limiting exposure to noise, and selecting quieter electronics.
Disclaimer:
This educational content on symptoms, treatment options, health conditions, and side effects is for informational purposes only. It does not substitute professional medical advice. Always seek advice from qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment.