Complete Guide to Asthma: Symptoms, Causes, Management, and Prevention
This comprehensive overview of asthma covers causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive tips. It highlights key triggers, diagnostic methods, medication types, and lifestyle strategies to effectively manage the condition. Understanding and controlling asthma can significantly improve quality of life for sufferers and reduce dangerous flare-ups. Whether mild or severe, proper management and prevention are essential to maintaining respiratory health and minimizing symptoms.
Complete Guide to Asthma: Symptoms, Causes, Management, and Prevention
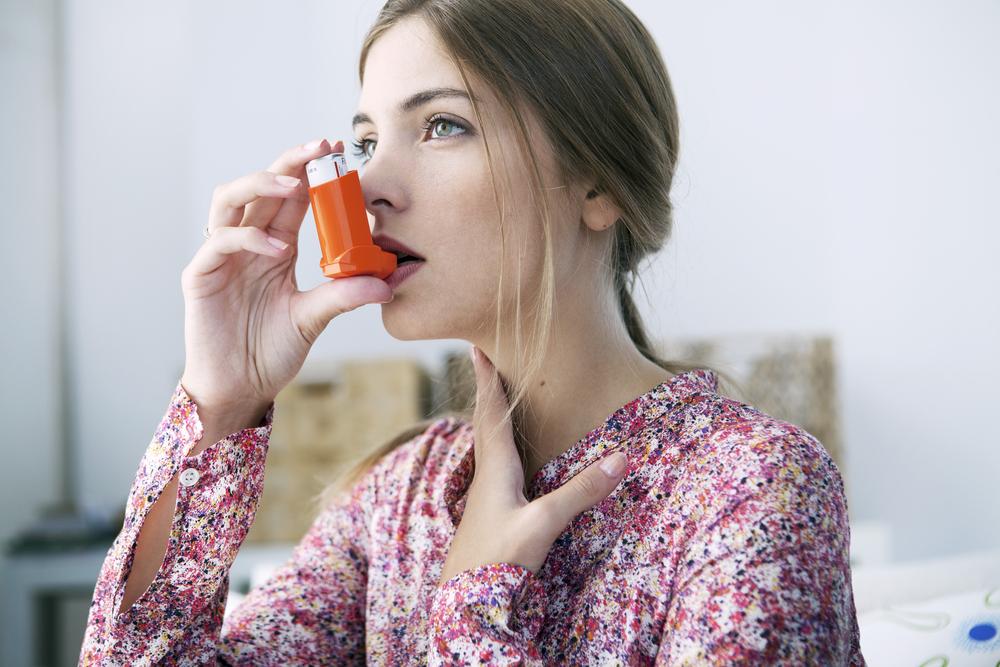
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease characterized by airway constriction and inflammation, often triggered by allergens or irritants. This causes symptoms like coughing, chest tightness, shortness of breath, and wheezing, which can vary from mild to severe and impact daily activities. Medical experts classify asthma into four levels: intermittent, mild persistent, moderate persistent, and severe persistent, based on symptom frequency and intensity.
Causes
Although the precise cause of asthma is unknown, it is thought to involve genetic predisposition and environmental influences. Common triggers include:
Allergens like dust mites, pollen, mold, or pet dander
Physical activity or exercise
Cold weather exposure
Respiratory infections such as colds
Environmental pollutants, smoke, or chemicals
Certain medications including aspirin, ibuprofen, and beta blockers
Stress levels
Food additives and sulfites
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Diagnosis
Pulmonologists evaluate symptoms through physical exams and medical history. Diagnostic tests include spirometry and peak flow measurements. Additional assessments, like methacholine challenge tests, imaging, allergy testing, nitric oxide measurement, and sputum analysis, help confirm asthma and identify specific triggers.
Treatment and Prevention
Treatment varies based on severity and may involve:
Long-term control: inhaled corticosteroids, combination inhalers, leukotriene modifiers, and beta stimulants
Relief medications: short-acting beta agonists and corticosteroids (oral or IV)
In severe cases, bronchial thermoplasty might be recommended. Prevention includes lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing reflux. To minimize attack risks, patients should:Clean their environment weekly to lessen allergens
Use air conditioning and humidifiers at home
Keep pets groomed regularly to reduce dander
Wear masks outdoors in cold weather


