Understanding Gout: Diagnosis and Testing Methods
Learn about the key diagnostic procedures for gout, including blood tests, imaging techniques, and joint fluid analysis. Early detection through these methods helps in effective management of the condition. Consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment options.

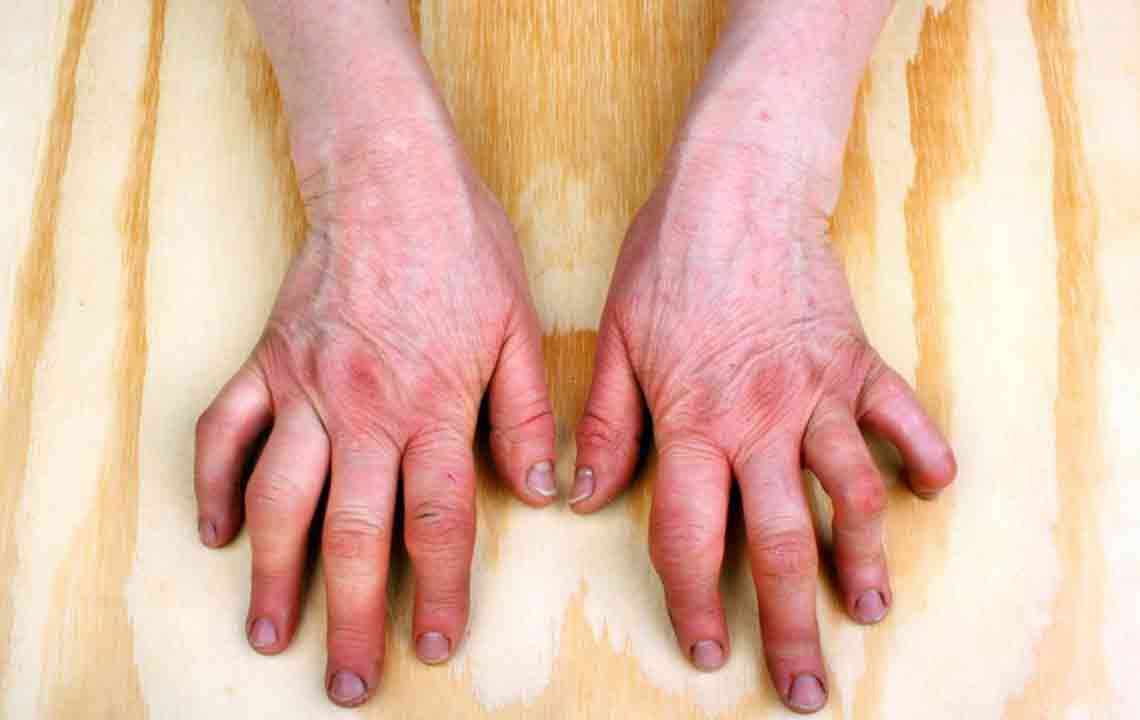
Gout often presents with symptoms similar to other joint conditions, such as swelling, pain, and inflammation. If you suspect gout, your healthcare provider will conduct a thorough assessment. Be ready to discuss your family history—especially if relatives have had gout—as well as detail your symptoms, their timing, and how often they occur. It's also important to inform your doctor about potential triggers like illness, stress, dietary choices, alcohol intake, and your overall health, medications, and lifestyle habits.
To confirm gout, various diagnostic tests may be ordered:
Blood Tests: To measure uric acid and kidney function, though results can vary.
X-ray Scans: To check for joint damage or inflammation causes.
Dual-energy CT: Identifies urate crystal deposits in joints even without inflammation.
Ultrasound: Commonly used in Europe to detect urate crystals in joints.
Joint Fluid Analysis: Removes fluid from the joint to find urate crystals directly.
Seeking advice from a rheumatologist is advisable for precise diagnosis and treatment. Please note, this article is for educational purposes and does not replace professional medical consultation.