Ultimate Guide to Flu Prevention and Care
This comprehensive guide offers essential insights into flu symptoms, transmission, and effective prevention and treatment methods. It highlights the importance of early recognition, proper care, and hygiene practices to manage and prevent flu outbreaks. Suitable for general readers seeking reliable health information, the article emphasizes staying proactive during flu season and understanding different strains like seasonal and pandemic influenza.

Ultimate Guide to Flu Prevention and Care
Complete Insights on the Flu Influenza, commonly called the flu, is a contagious viral illness impacting people worldwide. Though often mistaken for other ailments due to similar symptoms, it can lead to serious health issues if ignored. The virus spreads primarily through respiratory droplets when coughing or sneezing and can also be transmitted through contaminated surfaces. Early detection of symptoms is essential for effective management and prevention. Most individuals will face the flu at least once, highlighting the importance of awareness and proactive measures.
The incubation period varies from 1 to 4 days, with symptoms potentially lasting up to two weeks if untreated. Understanding different flu strains is vital for controlling outbreaks.
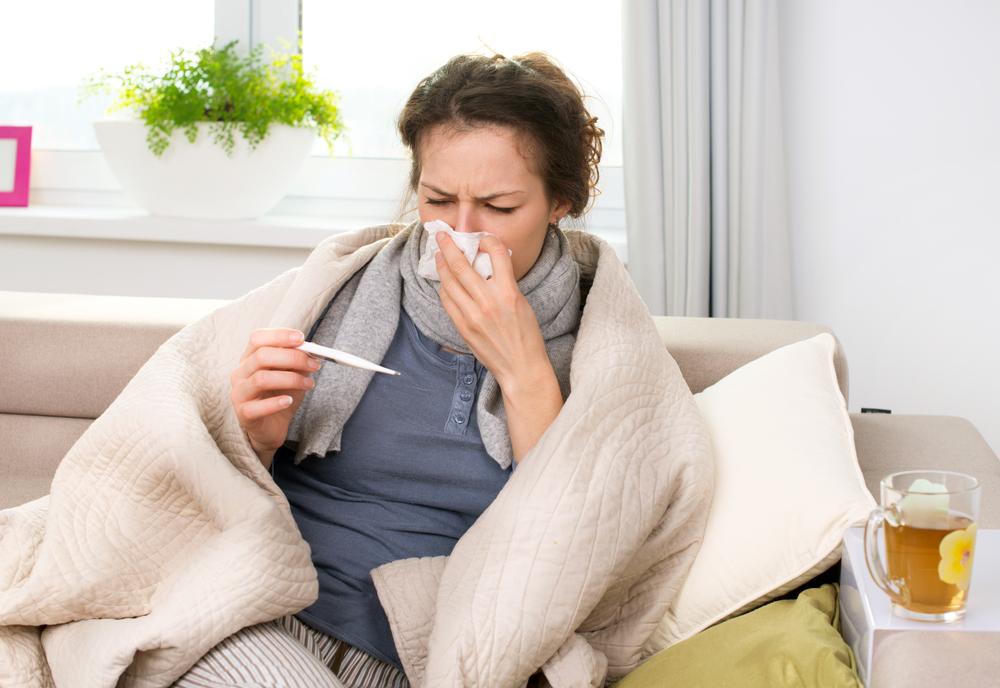
Symptoms tend to appear suddenly and include persistent cough, sore throat, fever, chills, muscle aches, and fatigue. Gastrointestinal issues like nausea or diarrhea may also occur. The virus spreads quickly via direct contact and airborne droplets, emphasizing the importance of hygiene and protective precautions.
Diverse flu strains circulate, with seasonal flu being most common. Typically peaking between October and April, it is caused mainly by types A, B, and C viruses. Type A, with various subtypes like H and N, is responsible for most outbreaks. Type B affects only humans and can trigger severe epidemics, whereas Type C generally results in mild illness. Pandemic strains such as H1N1 (swine flu) and H5N1 (bird flu) are particularly concerning due to their potential for widespread outbreaks. H1N1 emerged in 2009 globally, while H5N1 primarily infects birds but can impact humans, leading to severe illness and high mortality rates.
Early symptoms include abrupt fatigue, chills, body pain, fever, sore throat, and respiratory issues. Recognizing these signs early helps in controlling the spread and ensuring prompt treatment.
For mild cases, rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers are usually sufficient. Antiviral medications like oseltamivir (Tamiflu) or zanamivir (Relenza) may be prescribed, especially if administered early in illness onset. These can shorten the duration of symptoms. Always seek medical advice before starting medications.
Home remedies can promote recovery. Nourishing foods like chicken soup offer essential nutrients and warmth to support immunity. Ginger tea can soothe sore throats, and honey with lemon may ease cough and throat discomfort. Probiotics help strengthen immune defenses. Other remedies include gargling with salt water, applying vapor rubs, and taking warm baths to alleviate symptoms. Consistent self-care and hygiene practices are critical in managing and preventing the flu.
Note: This information aims to educate and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment options. The content provided is based on research but does not account for individual health differences or discrepancies in sources.