Identifying and Differentiating Common Insect Bites
Learn how to identify common insect bites, including signs for bed bugs, spiders, mosquitoes, fleas, and flies. Proper identification aids in choosing effective first aid and treatment. Always seek professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and care.
Identifying and Differentiating Common Insect Bites
Many insects bite or sting mainly when they feel threatened. While spiders, bees, and wasps tend to attack if disturbed, pests like mosquitoes, bed bugs, ants, fleas, and flies can bite unexpectedly. Quick first aid is vital to prevent infections and health issues. Correctly identifying the insect helps determine the best treatment approach. Recognizing specific symptoms enables targeted relief, easing discomfort and supporting faster healing.
Below are common indicators to distinguish various insect bites. When in doubt, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and prompt treatment.
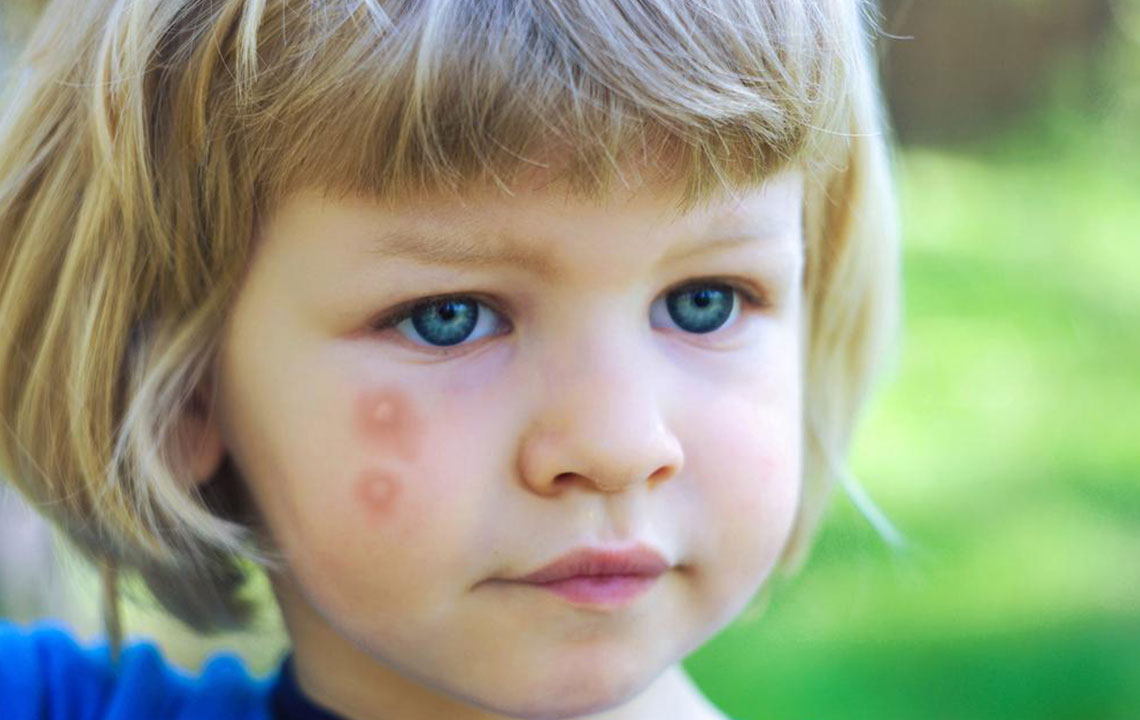
Bed bug bites: Typically present as swollen red patches with dark spots in the center, often appearing in lines or clusters. Comparing with online images can help differentiate them from other skin reactions.
Spider bites: Signs include blisters, puncture wounds, localized pain, redness, itching, skin discoloration, and sometimes systemic symptoms like cramps, sweating, or headaches. Recognizing these features helps identify bites from recluse or garden spiders.
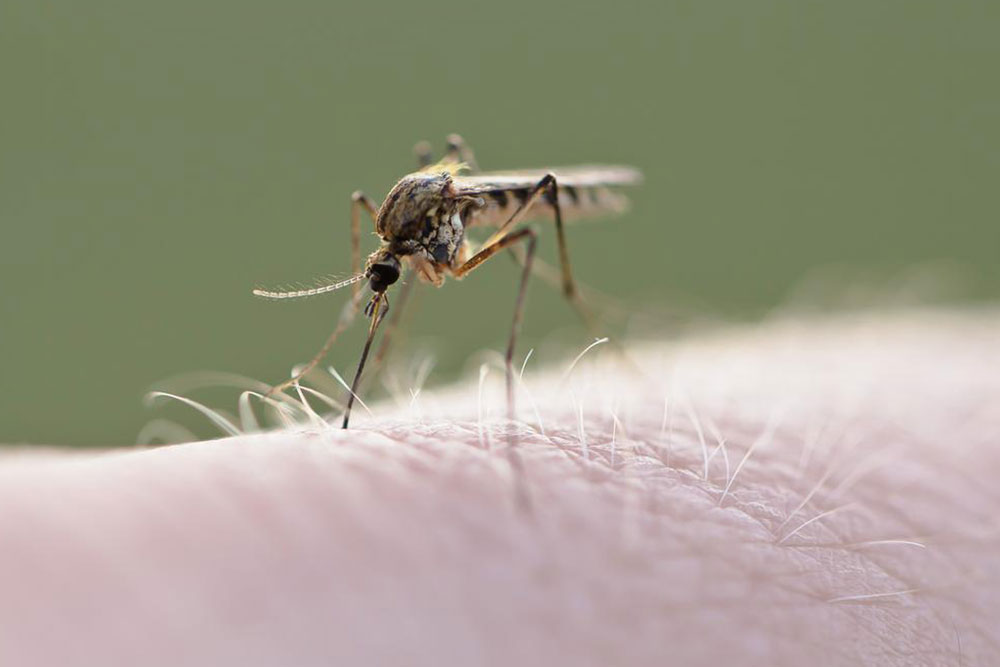
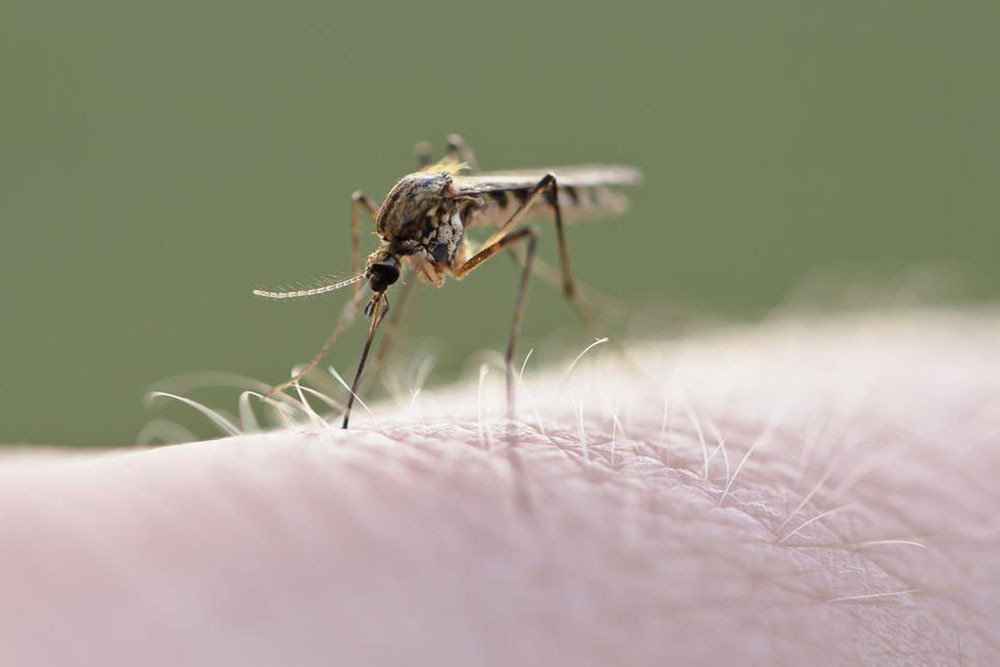
Mosquito bites: Usually cause itching, redness, and a circular swelling. Multiple bites are common and may be accompanied by a burning feeling and increasing swelling over time.
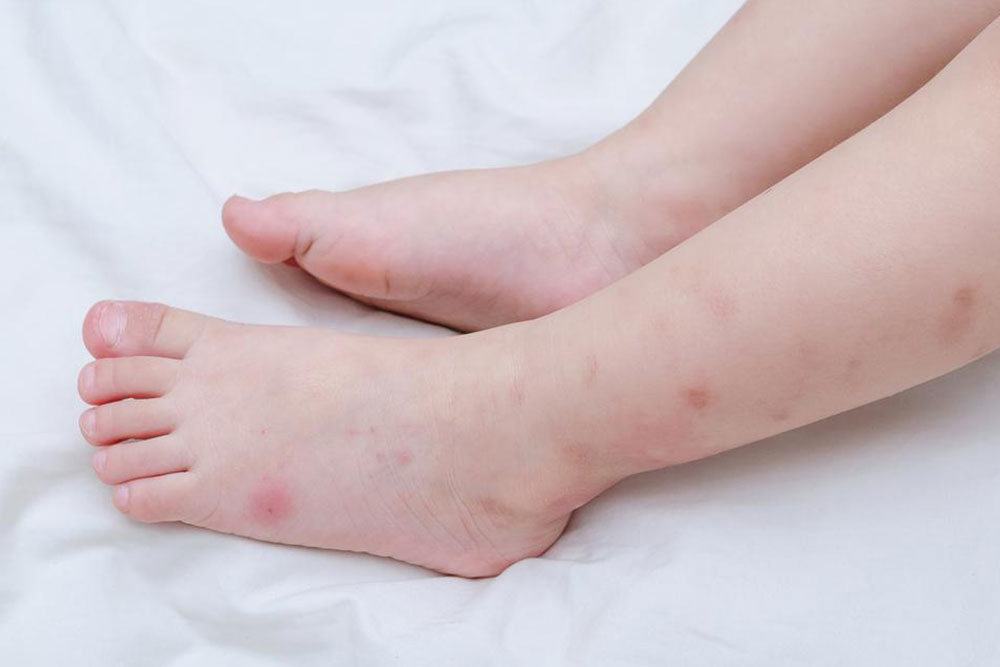
Flea bites: Often appear around ankles and lower legs as itchy bumps with reddish borders, usually appearing shortly after being bitten.
Fly bites: Bites from sand flies, tsetse flies, or deer flies produce painful red bumps and blisters. These insects feed on blood, raising the risk of infection if not treated properly.
Disclaimer:
Our blog offers helpful insights on various topics based on thorough research. However, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare experts for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Additional remedies or information may be available beyond what’s listed here.