Guide to Choosing the Right Digital Hearing Aid for You
Discover how to select the ideal digital hearing aid tailored to your needs. This guide covers various types, their advantages and limitations, and tips for choosing the right device to enhance your hearing experience. With options suited for different levels of hearing loss, find the best fit for your lifestyle and needs.
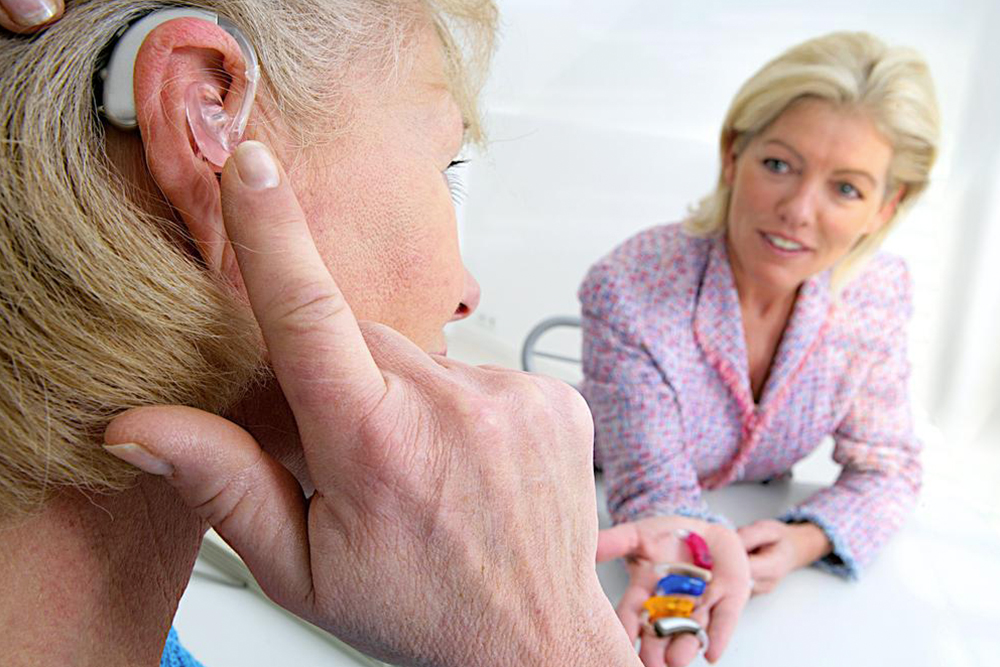

Selecting the Perfect Digital Hearing Assistance
If you often find yourself asking "What!" throughout the day, it might be time to explore hearing solutions. While these devices don't eliminate hearing loss, they improve sound detection by amplifying sounds. Modern digital hearing aids feature a microchip with an amplifier that converts incoming sounds into digital signals. These signals are processed according to your hearing loss and surroundings, then transformed back into sound and delivered through tiny speakers in your ears.
When choosing a digital hearing aid, customization to your ear shape and lifestyle is crucial, as there's no universal option.
There are six primary types of digital hearing aids to consider:
Complete-in-the-Canal (CIC) Devices: These fit snugly inside the ear canal, making them nearly invisible. Suitable for mild to moderate hearing loss.
Advantages
Discrete and compact
Reduces wind and background noise effectively
Limitations
Can be blocked by earwax
Limited controls due to small size
Use small batteries with shorter lifespan
In-the-Canal (ITC) Devices: Slightly larger, molded to sit in the ear canal for mild to moderate loss.
Benefits
Easy to handle and insert
Convenient for daily use
Drawbacks
Prone to earwax obstruction
Limited control options
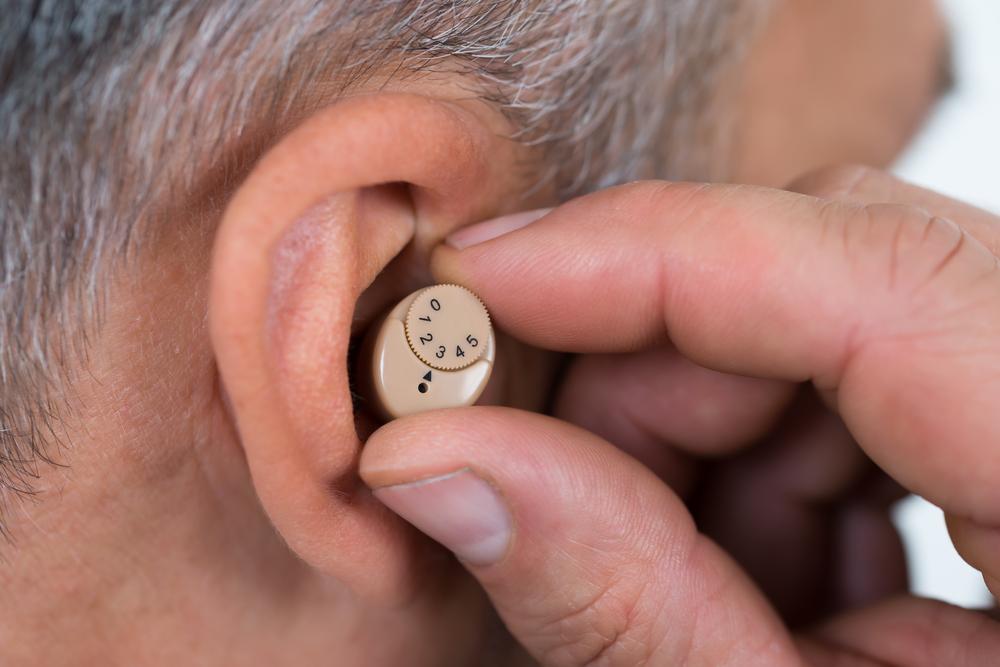
In-the-Ear (ITE) Devices: Designed for moderate to severe hearing impairment, covering most of the outer ear. Available in full or half-shell styles.
Advantages
Easy to operate and adjust
Accessible controls for volume and battery
Compatible with larger batteries for longer use
Drawbacks
More visible in the ear
Affected by environmental noise
Susceptible to earwax blockage
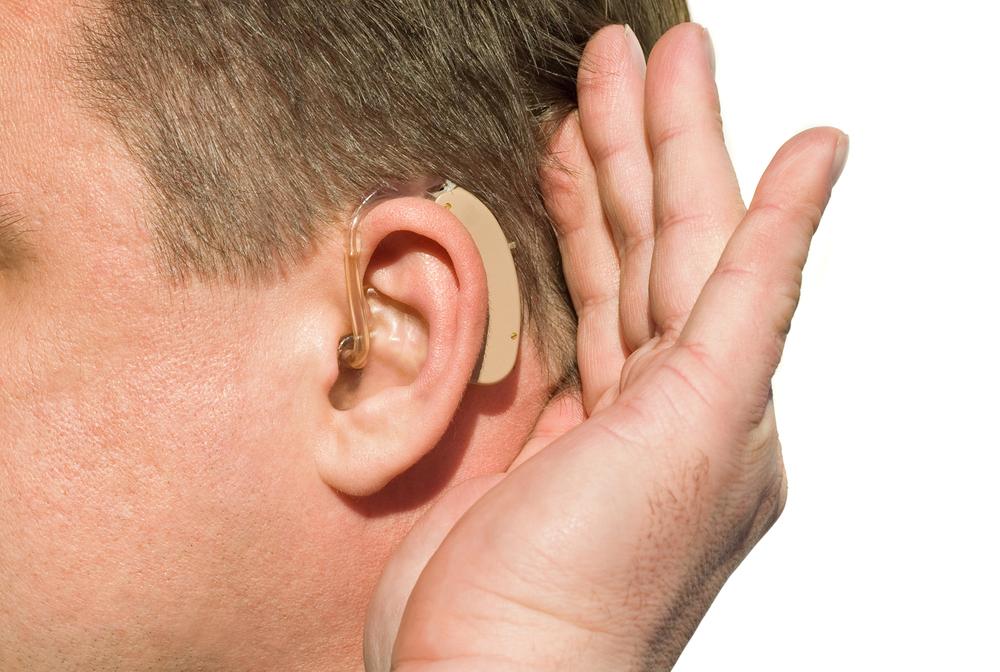
Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Devices: Features a component that rests behind the ear linked via a tube to an earpiece, suitable for various hearing levels.
Advantages
High amplification capacity
Simple to handle and maintain
Drawbacks
More noticeable appearance
Potential pickup of background noise
Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) Devices: Similar to BTE models but connected with a thin, discreet wire.
Prices for digital hearing aids start around $1,500, with costs increasing based on features, accessories, remote controls, professional tuning, warranty, noise reduction, and battery life. Trying out devices beforehand is recommended to ensure best fit and comfort.