Ultimate Guide to Detecting and Treating Scabies Infestation
This comprehensive guide explains how to identify, manage, and treat scabies effectively. It covers symptoms, spread, and treatment options, emphasizing early detection for successful relief. Learn about notable signs such as rashes, burrows, and intense nighttime itching, and discover safe treatment methods like topical creams and prescription medications. Understanding scabies ensures prompt action to prevent transmission and improve comfort. Perfect for those suspecting infestation or seeking general knowledge about this contagious skin condition.
Comprehensive Insights into Managing and Understanding Scabies
Scabies is a highly contagious skin disorder caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It results in intense, often nighttime itching and spreads through close skin contact. These tiny mites burrow beneath the skin, forming small tunnels that are difficult to see without microscopic tools. While they cannot jump or fly, they thrive in various temperatures and environments. This condition affects millions globally across all ages, with over 300 million cases reported annually. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment are key to control and relief.
If you notice a rash or persistent itching, consulting images online can help verify if it's scabies. The disease mainly spreads through skin-to-skin contact, including sexual activity and close familial interactions. Casual contact or sharing clothes is less risky. Promptly seeking medical advice prevents further spread and eases symptoms. Recognizing signs early enables effective intervention and quick relief, so any unusual skin rash warrants professional assessment.
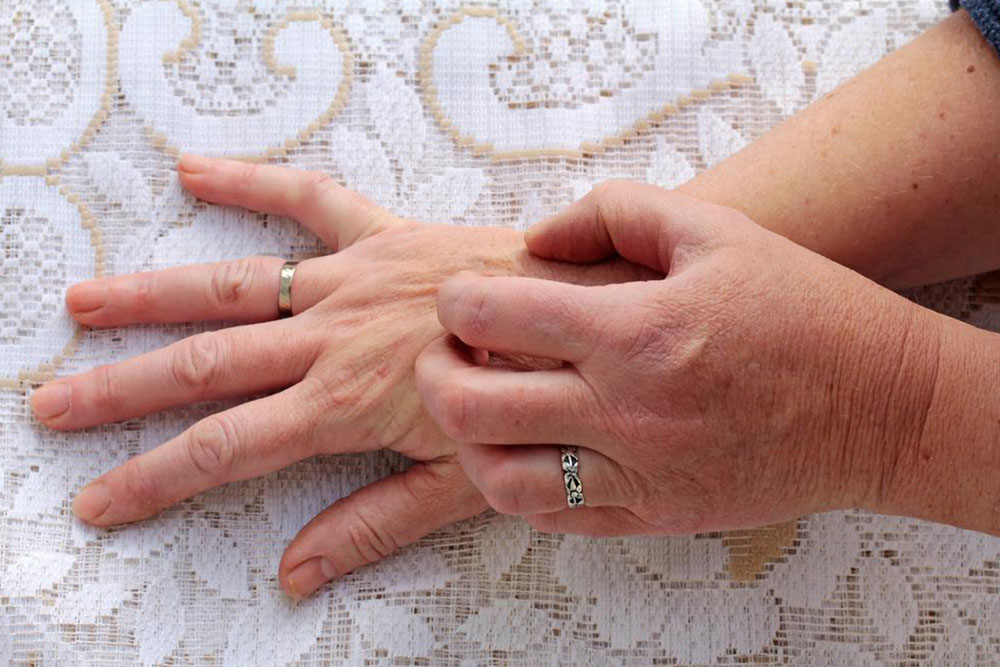
Recognizing Symptoms
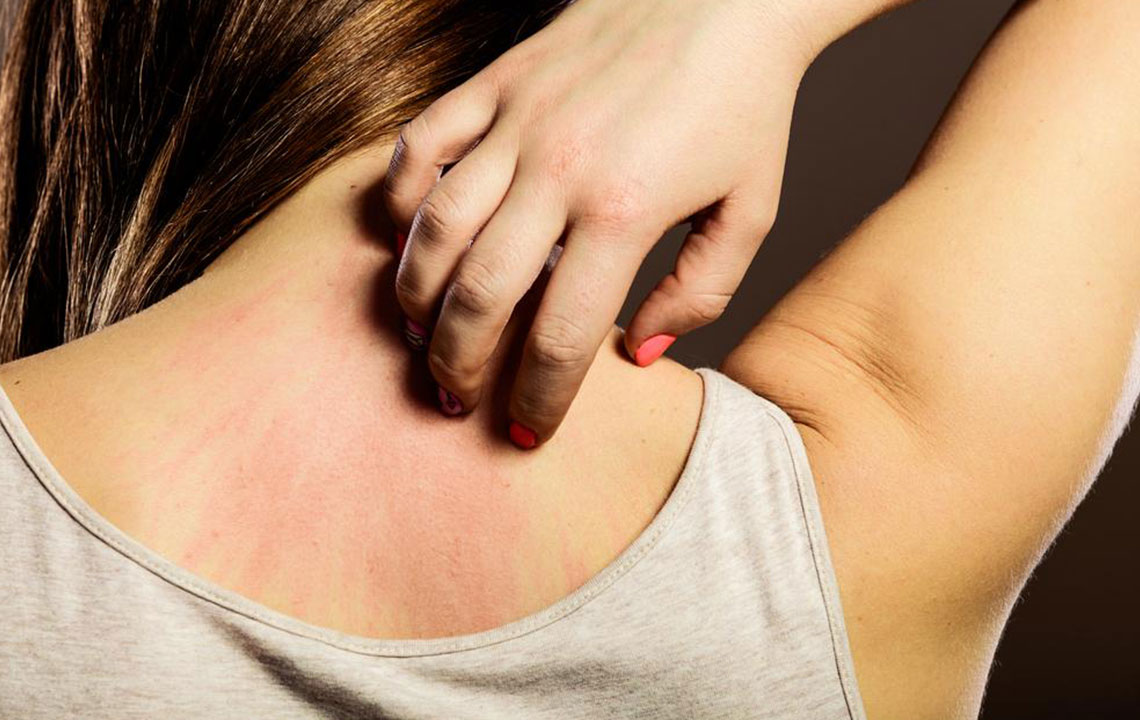
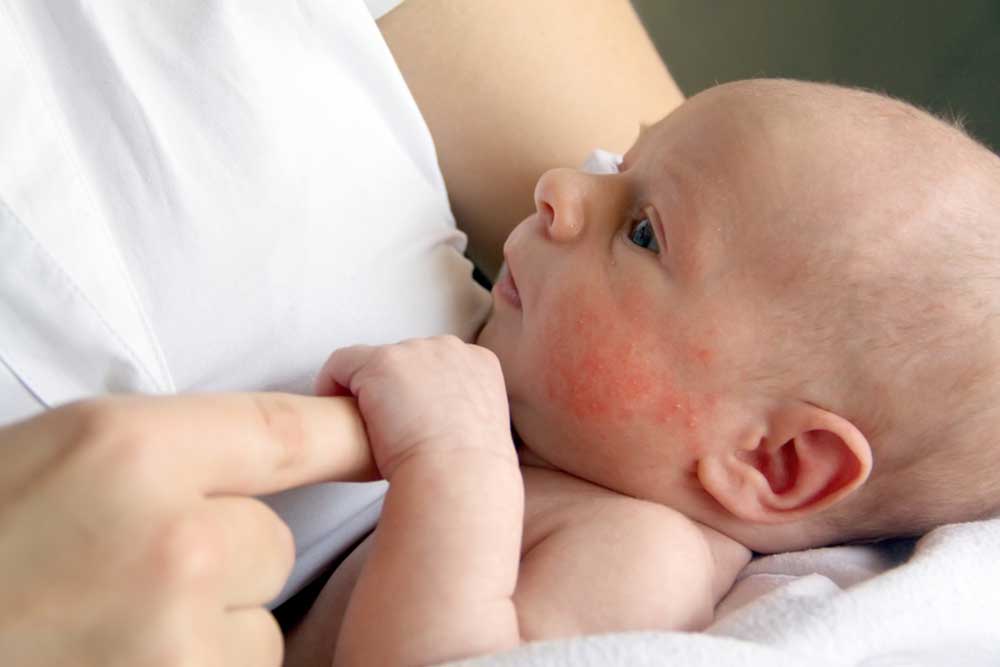
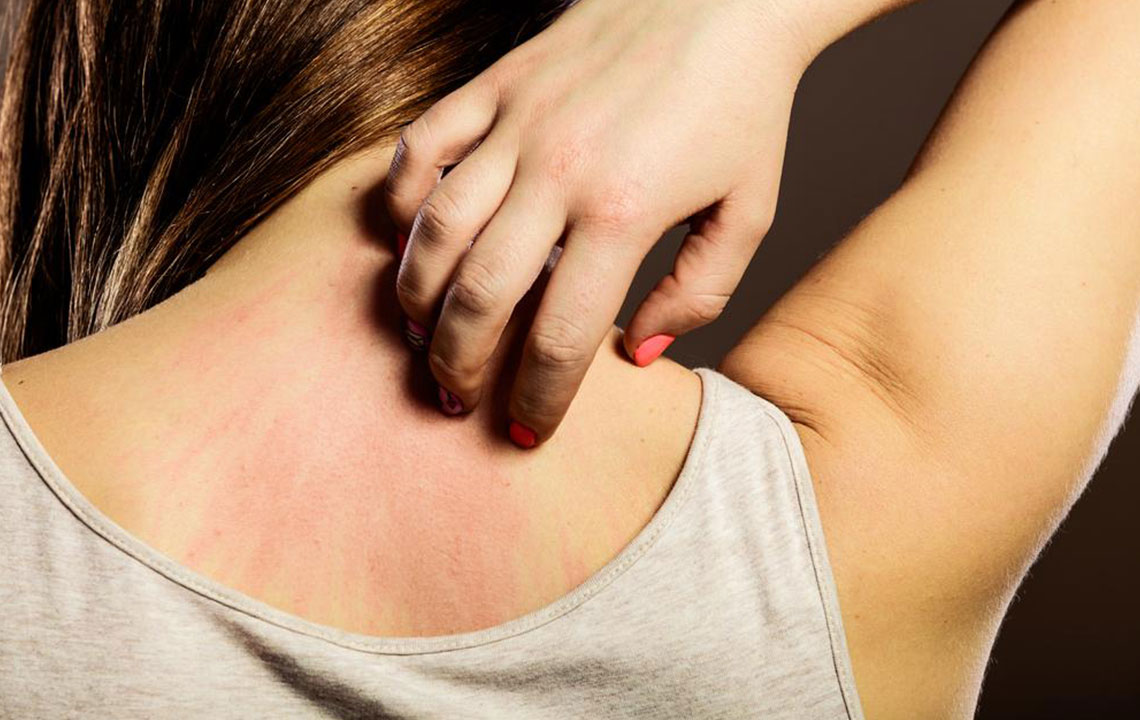
A typical scabies rash appears as tiny red bumps, blisters, or pimples, often found in skin folds like between fingers, wrists, elbows, buttocks, genitals, or feet. In children and infants, common areas include the palms, soles, face, and neck. Mites create fine, threadlike burrows visible as short lines that may be red, brown, or gray. Severe itching, especially at night, often accompanies these signs, disrupting sleep. Comparing images of scabies rash can help differentiate it from other skin conditions.
Additional Symptoms
Symptoms may take up to two months to appear, meaning the infestation can spread unnoticed. Nighttime itching becomes more intense over time. Scratching and burrowings can lead to skin wounds and bacterial infections. Unlike eczema, scabies symptoms tend to worsen significantly, impairing rest and daily comfort. Early detection through visual aids or professional consultation ensures timely treatment to curb spreading and reduce discomfort.
Treatment Options
Managing scabies effectively requires prescribed treatments like permethrin cream, applied overnight and washed off after several hours, repeated weekly. This method is safe for children older than two months. Alternative topical options include crotamiton lotion and sulfur-based ointments. In severe cases, oral medications such as ivermectin may be recommended. Avoid self-medicating; always consult healthcare providers. Improvements usually appear within 1 to 2 weeks. Confirm diagnosis with online images if unsure, then seek medical advice for proper treatment plan.