Essential Insights into Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Management
This comprehensive guide explores rheumatoid arthritis, highlighting its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatments. It emphasizes the autoimmune nature of RA, factors influencing its development, and ongoing research efforts. The article aims to educate readers about managing the condition and improving quality of life.
Essential Insights into Rheumatoid Arthritis and Its Management
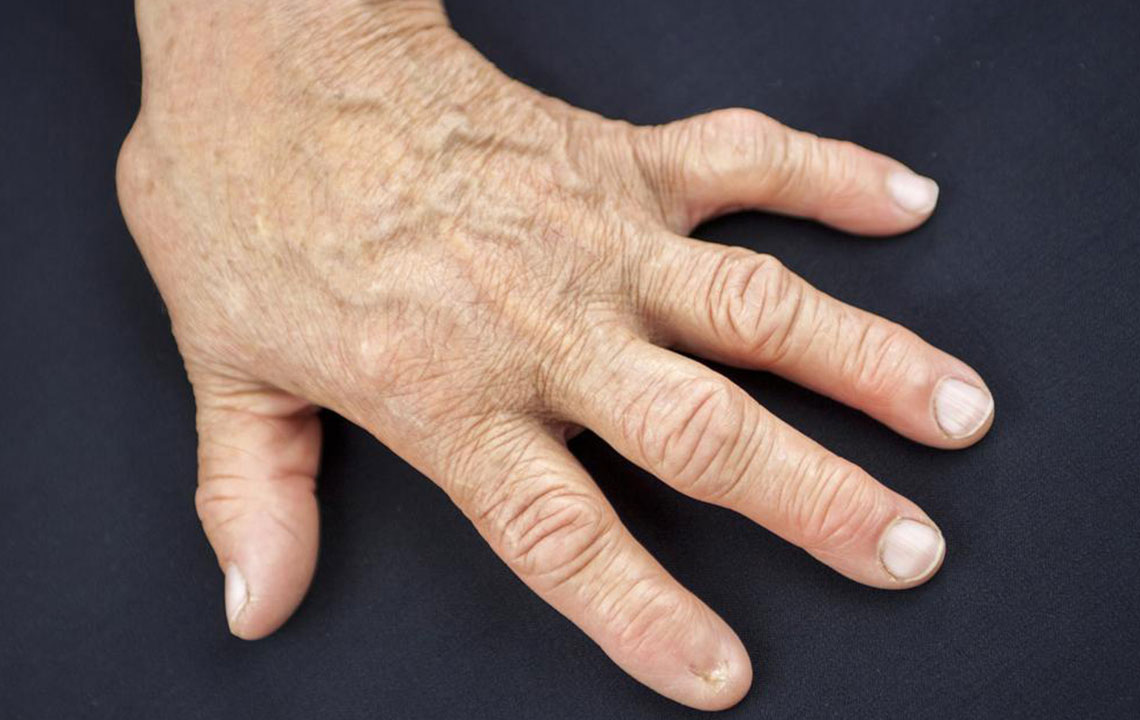
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune condition that primarily impacts joints such as wrists, elbows, fingers, and toes. It presents symptoms including joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, often involving multiple joints simultaneously. Early signs include fatigue, reduced appetite, overall discomfort, and morning stiffness. Temporary flare-ups of inflammation can occur, and prolonged inflammation may lead to systemic complications affecting other organs over time.
RA varies from mild to moderate severity, with symptoms fluctuating over years or lifelong. While its exact cause remains unclear, an abnormal immune response is believed to trigger joint inflammation and deterioration. Factors such as hormones, genetics, and lifestyle habits influence disease development. Diagnosis involves physical examination, blood tests, medical history, and imaging such as X-rays, helping distinguish RA from other joint conditions. Treatments focus on pain relief, reducing inflammation, preventing joint damage, and improving overall quality of life while controlling flare-ups. Research continues into infection links, genetic factors, and hormonal roles, with women being disproportionately affected—around 70%, often due to hormonal, obesity, or stress-related factors.