Early Detection and Strategies for Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early detection of rheumatoid arthritis is key to effective management. Recognizing symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, and fatigue allows for prompt treatment, which can prevent severe complications. This article covers symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options to help individuals seek timely medical care and maintain quality of life.

Recognizing Early Symptoms and Effective Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Essential information on initial signs and treatment approaches for rheumatoid arthritis
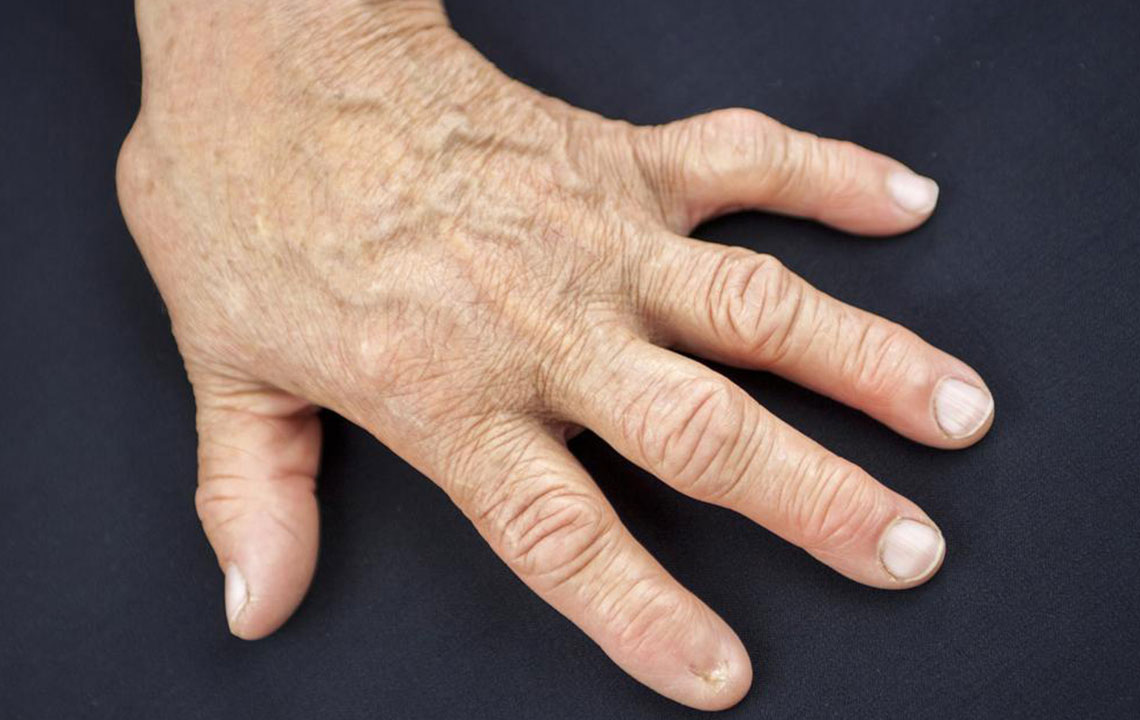
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease causing chronic joint inflammation, commonly affecting the hands, knees, feet, and fingers. Early symptom recognition and prompt medical consultation are critical for optimal management. In RA, the immune system erroneously attacks joint tissues, resulting in pain, swelling, and possible bone erosion. About 1.5 million Americans live with RA, impacting individuals of all ages and genders.
Women aged 30 to 60 are most frequently diagnosed, though men can also develop RA later in life. The disease typically presents symmetrically, affecting both sides of the body, including wrists, knees, and fingers.
Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to prevent severe complications, such as damage to blood vessels, lungs, eyes, and skin. Elevated inflammatory markers can lead to vascular issues, lung inflammation, eye dryness, mouth dryness, skin nodules, and systemic fatigue.
Initial RA symptoms include fatigue, morning stiffness, joint pain, swelling, mild joint stiffness, low-grade fever, numbness, tingling sensations, and limited mobility. Differentiating RA from fibromyalgia is important, as the latter shares symptoms like pain and fatigue but results from musculoskeletal causes.
Other signs might involve sleep disturbances, chest discomfort, appetite loss, general weakness, dry eyes and mouth, eye irritation, and unexplained weight loss.
If experiencing these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination of joints, blood tests for inflammation and auto-antibodies, and imaging such as ultrasound to evaluate joint damage. Treatments include pain relievers like acetaminophen, NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, and sometimes surgical options if medications fail. Early treatment prevents disease progression and preserves quality of life.
Neglecting RA symptoms can lead to serious health issues and hinder daily routines. Accurate diagnosis and timely management are crucial for controlling this chronic condition.