Differences Between COPD and Asthma Explained
This article highlights the key differences between COPD and asthma, focusing on causes, triggers, symptoms, and treatments. Understanding these distinctions can aid in proper diagnosis and management of these respiratory conditions, improving patient outcomes.
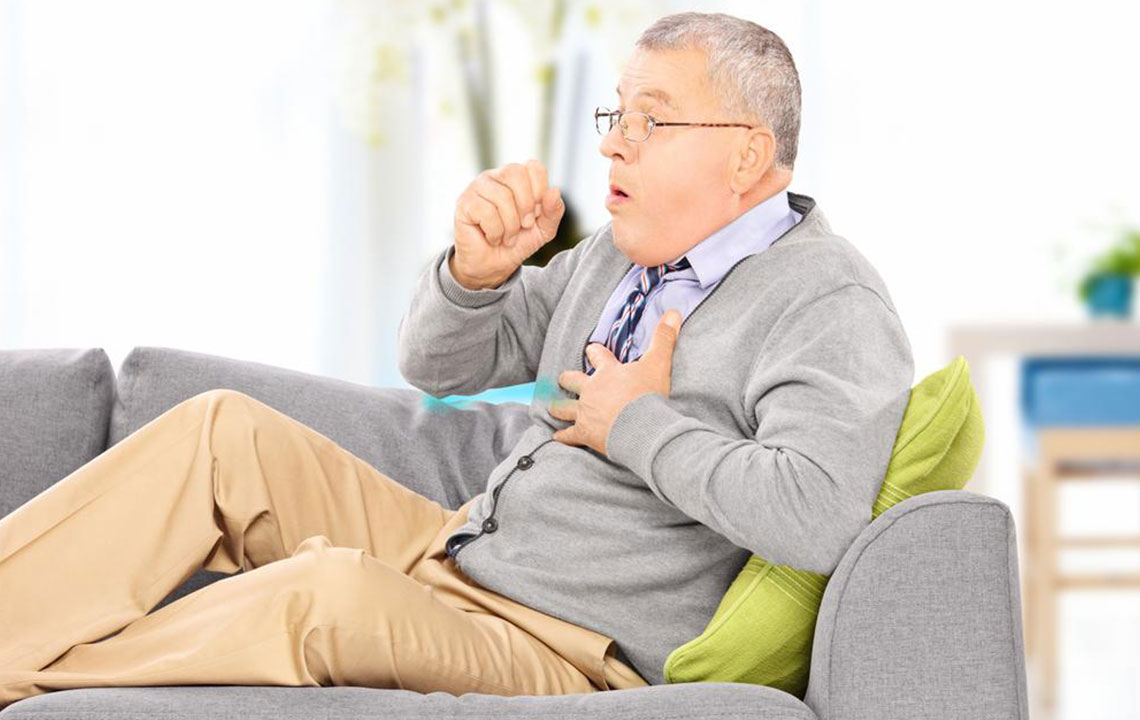

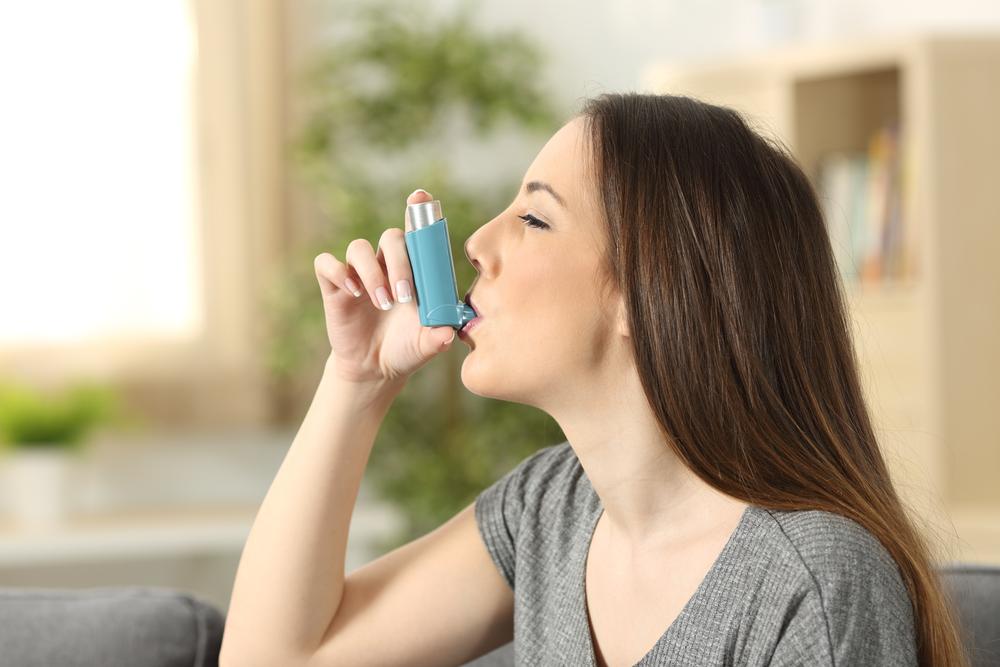
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) includes progressive lung illnesses such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis, characterized by irreversible airflow limitation. Conversely, asthma involves intermittent airway constriction caused by inflammation and spasms, often triggered by allergens. Both conditions exhibit symptoms like difficulty breathing, wheezing, chest tightness, persistent cough, and rapid heartbeat. Recognizing the differences in causes, triggers, age of onset, and treatments is vital for effective management and care of these respiratory disorders.
Asthma is mainly linked to genetic and environmental factors, especially allergies; COPD is often caused by smoking and environmental pollution.
Common triggers for asthma include allergens, cold air, and physical activity, while infections and pollutants dominate COPD exacerbations.
Asthma commonly begins in childhood, whereas COPD generally develops after age 40 due to prolonged smoking history.
Management strategies differ: asthma treatment includes bronchodilators, allergy control, and prevention, whereas COPD requires smoking cessation, medications, lung therapy, and sometimes surgery.