Signs of Hematuria: Understanding Blood in Urine Symptoms
This article offers a comprehensive overview of hematuria, including its causes, symptoms, risk factors, and initial steps for management. Recognizing blood in urine early helps in diagnosing underlying health issues, from urinary infections to serious conditions like tumors. Prompt medical consultation and proper testing are crucial for effective treatment. Understanding the different types of hematuria and their sources aids in better health decision-making and timely interventions to ensure optimal urinary health.

Signs of Hematuria: Understanding Blood in Urine Symptoms
Complete Overview of Blood in Urine and Its Significance
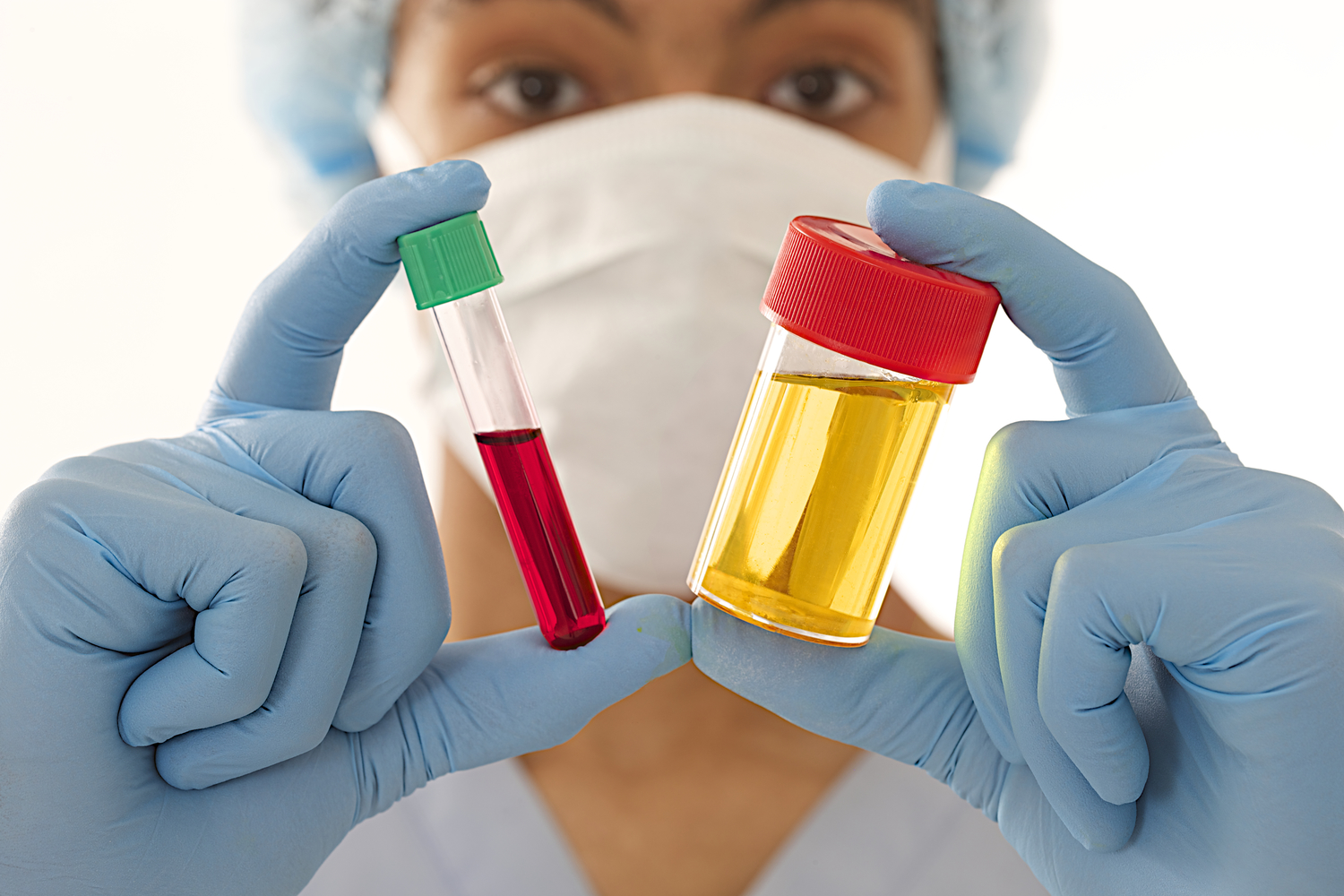
Hematuria, or blood appearing in urine, is often not an emergency but could indicate underlying health concerns. It generally reflects issues within the kidneys or urinary tract, requiring medical attention. Hematuria can be visible to the naked eye, appearing as red or brownish urine, or only detectable under a microscope. Distinguishing between these types aids in accurate diagnosis and management.
Common Causes of Hematuria
Originates mainly from the kidneys, which generate urine.
Other sources include the ureters, which connect kidneys to the bladder.
Blood may also come from the bladder where urine is stored.
The urethra can be a bleeding source too.
Symptoms to Watch For
Urine may be pink, bright red, dark brown, or tea-colored if blood is visible.
In hidden cases, urine appears normal but contains blood on lab tests.
Hematuria may accompany urinary tract infections, causing burning, pain, fever, sleep issues, or decreased appetite in children.
Individuals at Increased Risk
Those with a family history of kidney disorders.
Men, particularly with enlarged prostate glands.
People prone to kidney stones.
Individuals taking blood thinners, painkillers, or antibiotics.
Recent systemic infections may also increase risk.
Likely Causes of Blood in Urine
Menstrual cycle, intense physical activity, sexual activity, UTIs, or pelvic injuries.
Serious health issues like kidney or bladder tumors, swelling, prostate problems, polycystic kidneys, blood clots, or infections.
First Actions to Take
Do not dismiss blood in urine, especially if persistent.
Seek medical advice promptly unless caused by menstruation or recent injury.
Doctors may request urine analysis to determine cause.
Depending on findings, treatments like antibiotics or further testing will be recommended.
Early consultation is vital for hematuria, as it may be benign or indicate a more serious condition.
Reminder:
This blog provides well-researched health information. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult healthcare providers for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Our content may not cover all latest medical advances or treatment alternatives.