Proven Methods to Heal Toenail Fungal Infections
Discover effective strategies to treat and prevent toenail fungal infections, including home remedies and professional options. Learn to recognize symptoms early and maintain proper foot hygiene to ensure successful recovery and reduce recurrence. Consult healthcare providers for persistent cases or underlying health concerns to achieve optimal results in managing toenail fungus.
Proven Methods to Heal Toenail Fungal Infections
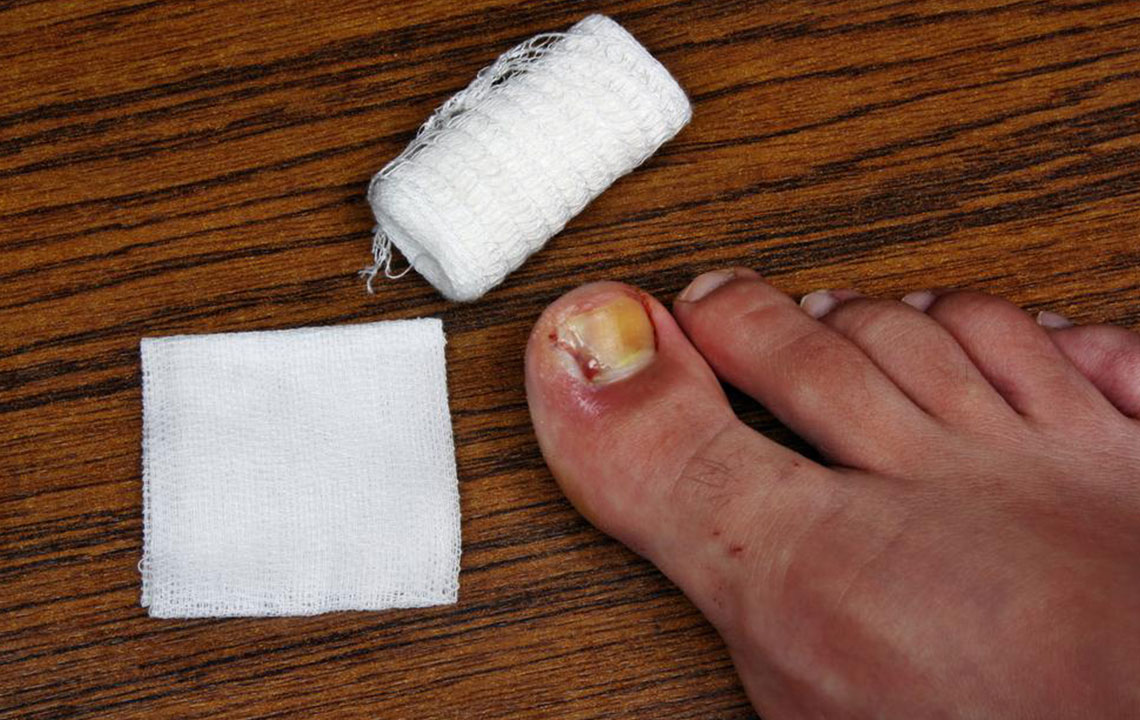
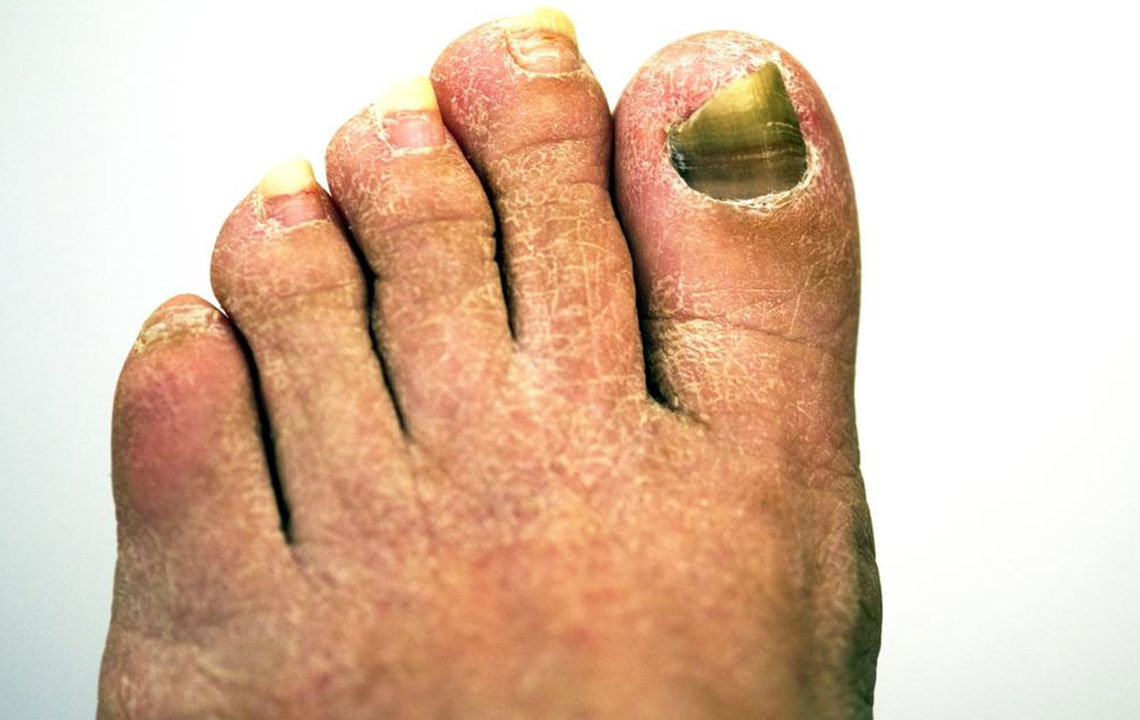
Fungal infections of the toenails, also known as onychomycosis, can be both embarrassing and difficult to treat. Left untreated, the infection can spread to adjacent nails, skin, or even fingernails. Early detection and action are key to preventing deterioration. Several effective treatments are available to eliminate toenail fungus. While reinfection can occur, proper management and hygiene can enhance recovery and improve daily comfort.
Toenail fungus affects people of all ages, with seniors and men being more vulnerable. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and health conditions increase the risk of developing this condition.
Common risk factors include a family history of fungal infections, close contact with infected individuals, excessive sweating, poorly ventilated footwear, and walking barefoot in moist environments. Underlying health issues like immune system suppression, diabetes, or genetic conditions such as Down syndrome can also heighten susceptibility.
Signs of toenail fungus include thickened, fragile nails, discoloration, crumbling edges, and a dull appearance. Recognizing these early symptoms is vital for timely treatment.
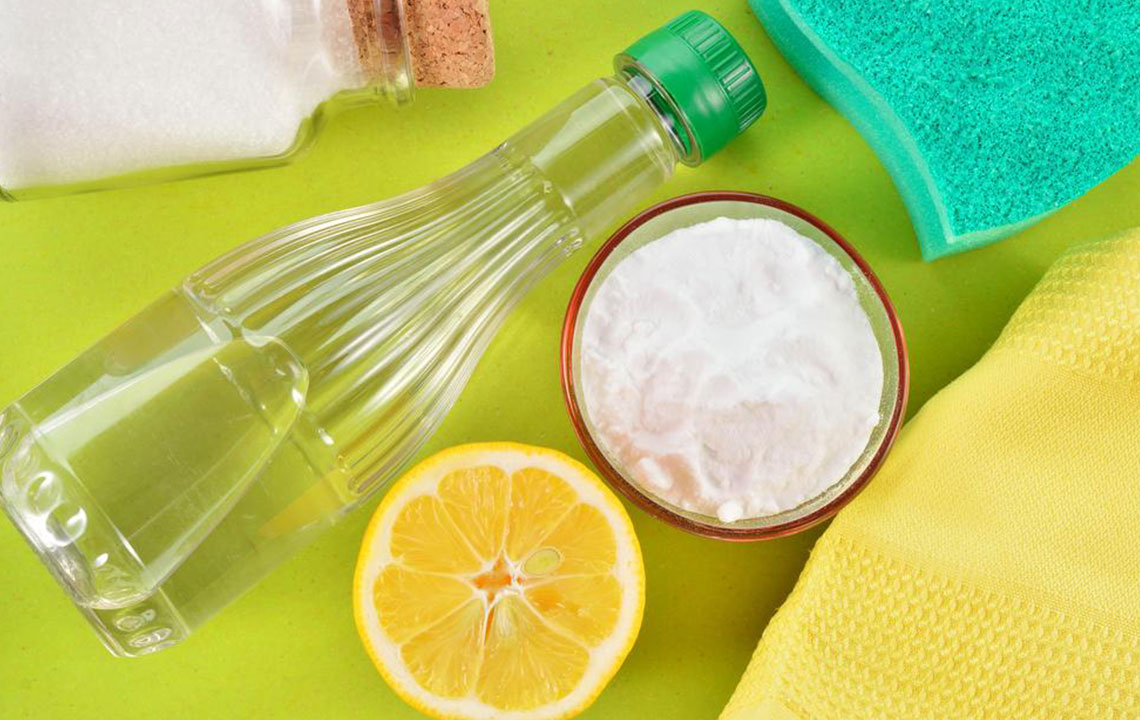
Home Remedies
Apple Cider Vinegar: Its antifungal properties make it a popular natural remedy. Dilute with water and soak the feet for about thirty minutes daily, then dry thoroughly.
Baking Soda: Known to fight fungi, create a paste with water, apply on affected nails, leave for a few minutes, then rinse and dry completely. Consistent use can promote healthy nail regrowth.
Tea Tree Oil: A traditional antifungal agent, apply using a cotton ball directly onto infected nails, allowing it to air dry.
Medical Treatments
If home solutions are ineffective, consult a healthcare professional. They can verify the diagnosis and recommend appropriate therapy, such as topical antifungal creams, nail lacquers applied weekly, or oral medications. Severe or persistent cases may require nail removal. Your doctor will consider your overall health to choose the best treatment option, accounting for potential side effects.
When to Seek Medical Help
If symptoms include ongoing discoloration, pain, swelling, pus, or if you have underlying conditions like diabetes or immune compromise, seek medical attention promptly. Ignoring these signs can lead to worsening infection, permanent nail damage, or secondary bacterial infections. Immediate care is necessary if fever or increasing tenderness develops.
Although toenail fungus may resolve on its own at times, maintaining good foot hygiene is essential. Keep nails clean, trimmed, and dry, wear breathable footwear, and avoid walking barefoot on damp surfaces. Be cautious, as infection can spread to other nails or body parts. Always wash hands after touching infected nails to prevent transmission. Consistent care and early intervention significantly enhance recovery chances and lower recurrence risks.