Smart Approaches to Managing Gluten Intolerance
This article explores practical methods to manage gluten intolerance, emphasizing medical advice, dietary adjustments, and nutritional support. It provides guidance on eliminating gluten from your home, working with professionals, and choosing safe, nutrient-rich foods to improve health and reduce symptoms effectively.

Smart Approaches to Managing Gluten Intolerance
Gluten intolerance, often confused with celiac disease due to similar symptoms, is an immune response caused by gluten ingestion in wheat and related grains. Symptoms typically include abdominal bloating, cramps, gas, diarrhea, and skin irritations after consuming gluten-rich foods. Many sufferers find relief by adopting a gluten-free diet. While no cure exists, various strategies can help control gluten intolerance effectively.
Consult Healthcare Professionals: If gluten consumption leads to discomfort, seek medical guidance. Proper testing such as blood analysis, endoscopy, or capsule exams can differentiate gluten intolerance from celiac disease.
The healthcare provider will accurately diagnose your condition and suggest suitable treatments. Primarily, avoiding gluten is essential. Medications and supplements may be advised to alleviate specific symptoms, including inflammation and nutritional deficiencies.
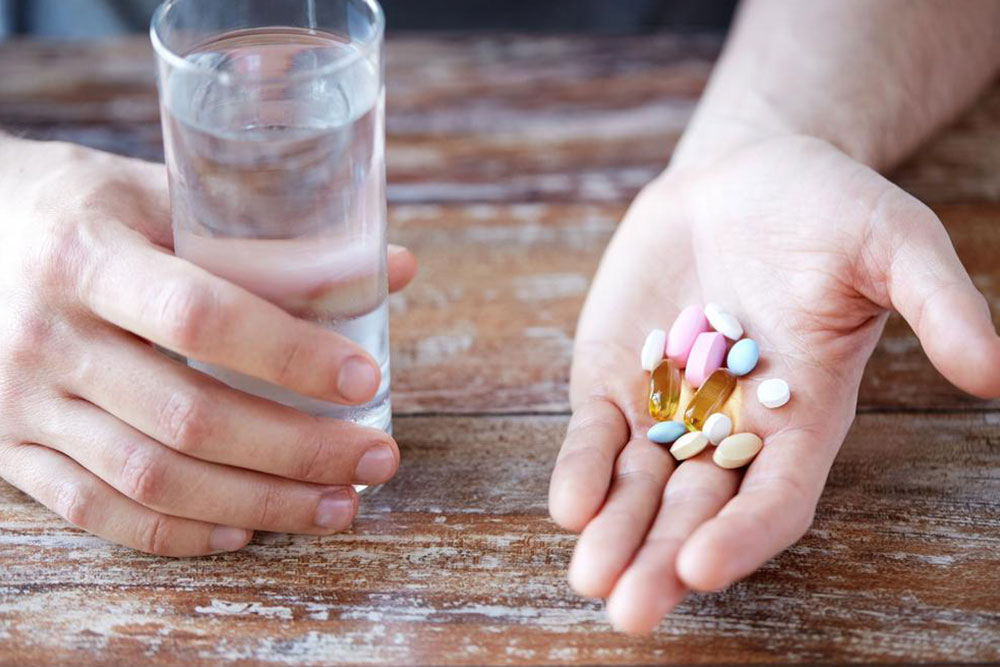
Medication and Nutritional Care: Supplements like calcium, iron, vitamin B12, D, K, and zinc support overall wellness. Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids, can reduce symptoms. For skin issues like dermatitis, treatments like dapsone might be recommended.
Work with a Nutrition Specialist: Nutritionists help identify gluten-free foods, detect hidden gluten sources, and recommend safe alternatives, especially when eating out.
Remove Gluten from Your Kitchen: Eliminating wheat, rye, barley (including malt and vinegars), and triticale prevents accidental gluten ingestion and related reactions.
Create a Gluten-Free Food Supply: Focus on naturally gluten-free foods like eggs, meats, fish, poultry, beans, and dairy. Many stores now stock a variety of gluten-free products to support a balanced diet.