Complete Overview of Herpes: Causes, Types, and Modes of Transmission
This comprehensive guide explores herpes, detailing its causes, different types, and how it spreads. Most notably, HSV-1 and HSV-2 are the most common forms, transmitting through skin contact and sexual activity. Other herpesviruses can cause diseases like chickenpox, mononucleosis, and more. Herpes infection is widespread globally, emphasizing the importance of understanding transmission methods and managing symptoms effectively.

Herpes Uncovered: Origins, Variants, and How It Is Transmitted
What is Herpes?
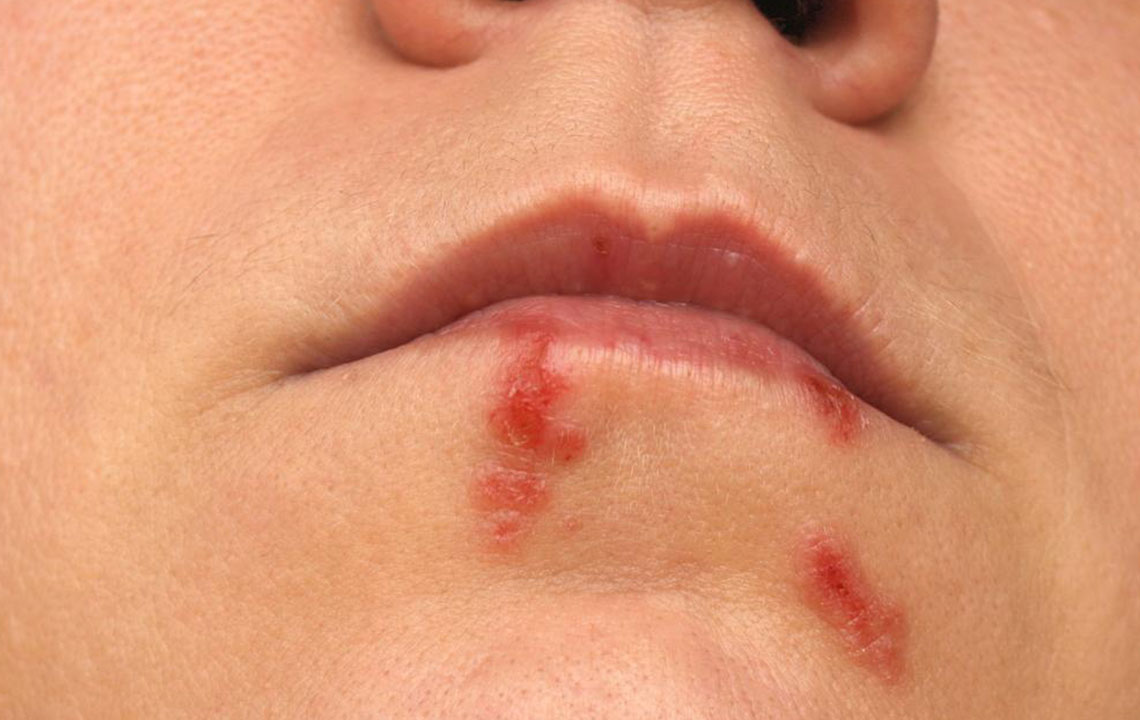
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the Highly contagious Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV). There are eight recognized types of HSV, with HSV-1 and HSV-2 being the most common. HSV-1 usually leads to oral sores or cold sores, while HSV-2 mainly causes genital herpes. Both strains are highly infectious and can spread easily between individuals.
In what ways does Herpes spread?
The World Health Organization estimates that around 67% of people worldwide carry HSV-1. The virus transmits through skin-to-skin contact, especially during active outbreaks, and can be spread by sharing personal items such as towels, razors, or utensils. HSV-2 primarily spreads via sexual activity, affecting genital regions but can also infect facial areas.
Is Herpes a common condition?
Health experts recognize that Herpes infection is widespread, comparable to chickenpox. Asymptomatic cases usually don’t require treatment, but symptomatic infections should be managed effectively.
Other Herpesvirus Strains
Besides HSV 1 and HSV 2, six other herpesvirus types can cause illnesses.
HHV-3 causes chickenpox and shingles, affecting skin and nerve tissues, leading to persistent sores and discomfort.
HHV-4, known as Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), results in Mononucleosis or "Kissing Disease," spreading through saliva, coughing, or sharing items.
HHV-5 relates to Cytomegalovirus infections, which can transmit from mother to child, blood transfusions, or organ transplants, potentially leading to hepatitis or immune suppression.
HHV-6 and HHV-7 cause Roseola, characterized by rashes and high fever.
HHV-8 is associated with certain cancers including lymphoma and tumors.