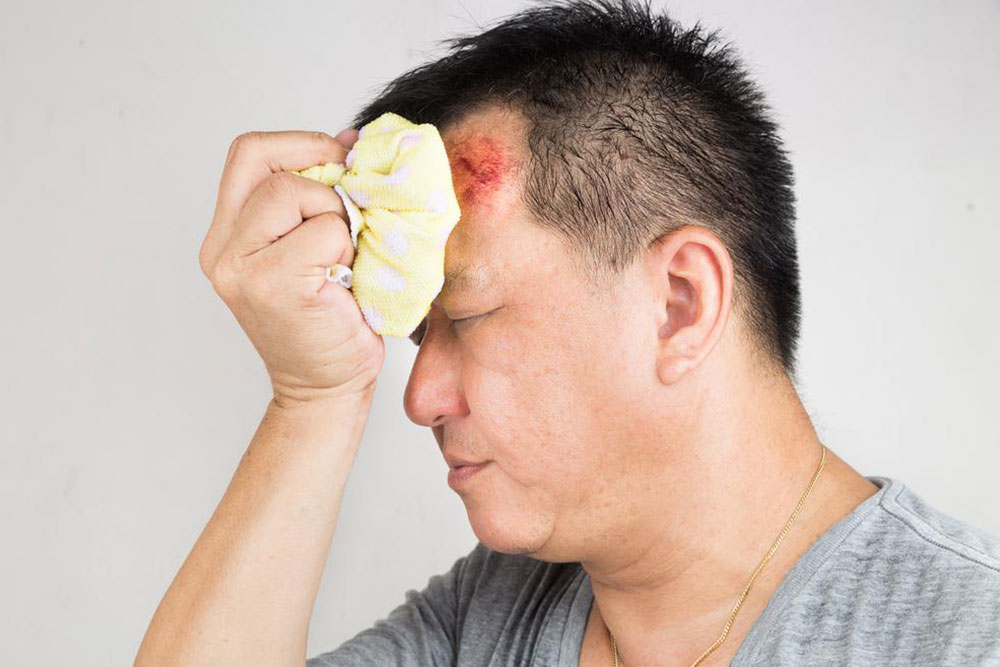
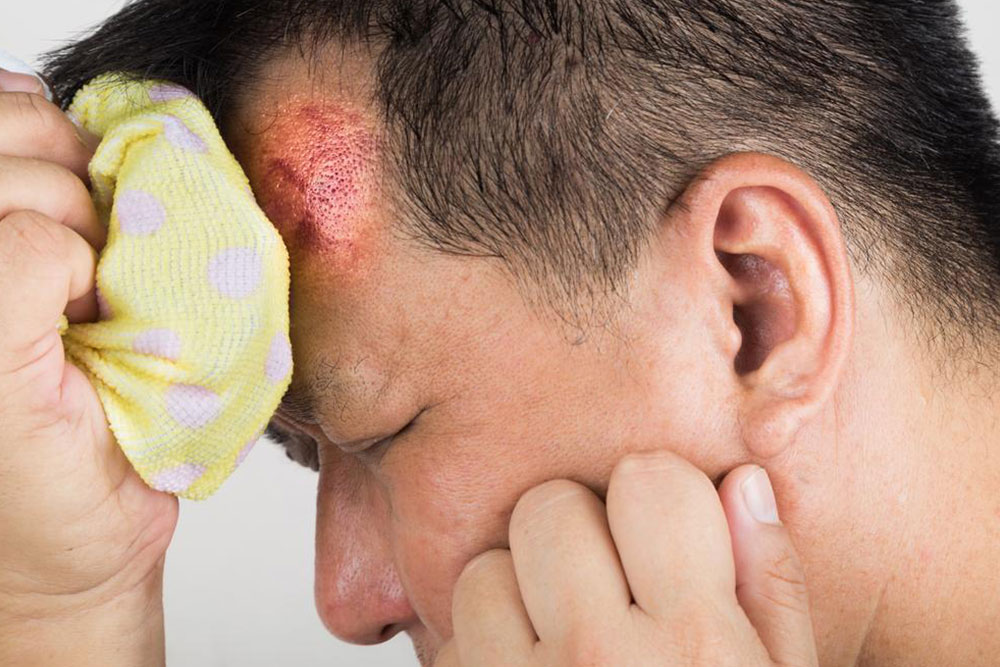
Recognizing Head Injury Signs and Symptoms in Kids and Adults
This article highlights key signs of head injuries in both adults and children, including behavioral, physical, sensory, and cognitive symptoms. Recognizing these signs promptly can save lives. Parents and caregivers are especially encouraged to monitor for subtle changes in children after head trauma and seek immediate medical help to prevent complications.
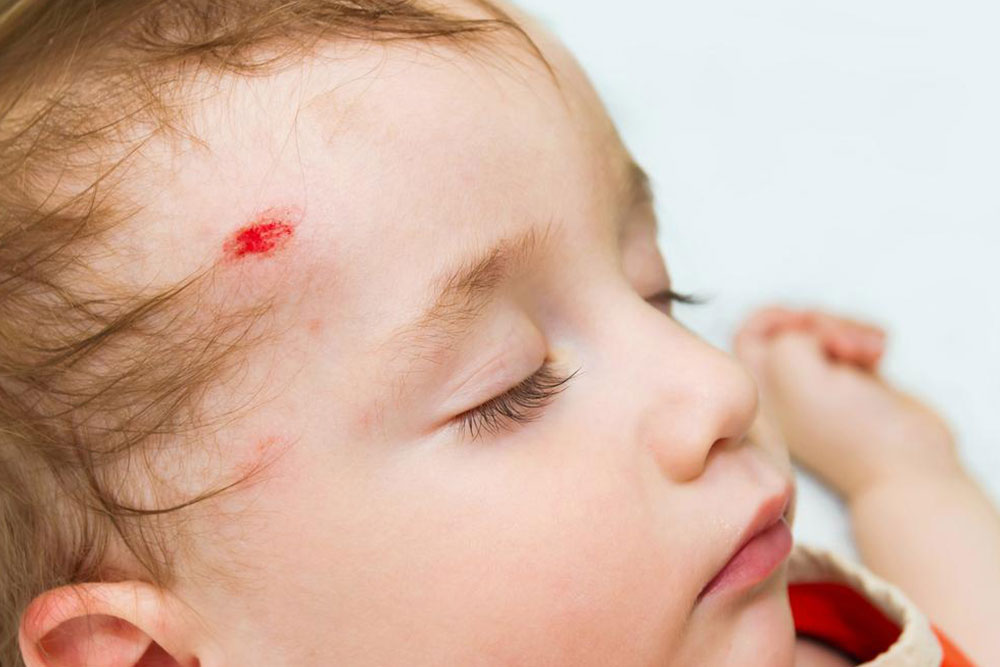
Detecting Head Traumas: Key Symptoms in Children and Adults
Head injuries show a range of signs, from visible bruises to changes in mental state. Prompt identification is vital, no matter how mild or severe the trauma. Symptoms may appear instantly or develop gradually over days. Here are common indicators to watch for.
Cognitive and Mental Signs
These include forgetfulness, difficulty focusing, mood swings, depression, anxiety, speech problems, confusion, recognition difficulties, partial memory loss, agitation, slurred speech, and unconsciousness.
Behavioral and Emotional Changes
Some head injuries can cause unusual behaviors such as excessive crying or laughter, irritability, aggression, impulsiveness, repetitive motions, and lack of restraint.
Sensory Symptoms
Feelings of blurred vision, ringing ears, strange tastes, altered smell, and increased sensitivity to light and sound are common.
Physical Symptoms
Physical issues range from mild to critical, including persistent headaches, seizures, nerve damage, bleeding, muscle stiffness, bruises, fractures, and other symptoms.
Loss of consciousness
Prolonged nausea or vomiting
Fluid drainage from ears or nose
Numbness in extremities
Difficulty waking or drowsiness
Pupil dilation or responsiveness issues
Dazed or confused appearance
Extreme tiredness or sleepiness
Problems with balance or coordination
Sleep disturbances or insomnia
Extended sleep episodes or lethargy
Symptoms in Kids
Infants and young children often fall, making early intervention critical. Though they can't fully communicate, parents should note persistent crying, irritability, sleep or eating changes, disinterest in toys, or fussiness. Immediate medical attention is recommended if symptoms are observed.