Early Symptoms and Warning Signs of Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a rare autoimmune disorder causing skin thickening and internal organ issues. Early signs include skin tightening, organ symptoms, digestive problems, and extremity changes. Recognizing these signs early enhances management and treatment options, preventing severe complications. This article outlines key early symptoms to watch for and highlights the importance of prompt medical evaluation to improve patient outcomes.

Scleroderma is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by hardening and thickening of the skin due to excess collagen production. It primarily affects the upper layers of skin but can extend to internal organs, blood vessels, and the digestive tract. Most common in women aged 30 to 50, this condition currently has no cure. Early recognition of symptoms such as skin tightening, organ dysfunction, digestive issues, calcium buildup, and changes in extremities is vital for effective management. Prompt diagnosis allows for better control and improved quality of life.
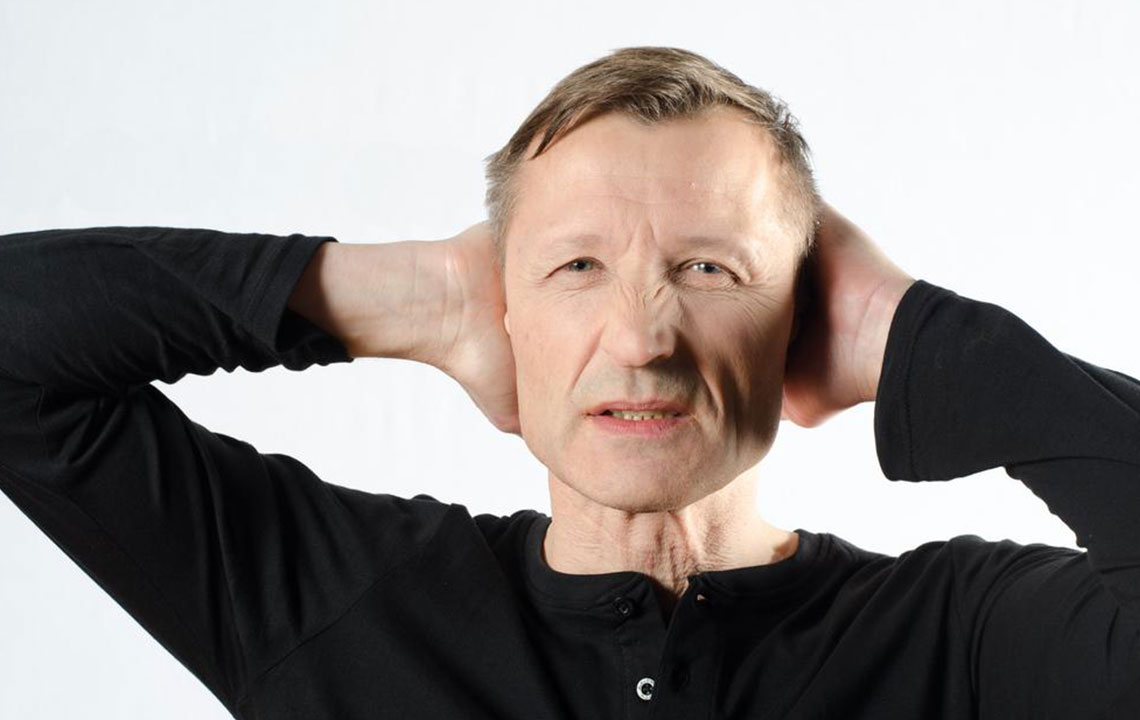
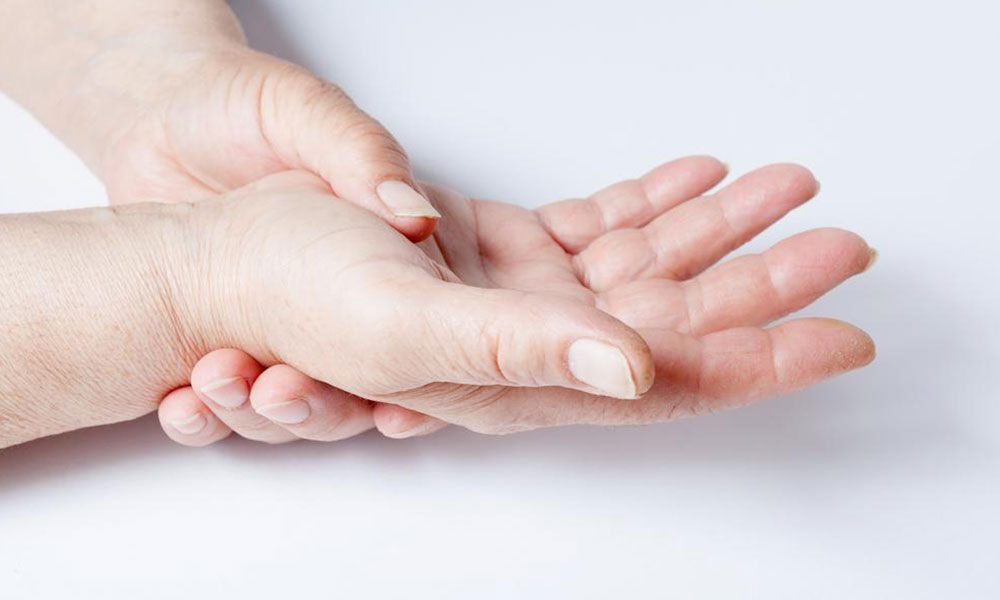
Skin Firming – Initial signs include skin becoming firm and tight, forming oval or linear patches that restrict movement. The location, size, and shape of these patches help identify scleroderma subtypes.
Impact on Organs – The disease can affect lungs, kidneys, and heart, leading to inflammation, irregular heartbeat, or hypertension, requiring urgent medical care.
Digestive Difficulties – Common early symptoms include acid reflux and poor nutrient absorption, stemming from esophageal damage and slowed intestinal movements.
Calcium Accumulation – Deposits of calcium can develop within connective tissues, noticeable as lumps or bumps.
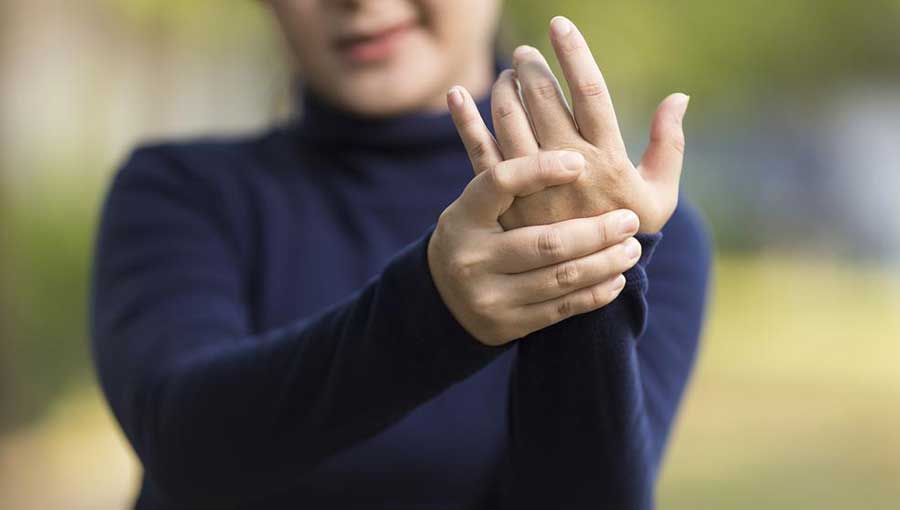
Extremity Changes – Discoloration, pain, or numbness in fingers and toes during cold exposure or emotional stress are typical early indicators.
If limited to the skin, symptoms may resolve within five to seven years. However, if internal organs are involved, disease progression can occur without timely intervention.
Disclaimer:
This website offers general health information for educational purposes. Always consult qualified healthcare providers for diagnosis and treatment. We do not guarantee the accuracy of external sources or specific conditions. Availability of services and offers may vary, so verify details independently.