Effective Methods for Achieving Clear, Acne-Free Skin
Discover effective techniques to achieve clear, acne-free skin. From OTC treatments with benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid to advanced therapies like light-based methods and retinoids, learn how to manage and prevent acne. Consulting a dermatologist is recommended for tailored solutions.
Effective Methods for Achieving Clear, Acne-Free Skin
Acne, known medically as "Acne Vulgaris," is a persistent skin condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes cysts. Human skin has countless tiny hair follicles called pores, which contain oil-producing sebaceous glands. These glands secrete sebum to keep skin moist. When excess sebum mixes with dead skin cells and blocks a pore, it can lead to acne. Bacterial growth in blocked pores can cause redness and swelling, intensifying the problem.
Proper treatment approaches are key to managing acne effectively. Below are some leading strategies:
In 2017, several proven acne treatments gained popularity, including OTC products, targeted therapies, and prescription options:
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Products: Gels, creams, and cleansers with ingredients such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, azelaic acid, and sulfur help reduce bacteria, unblock pores, and lessen inflammation.
Benzoyl Peroxide: An FDA-approved agent that quickly kills P. acnes bacteria and clears dead skin. Suitable for most skin types but may bleach fabrics and affect lighter skin tones.
Salicylic Acid: Penetrates pores to clear blockages, reduces bacteria, and calms inflammation. Sensitive skin may experience stinging from use.
Azelaic Acid: Effective for mild to moderate acne by minimizing skin cell buildup and providing anti-inflammatory benefits, though it may cause irritation in some cases.
Sulfur: Assists in drying excess oil, removing dead skin, and fighting bacteria. It might have a strong smell but is beneficial for those who tolerate it.
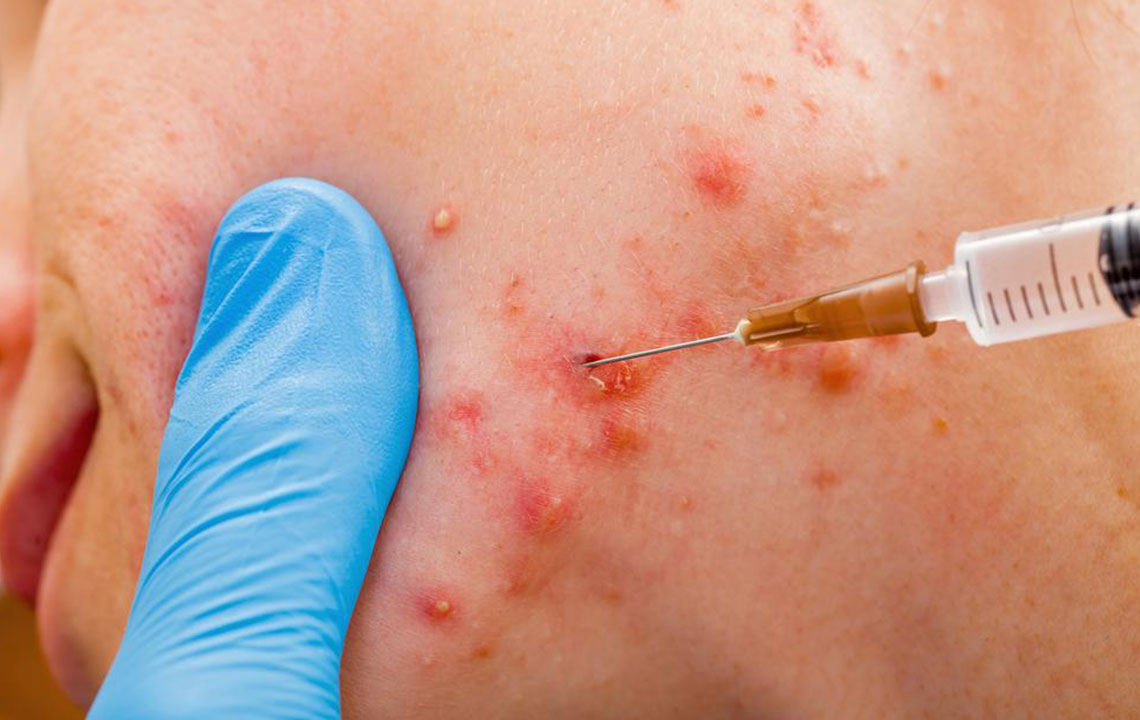
Corticosteroid Injections: Used for cystic acne, these shots swiftly reduce inflammation and cyst size within hours, though they do not address bacteria.
Light-Based Treatments: Photodynamic blue light therapy involves applying a photosensitizer followed by light exposure to target acne-causing bacteria and lesions effectively.
Retinoids and Vitamin A Derivatives: Topical options like tretinoin, adapalene, and retinol, along with oral isotretinoin for severe cases, help unclog pores, control oil production, and prevent future breakouts. Side effects can include dryness, redness, and in oral forms, pregnancy risks and mood changes.
Note: This article provides general research-based insights. For personalized skin care advice, consult a healthcare professional. We do not guarantee the accuracy of all information or promotional offers from other sites.