Essential Foods to Avoid for Successful Gout Management
Discover essential dietary tips to prevent gout flare-ups by avoiding high-purine foods. Learn which foods to limit, including seafood, alcohol, organ meats, and sugary drinks, to manage uric acid levels effectively. The guide emphasizes the importance of dietary control, especially for men and overweight individuals, in reducing joint pain and inflammation associated with gout.
Gout is characterized by severe joint pain due to high uric acid levels in the blood. Excess uric acid forms crystal deposits around joints, causing inflammation and discomfort. Commonly classified as a severe form of arthritis, gout primarily affects the big toe but can also impact the ankles, knees, and hands.
The body breaks down purines—both from natural sources and certain foods—into uric acid. Consuming foods rich in purines can trigger gout episodes by raising uric acid levels.
Men and individuals with higher body weight are more prone to gout. Managing your diet by avoiding specific foods can help reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Gout-friendly Diet Tips
Following a diet that minimizes uric acid can ease symptoms but does not cure gout. It helps in decreasing the severity and frequency of attacks.
Foods to Limit or Avoid
Foods high in purines should be reduced to avoid worsening gout symptoms. It is crucial for those susceptible to gout to avoid certain dietary triggers.
Since gout is more common in men and overweight people, controlling purine intake is essential. Here are the key foods to watch out for:
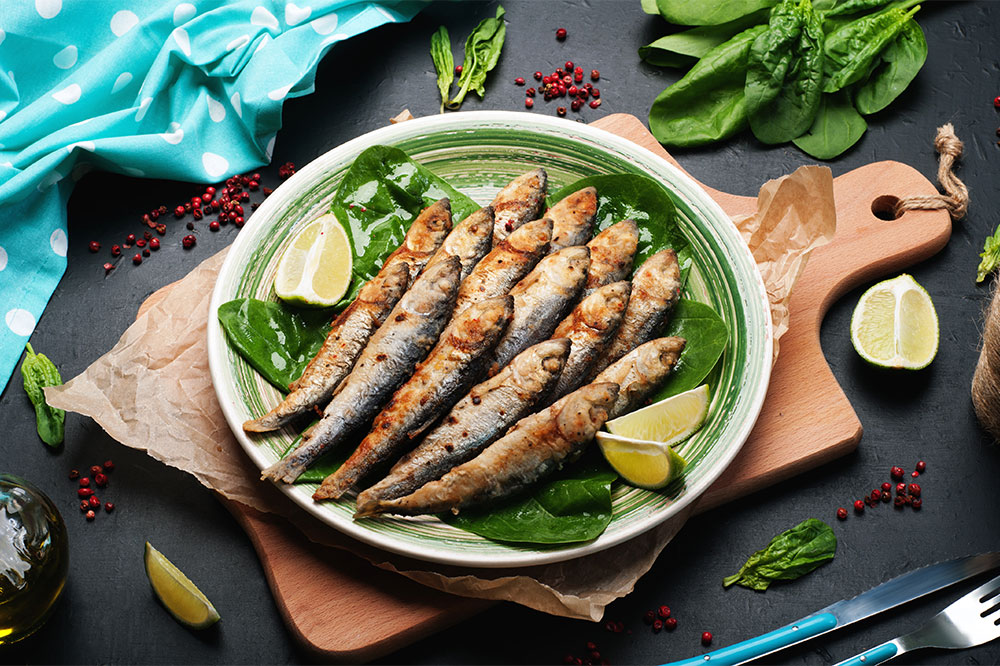
1. Seafood
Seafood such as salmon, herring, tuna, sardines, mackerel, carp, trout, anchovies, and cod contain high purine levels. Regular consumption may intensify gout issues.
2. Alcoholic Drinks
Alcohol, especially beer, dramatically increases gout risk due to its purine content. Drinking just one beer daily can nearly double the chances of developing gout. Alcohol also hampers uric acid elimination.
3. Organ Meats
Liver, kidneys, spleen, and brain are rich in purines and should be avoided by those with gout.
4. Red Meat
Beef, pork, and lamb provide moderate to high purine levels. Cuts like ribs and filet contribute to increased uric acid risk, and their fat content may further influence gout symptoms.
5. Sugary Beverages
Sodas and fruit drinks with added fructose can promote uric acid crystal formation, aggravating gout. Although not high in purines, these beverages still pose a risk due to sugar content.
6. Certain Fruits
Apples, oranges, watermelons, and raw dates contain moderate purines. Gout patients should consume these carefully, particularly during attacks or if overweight.
7. Fried Foods
Fried foods can lead to weight gain and inflammation, potentially triggering gout. Limiting fried items can support better symptom management.
Note: This overview offers general guidance for gout management but does not replace medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for tailored treatment and dietary planning.


