Essential Tips to Enhance Contraceptive Effectiveness
This article highlights key factors to enhance contraceptive effectiveness, including maintenance, scheduling, permanence, and cost considerations. It emphasizes the importance of partner communication, healthcare consultation, and STD protection, helping individuals choose the most suitable family planning options based on their lifestyle and health needs.
Essential Tips to Enhance Contraceptive Effectiveness
Contraceptive methods include devices, pills, and procedures designed to prevent pregnancy. Although most options target women, men also have access to certain products and methods. The market provides a wide array of contraceptives, each with different mechanisms tailored to individual needs.
Some methods excel at preventing unintended pregnancies, while others prioritize ease of use. Certain options are effective during menstruation or are low-hormone alternatives. Here are some common contraceptive choices, devices, and techniques.
Low-maintenance options
Implants and IUDs require minimal attention. Implants last up to five years, while intrauterine devices can prevent pregnancy for as long as 12 years.
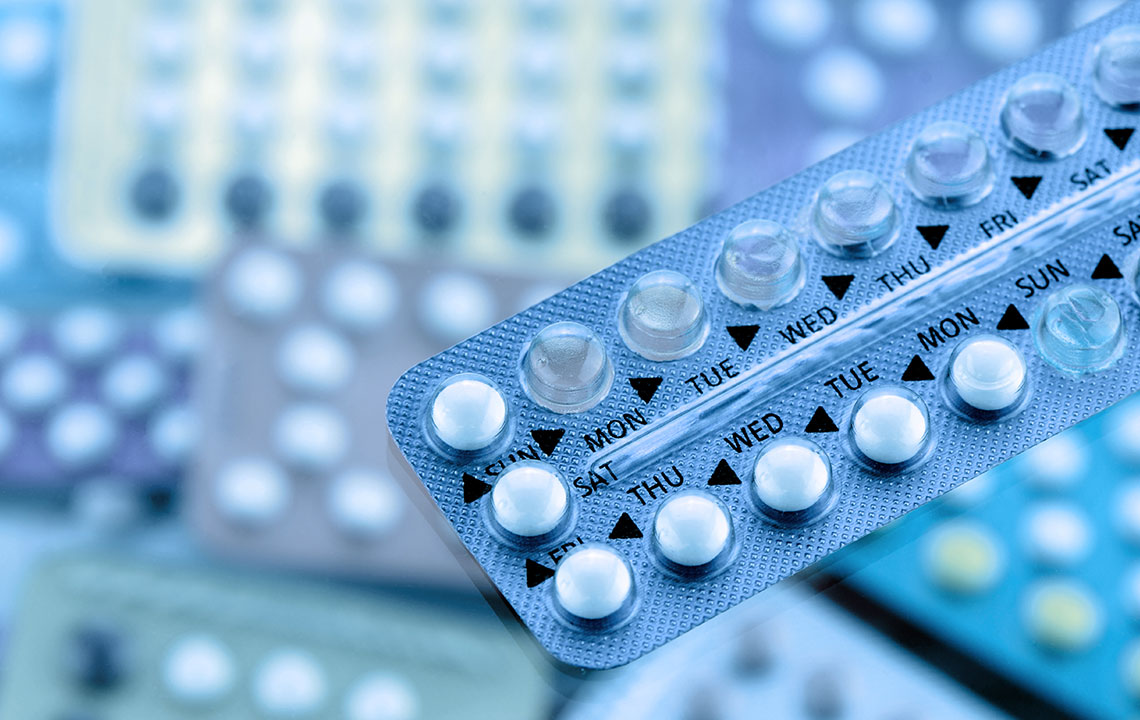
Scheduled methods
Birth control shots, vaginal rings, patches, and pills must be used consistently following their schedules. Their success rates are generally lower than long-term solutions, with usage varying from daily to monthly.
Daily use methods
Condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps, sponges, and spermicides need to be applied with each sexual act for optimal protection. Among them, condoms provide the highest reliability.
Permanent options
Procedures like tubal ligation for women or vasectomy for men serve as permanent family planning methods. Vasectomy is typically more affordable.
While most contraceptives are effective, keeping emergency contraceptive pills accessible is recommended. These pills can prevent pregnancy if taken within five days after unprotected sex.
Key considerations before selecting a method
Factors such as relationship status, age, and health conditions should guide your choice.
Reversible versus permanent
Many methods are reversible, suitable for those planning future pregnancies. Sterilization and vasectomy are permanent options.
Potential side effects
Hormonal pills containing estrogen and progesterone may alter natural hormone balance. Consult your healthcare provider to understand and manage any side effects.
Protection against STDs
Male and female condoms are the only contraceptives that also protect against sexually transmitted infections. Using a new condom for each partner significantly reduces infection risk, especially in casual encounters.
Cost factors
Contraceptive costs vary. Implants and IUDs may require high initial investments, whereas condoms and spermicides are more budget-friendly but need frequent replacement. Permanent procedures like vasectomy and tubal ligation involve higher costs and are irreversible.
Additional advantages
Certain contraceptives may lead to lighter periods, decreased risk of infections, and lower chances of specific cancers. Personal preferences and lifestyle impact the best choice.
Method effectiveness
Techniques like withdrawal and outercourse depend heavily on user discipline, making them less reliable.
Partner collaboration
Successful family planning often requires open communication. Discuss your options thoroughly with your partner and consult healthcare providers for informed decisions.
Insurance coverage
Many insurance plans, including Medicaid, cover contraceptive methods and procedures. Verify your coverage with your provider to access available support for family planning needs.