A Complete Overview of Joint Pain and Its Causes
This comprehensive guide explains joint discomfort, its common causes like arthritis and injuries, symptoms such as swelling and pain, and treatment options including medications and physiotherapy. Understanding these factors is essential for managing joint health and seeking timely care to prevent further damage.

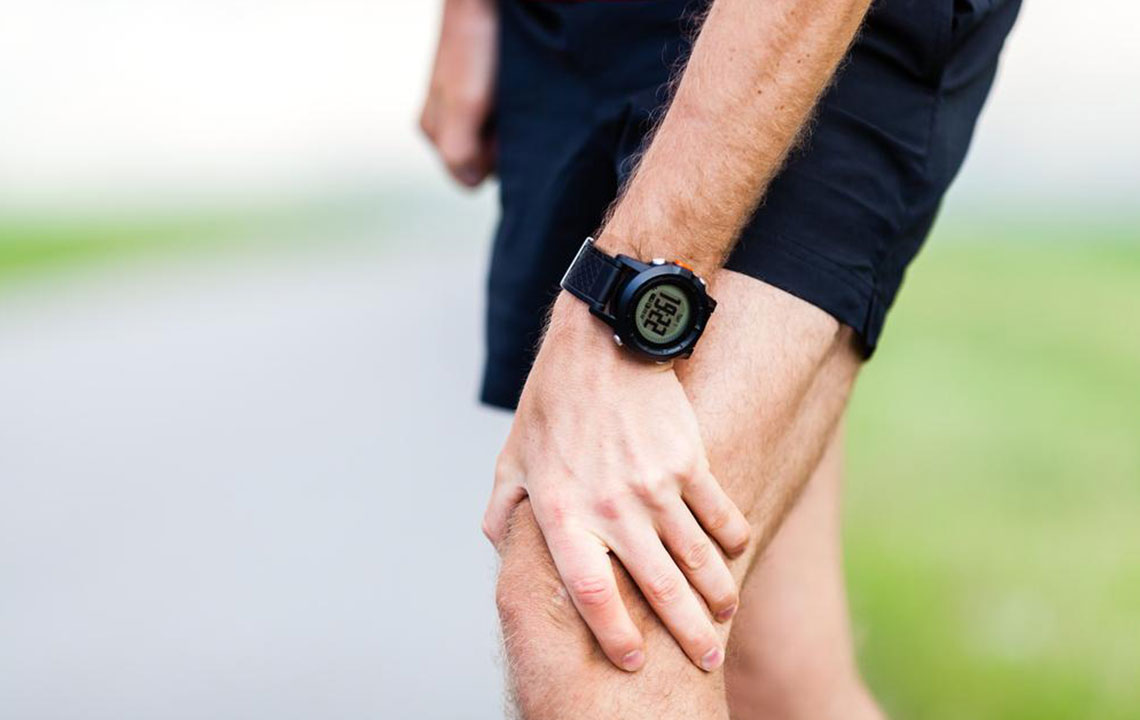
Joint pain involves discomfort, swelling, or tenderness arising from structures such as bones, cartilage, ligaments, muscles, or tendons within the joints. Commonly referred to as arthritis or arthralgia, this condition is characterized by inflammation or pain localized in a joint area. The intensity can range from mild, non-interfering discomfort to severe pain limiting movement. Joints connect bones to enable motion, and damage to these parts often leads to significant suffering and impacts daily life. Surveys show that roughly one-third of adults experience joint problems, with knee pain being the most frequent, followed by issues in the hips and shoulders.
Joint discomfort can occur suddenly (acute) or last over time (chronic), often causing considerable pain. Even short episodes can restrict mobility and affect overall well-being. As people age, joint issues tend to worsen and become harder to treat. Therefore, seeking medical advice promptly for ongoing or unexplained pain is important.
Common Causes of Joint Pain
Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: A rare inflammatory illness characterized by fever, rash, and joint pain, sometimes damaging joints like the wrists.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: An inflammatory disease that fuses spinal vertebrae, limiting flexibility and potentially affecting breathing when ribs are involved.
Avascular Necrosis: Bone tissue death due to inadequate blood supply, which can cause bone collapse and fragmentation.
Dislocation: Displacement of bones caused by injury, leading to painful joint deformity temporarily.
Bursitis: Inflammation of fluid-filled sacs around joints, such as in shoulders, hips, elbows, knees, or toes, resulting in pain.
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Persistent limb pain often following injury, surgery, stroke, or heart attack, sometimes with unclear causes.
Signs and Symptoms of Joint Pain
Indicators include redness, swelling, warmth, stiffness, and tenderness near the joint. Damage to ligaments, tendons, cartilage, or joint capsules can produce these symptoms. Inflammatory conditions like arthritis typically cause swelling, redness, and decreased function.
Treatment Options
Approaches depend on the specific cause. For injury-related pain, rest, ice or heat applications, anti-inflammatory drugs, and analgesics are common. Physical therapy may aid in restoring movement. For arthritis, medications like NSAIDs or disease-modifying agents (DMARDs) are used to control inflammation. In some cases, surgery might be necessary to repair damaged ligaments, bones, or cartilage.
Important Reminder:
All health information provided is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Consult healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and treatment options.